2005 Honda Accord Throttle Position Sensor
Let's dive into the throttle position sensor (TPS) on the 2005 Honda Accord. This sensor, while seemingly simple, plays a critical role in your engine's performance. We'll cover its function, common failure modes, testing procedures, and replacement tips. This information is geared towards the experienced DIYer who isn't afraid to get their hands dirty.
What is the Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)?
The TPS is a potentiometer that measures the angle of the throttle plate within the throttle body. In simpler terms, it tells the engine's computer (the ECU, or Engine Control Unit) how much you're pressing the accelerator pedal. The ECU uses this information, along with data from other sensors like the MAF (Mass Airflow Sensor) and O2 sensors, to determine the correct amount of fuel to inject and the appropriate ignition timing for optimal combustion.
Think of the accelerator pedal as a request. The TPS is the translator, communicating the *intensity* of that request to the brain (ECU) of the engine.
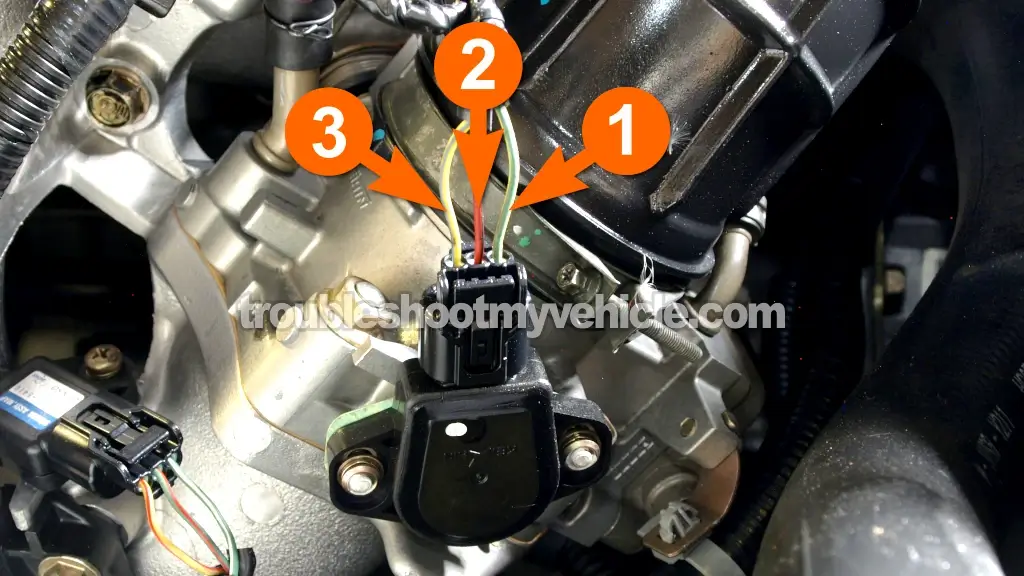
On the 2005 Accord, the TPS is typically a three-wire sensor. These wires are:
- Ground (GND): Provides a stable reference voltage.
- Voltage Reference (VREF): A stable 5V signal supplied by the ECU.
- Signal Output: This wire carries the voltage signal that varies according to the throttle plate angle. This is the crucial data point for the ECU.
How Does the TPS Work?
As the throttle plate moves (when you press the accelerator), the wiper arm inside the TPS moves along a resistive strip. This movement changes the resistance between the VREF and signal output wires, causing the voltage on the signal wire to change proportionally. A closed throttle will typically read around 0.5V, and a fully open throttle will read close to 4.5V. The ECU interprets this voltage change as the amount of throttle opening.
Imagine a dimmer switch controlling a light bulb. The dimmer switch is like the throttle pedal, and the TPS is like the internal mechanism of the dimmer that varies the resistance and, therefore, the brightness of the light.
Common Symptoms of a Failing TPS
A failing TPS can manifest in a variety of ways, as the ECU is relying on faulty data. Here are some common symptoms:
- Erratic Idling: The engine might idle too high, too low, or fluctuate up and down.
- Stalling: Especially when coming to a stop, the engine may stall due to incorrect fueling.
- Hesitation or Stumbling: The engine might hesitate or stumble during acceleration, feeling like it's lacking power.
- Poor Fuel Economy: Incorrect fueling can lead to increased fuel consumption.
- Check Engine Light (CEL): The ECU will likely store a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) related to the TPS, such as P0121 (Throttle/Pedal Position Sensor A Circuit Range/Performance) or P0122 (Throttle/Pedal Position Sensor A Circuit Low Input).
- Surging: The engine speed may increase and decrease erratically.
- Transmission Issues: In some cases, a faulty TPS can affect automatic transmission shifting, causing harsh or delayed shifts. This is because the ECU uses TPS data for transmission control as well.
Diagnosing a Faulty TPS
Before replacing the TPS, it's important to properly diagnose the issue. Here's a step-by-step guide:
- Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve any stored DTCs. Note down the codes and their descriptions. This will help narrow down the problem.
- Visual Inspection: Carefully inspect the TPS connector and wiring for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Voltage Test (Key On, Engine Off):
- Locate the TPS connector.
- Identify the ground, VREF, and signal wires (refer to a wiring diagram for your specific 2005 Accord engine).
- With the key in the "ON" position (engine off), use a multimeter to check for 5V on the VREF wire. If no voltage is present, there may be an issue with the ECU or the wiring to the sensor.
- Check for a good ground connection on the ground wire.
- Backprobe the signal wire (carefully insert the multimeter probe into the back of the connector without damaging the wire).
- With the throttle closed, the signal voltage should be around 0.5V.
- Slowly open the throttle plate manually and observe the voltage change on the multimeter. The voltage should increase smoothly and linearly, without any jumps or dead spots, up to approximately 4.5V at wide-open throttle (WOT).
- Resistance Test (Sensor Removed):
- Disconnect the TPS connector.
- Use a multimeter to measure the resistance between the VREF and signal pins.
- Slowly rotate the TPS shaft. The resistance should change smoothly and linearly. Any sudden jumps or dead spots indicate a faulty sensor.
- Compare the resistance values to the specifications in the Honda service manual.
- Scan Tool Data: If you have access to a scan tool that can read live data, monitor the TPS voltage and throttle position percentage as you slowly open and close the throttle. Look for any erratic readings or dropouts.
Important Note: Always disconnect the negative battery terminal before working on any electrical components to prevent accidental shorts or damage.
Replacing the TPS
If your testing confirms that the TPS is faulty, replacement is the best course of action. Here's a general procedure, but always refer to your vehicle's repair manual for specific instructions and torque specifications:
- Disconnect the Negative Battery Terminal: Safety first!
- Disconnect the TPS Connector: Carefully disconnect the electrical connector from the TPS.
- Remove the TPS Mounting Screws: The TPS is typically held in place by two or three screws. Use the appropriate screwdriver or socket to remove them. Be careful not to strip the screw heads.
- Remove the Old TPS: Gently remove the old TPS from the throttle body.
- Install the New TPS: Install the new TPS, aligning it correctly with the throttle shaft.
- Tighten the Mounting Screws: Tighten the mounting screws to the specified torque (consult your repair manual). Over-tightening can damage the sensor.
- Connect the TPS Connector: Reconnect the electrical connector to the TPS.
- Reconnect the Negative Battery Terminal:
- Clear DTCs: Use an OBD-II scanner to clear any stored DTCs.
- Throttle Position Sensor Adjustment (If Required): Some TPS sensors require adjustment after installation. This involves setting the base voltage of the TPS using a scan tool or multimeter. Refer to your repair manual for the correct procedure and specifications. The 2005 Accord TPS is typically *not* adjustable, but it's always a good idea to double-check.
- Test Drive: Test drive the vehicle to ensure that the problem is resolved and that the engine is running smoothly.
Important: Use only a high-quality replacement TPS from a reputable manufacturer (Denso is often the OEM supplier for Honda). Cheap aftermarket sensors can be unreliable and may not function correctly.
Throttle Body Cleaning
While you're replacing the TPS, it's a good idea to clean the throttle body. A dirty throttle body can contribute to idling problems and poor performance. Use a throttle body cleaner specifically designed for this purpose. Follow the instructions on the cleaner can carefully. Do *not* spray cleaner into the TPS itself.
Final Thoughts: Replacing the TPS on your 2005 Honda Accord is a manageable task for the experienced DIYer. By understanding its function, symptoms of failure, and proper testing procedures, you can accurately diagnose the problem and save yourself money on expensive mechanic fees. Remember to always consult your vehicle's repair manual for specific instructions and torque specifications.
