2020 Chevy Traverse Exhaust System Diagram
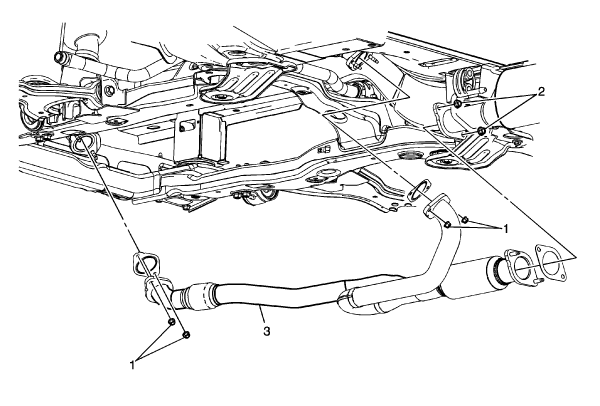
The 2020 Chevrolet Traverse, a popular choice for families needing spacious three-row seating, relies on a carefully engineered exhaust system to manage engine emissions and optimize performance. Understanding the system's layout and components is crucial for both routine maintenance and diagnosing potential issues. This article provides a detailed overview of the 2020 Traverse's exhaust system, focusing on its diagram and key components.
Exhaust System Overview
The exhaust system's primary function is to safely channel harmful exhaust gases away from the engine and out of the vehicle. It also plays a role in reducing emissions and minimizing engine noise. The 2020 Traverse's exhaust system is designed to comply with stringent emissions standards while delivering acceptable performance and fuel economy. The system begins at the engine and extends to the rear of the vehicle, incorporating several critical components.
Key Components and Diagram Breakdown
Let's break down the major components of the 2020 Traverse exhaust system, referencing what you would see on a typical exhaust diagram:
- Exhaust Manifolds: Bolted directly to the cylinder heads, the exhaust manifolds collect exhaust gases from each cylinder. The 2020 Traverse, equipped with the 3.6L V6 engine (LGZ engine code), features two exhaust manifolds, one for each cylinder bank. These manifolds are typically made of cast iron or stainless steel, designed to withstand high temperatures and corrosive gases.
- Catalytic Converters: Arguably the most crucial component for emissions control, the catalytic converters use chemical reactions to reduce harmful pollutants like hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO), and nitrogen oxides (NOx) into less harmful substances like carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O), and nitrogen (N2). The 2020 Traverse employs multiple catalytic converters, usually two or three, strategically placed to maximize their effectiveness. The diagram will show their precise locations within the exhaust stream.
- Oxygen Sensors (O2 Sensors): Positioned upstream and downstream of the catalytic converters, the oxygen sensors monitor the oxygen content in the exhaust gases. The upstream O2 sensors provide feedback to the engine control module (ECM) about the air-fuel mixture, allowing the ECM to make adjustments for optimal combustion. The downstream O2 sensors monitor the efficiency of the catalytic converters. The diagram will clearly indicate the number and placement of these sensors. Faulty O2 sensors can significantly impact engine performance and fuel economy.
- Resonator: The resonator is a chamber designed to reduce specific frequencies of sound, helping to dampen the overall exhaust noise. It's typically a cylindrical component located along the exhaust pipe.
- Muffler: The muffler is the primary sound-dampening device in the exhaust system. It uses a series of chambers and baffles to reduce exhaust noise to an acceptable level. The 2020 Traverse utilizes a strategically designed muffler to provide a comfortable and quiet ride.
- Pipes and Connections: Connecting all these components are various pipes and flanges. These are usually constructed from steel and must withstand high temperatures and vibrations. Exhaust leaks often occur at these connections, leading to increased noise and potentially affecting engine performance.
- Exhaust Hangers: Rubber exhaust hangers are used to support the exhaust system and isolate it from the vehicle's chassis. This prevents vibrations from being transmitted into the cabin. These hangers can deteriorate over time, causing the exhaust system to sag and potentially damage other components.
Diagram Interpretation
A typical exhaust system diagram will illustrate the flow of exhaust gases from the engine to the tailpipe. The diagram will show the relative positions of each component, including the catalytic converters, resonators, and muffler. It will also indicate the locations of the oxygen sensors and any heat shields used to protect surrounding components from the exhaust's high temperatures. When referencing a diagram, pay close attention to the orientation of the components and the direction of the exhaust flow.
Common Issues and Maintenance
Several issues can arise with the 2020 Traverse's exhaust system. Exhaust leaks are a common problem, often caused by corrosion or damage to the pipes or connections. A damaged or clogged catalytic converter can lead to reduced engine performance and increased emissions. Faulty oxygen sensors can also cause a variety of problems, including poor fuel economy and rough idling. Regular inspections of the exhaust system, including checking for leaks and inspecting the condition of the hangers, can help prevent these issues. Addressing problems promptly can prevent further damage and ensure the vehicle continues to operate efficiently and within emissions regulations.
By understanding the components and layout of the 2020 Chevy Traverse's exhaust system, automotive enthusiasts, mechanics, and professionals can effectively diagnose and repair exhaust-related issues, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
