Automotive Wire Color Code Chart
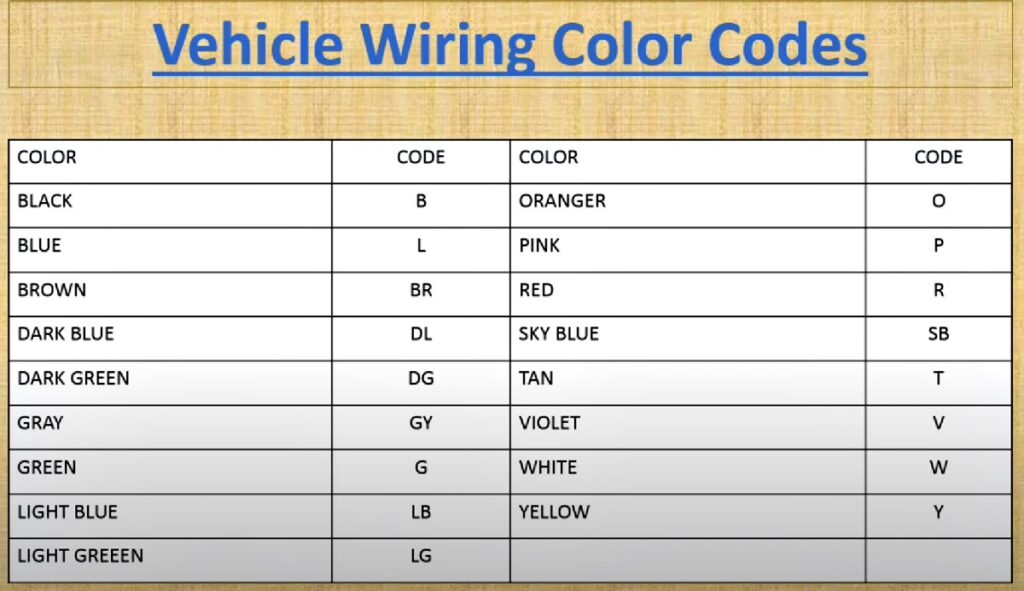
Understanding the automotive wire color code chart is crucial for anyone working on car electrical systems, from seasoned mechanics to enthusiastic DIYers. Electrical problems can be complex, and deciphering the wiring can be like trying to solve a puzzle. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of automotive wire colors, their common uses, and why understanding these codes is essential for safe and effective automotive repairs and modifications.
Why Automotive Wire Color Codes Matter
Automotive wiring harnesses are a complex network of wires that power everything from your headlights to your engine management system. Without a standardized system, identifying the function of each wire would be incredibly difficult, time-consuming, and prone to error. That's where the automotive wire color code chart comes in. It provides a standardized system, allowing technicians and individuals to quickly identify the purpose of each wire in the system.
Here are some key benefits of understanding wire color codes:
- Safety: Incorrectly wiring electrical components can lead to short circuits, fires, and damage to your vehicle. Knowing the color code minimizes the risk of making these dangerous mistakes.
- Efficiency: Identifying the correct wire quickly saves time and reduces the frustration of troubleshooting electrical issues.
- Accuracy: Reduces the chance of making errors during repairs or modifications.
- Professionalism: Demonstrates a solid understanding of automotive electrical systems, which is essential for mechanics and technicians.
Decoding the Automotive Wire Color Code Chart
While there isn't a single, universally enforced standard, there are widely accepted conventions for automotive wire color code across manufacturers and regions. It's important to note that variations *do* exist, especially between different makes (Ford, GM, Toyota, etc.) and model years. Always consult the specific wiring diagram for your vehicle before making any electrical connections.
Here's a breakdown of common wire colors and their typical functions:
Primary Colors:
- Red (RED): Often used for constant power, directly from the battery. Think of this as the "hot" wire.
- Black (BLK): Commonly used for ground. Connects to the vehicle's chassis, providing a return path for electrical current.
- White (WHT): Typically used for lighting circuits, like headlights, taillights, and interior lights.
- Blue (BLU): Frequently found in accessory circuits, such as power windows, power locks, and radios.
- Yellow (YEL): Often used for ignition-related circuits, like the starter or fuel pump.
- Green (GRN): Commonly associated with turn signals, brake lights, and other indicator lights.
- Brown (BRN): Often used for accessory circuits that are switched by the ignition, such as the radio or cigarette lighter.
- Orange (ORG): Frequently used for circuits that are protected by fuses or relays, often related to the engine control system.
- Purple (PUR): Commonly used in circuits related to the starting system or the ignition switch.
- Gray (GRY): Frequently used for lighting circuits, especially those that are controlled by a dimmer switch.
Secondary Colors (Stripes):
Many wires will have a base color with a stripe of another color running along its length. This stripe provides further differentiation and indicates a specific function within the system. For example:
- Red with White Stripe (RED/WHT): Could indicate a specific power feed to a particular component.
- Black with White Stripe (BLK/WHT): Often used for a ground connection to a specific sensor or module.
- Green with White Stripe (GRN/WHT): May be used for a specific signal in a lighting circuit.
The combination of the base color and the stripe color provides a more detailed identification of the wire's purpose.
Beyond the Basics: Manufacturer-Specific Codes and Wiring Diagrams
As mentioned earlier, while there are common conventions, manufacturers often use their own variations of the automotive wire color code chart. Therefore, it's absolutely crucial to consult the specific wiring diagram for your vehicle. These diagrams provide detailed information about the wiring layout and color codes for each circuit.
Here's where to find these diagrams:
- Vehicle Repair Manuals: Haynes and Chilton manuals often include wiring diagrams, though they may not be as comprehensive as factory service manuals.
- Factory Service Manuals: These are the most detailed and accurate source of wiring diagrams. They are often available from the manufacturer or online.
- Online Databases: Some online databases provide access to wiring diagrams for various vehicles, often for a subscription fee.
- Vehicle-Specific Forums: Online forums dedicated to your vehicle's make and model can be a valuable resource for finding wiring diagrams and getting advice from other owners.
When using a wiring diagram, pay attention to the following:
- Legend: The diagram will have a legend that explains the abbreviations and symbols used.
- Circuit Numbers: Wires are often identified by circuit numbers, which can help you trace the wiring path.
- Component Locations: The diagram will show the location of components and how they are connected.
- Ground Points: Pay close attention to the location of ground points, as these are critical for proper electrical function.
Tools and Best Practices for Working with Automotive Wiring
Working with automotive wiring requires the right tools and a careful approach. Here are some essential tools and best practices:
Essential Tools:
- Multimeter: Used to measure voltage, current, and resistance. Essential for diagnosing electrical problems.
- Wire Strippers: Used to remove insulation from wires without damaging the conductors.
- Crimping Tool: Used to crimp connectors onto wires.
- Test Light: Used to check for power and ground.
- Wiring Diagram: As mentioned earlier, essential for understanding the wiring layout.
- Heat Shrink Tubing: Used to insulate and protect electrical connections.
- Soldering Iron and Solder: For making permanent electrical connections.
- Electrical Tape: For insulating and protecting electrical connections (use high-quality automotive-grade tape).
- Wire Tracer: Used to trace wires through the wiring harness.
Best Practices:
- Disconnect the Battery: Always disconnect the negative battery cable before working on any electrical system. This prevents accidental shorts and potential damage.
- Use Proper Connectors: Use the correct type of connector for the application. Crimp connectors should be properly crimped to ensure a secure connection.
- Insulate Connections: Always insulate electrical connections with heat shrink tubing or electrical tape.
- Avoid Over-Stripping Wires: Only strip enough insulation to make the connection. Over-stripping can expose too much bare wire and increase the risk of shorts.
- Protect Wires from Damage: Route wires carefully to avoid sharp edges or hot surfaces. Use wire loom or other protective coverings to prevent damage.
- Double-Check Your Work: Before reconnecting the battery, double-check all connections to ensure they are secure and properly insulated.
- Consult a Professional: If you are unsure about any aspect of automotive electrical work, consult a qualified mechanic or electrician.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Several common mistakes can lead to problems when working with automotive wire color code and electrical systems:
- Ignoring Wiring Diagrams: This is a recipe for disaster. Always consult the wiring diagram for your specific vehicle.
- Assuming Wire Colors are Universal: As mentioned, manufacturers use variations. Don't assume that a red wire always means constant power.
- Using Incorrect Connectors: Using the wrong type of connector can lead to loose connections and electrical problems.
- Poor Crimping: A poorly crimped connection can cause resistance and heat, leading to failure.
- Over-Tightening Connections: Over-tightening screws or bolts can damage connectors and wires.
- Neglecting Ground Connections: Poor ground connections can cause a variety of electrical problems.
- Working Without Disconnecting the Battery: This is a safety hazard and can damage electrical components.
Conclusion
Understanding the automotive wire color code chart is a valuable skill for anyone working on vehicles. By familiarizing yourself with the common color codes, consulting wiring diagrams, using the right tools, and following best practices, you can safely and effectively troubleshoot and repair automotive electrical systems. Remember to always prioritize safety and consult a professional if you are unsure about any aspect of the work. Proper wiring and understanding the color codes can save you time, money, and potential headaches down the road.
By taking the time to learn and apply these principles, you can ensure the reliability and safety of your vehicle's electrical system.
