Chevy 350 Intake Manifold Diagram
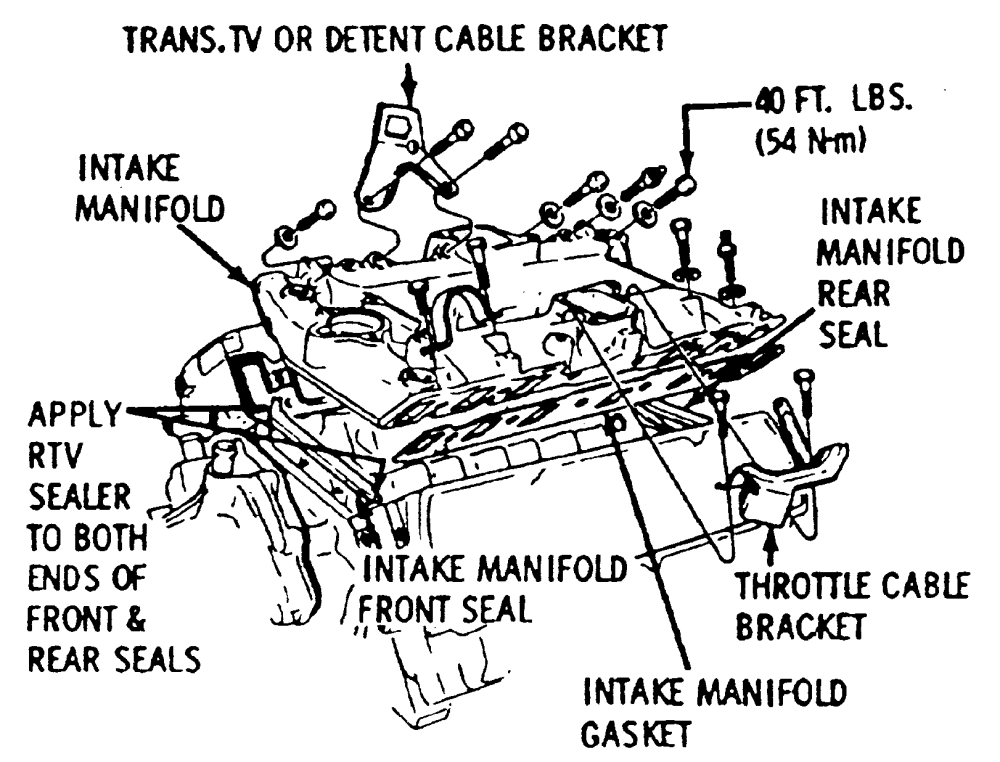
The Chevy 350, a staple in American automotive history, owes much of its reliability and performance to well-engineered components. Among these, the intake manifold plays a crucial role in delivering the air-fuel mixture to the cylinders. Understanding the intricacies of a Chevy 350 intake manifold diagram is essential for anyone looking to optimize performance, diagnose issues, or perform maintenance on this iconic engine.
Understanding the Chevy 350 Intake Manifold
The intake manifold's primary function is to evenly distribute the air-fuel mixture to each cylinder of the engine. It sits atop the engine block, connecting to the cylinder heads and the carburetor (in older models) or throttle body (in fuel-injected models). The manifold's design significantly impacts the engine's power output, torque curve, and overall efficiency. Different manifold designs are tailored for various applications, from low-end torque for trucks to high-RPM horsepower for performance vehicles.
Basic Components and Their Functions
A typical Chevy 350 intake manifold diagram will illustrate the following key components:
- Intake Runners: These are the individual passages that channel the air-fuel mixture from the plenum to each cylinder. Their length, diameter, and shape directly affect the engine's volumetric efficiency (VE) at different RPMs. Longer runners generally boost low-end torque, while shorter runners favor high-end horsepower.
- Plenum: This is the central chamber that acts as a reservoir for the air-fuel mixture. Its size and shape influence the engine's throttle response and overall airflow.
- Carburetor/Throttle Body Mounting Flange: This is the surface where the carburetor or throttle body is attached to the manifold. Its design ensures a secure and airtight seal.
- Water Passages: Many intake manifolds incorporate water passages to circulate coolant, helping to regulate the engine's temperature and prevent overheating. These passages are crucial for maintaining optimal operating conditions.
- EGR Valve Port (if applicable): Some manifolds include a port for the EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) valve, which helps to reduce emissions by recirculating a portion of the exhaust gases back into the intake stream.
- Vacuum Ports: Various vacuum ports are present for connecting vacuum lines to control systems like the distributor advance, power brakes, and other accessories.
- Intake Gaskets: These gaskets seal the manifold to the cylinder heads, preventing air leaks and ensuring proper engine operation. Choosing the correct gasket is essential for preventing vacuum leaks and coolant leaks.
Types of Chevy 350 Intake Manifolds
The Chevy 350 has seen a wide variety of intake manifolds throughout its production run, each designed for specific applications and performance characteristics. Here's a look at some common types:
Stock Cast Iron Manifolds
These manifolds were commonly found on older Chevy 350 engines and are characterized by their durability and affordability. While not optimized for high-performance, they provide adequate airflow for everyday driving. They are typically heavier than aluminum manifolds and less efficient at dissipating heat.
Aftermarket Aluminum Manifolds
Aftermarket aluminum manifolds are a popular upgrade for Chevy 350 engines, offering improved airflow, reduced weight, and better heat dissipation compared to stock cast iron manifolds. They come in various designs, including:
- Dual-Plane Manifolds: These manifolds are designed to improve low-end torque and throttle response. They feature separate intake runners for each cylinder bank, creating a smoother airflow path at lower RPMs. A common example would be the Edelbrock Performer series.
- Single-Plane Manifolds: Single-plane manifolds are optimized for high-RPM horsepower. They feature a large plenum and short, direct intake runners, allowing for maximum airflow at higher engine speeds. These are often favored in racing applications. The Weiand Stealth or Edelbrock Victor Jr. are popular examples.
- High-Rise Manifolds: These manifolds feature taller intake runners, which can further enhance high-RPM horsepower. However, they may require modifications to the hood and other components to fit properly.
Fuel Injection Manifolds
For Chevy 350 engines equipped with fuel injection, the intake manifold design is critical for proper fuel distribution. These manifolds often feature individual runners for each cylinder with fuel injector bungs located near the intake ports. They are designed to work with specific fuel injection systems, such as Throttle Body Injection (TBI) or Multi-Port Fuel Injection (MPFI).
Interpreting a Chevy 350 Intake Manifold Diagram
A detailed Chevy 350 intake manifold diagram will provide valuable information for diagnosing problems and performing repairs. Here are some key things to look for:
- Runner Length and Diameter: This information can help you understand the manifold's performance characteristics and whether it's suitable for your intended application.
- Vacuum Port Locations: Identifying the vacuum port locations is essential for connecting vacuum lines correctly and ensuring proper operation of various engine components.
- Water Passage Routing: Understanding the water passage routing is crucial for diagnosing coolant leaks and ensuring proper cooling system function.
- EGR Valve Port (if applicable): If the manifold is equipped with an EGR valve port, the diagram will show its location and how it connects to the exhaust system.
- Gasket Surfaces: The diagram will illustrate the gasket surfaces and the recommended gasket type.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Several issues can arise with a Chevy 350 intake manifold, affecting engine performance and reliability. Here are some common problems and how to diagnose them using a diagram:
Vacuum Leaks
Vacuum leaks are a common issue that can cause poor engine performance, rough idle, and increased fuel consumption. A Chevy 350 intake manifold diagram can help you identify potential leak points, such as:
- Intake Gasket Surfaces: Check the intake gaskets for signs of damage or deterioration. A cracked or worn gasket can allow air to leak into the engine.
- Vacuum Ports: Inspect the vacuum ports and hoses for cracks, leaks, or loose connections.
- EGR Valve Port: If the manifold has an EGR valve, check the EGR valve gasket for leaks.
You can use a vacuum gauge or a spray bottle with soapy water to help locate vacuum leaks. Spray the soapy water around potential leak points and look for bubbles.
Coolant Leaks
Coolant leaks can cause overheating and engine damage. A Chevy 350 intake manifold diagram can help you trace the coolant passages and identify potential leak sources, such as:
- Water Passage Gaskets: Check the gaskets around the water passages for signs of leaks.
- Manifold Cracks: Inspect the manifold for cracks, especially around the water passages.
Look for signs of coolant leaks, such as puddles of coolant under the engine or white smoke from the exhaust.
Carburetor/Throttle Body Mounting Issues
Problems with the carburetor or throttle body mounting can cause poor engine performance and fuel delivery issues. A Chevy 350 intake manifold diagram can help you ensure that the carburetor or throttle body is properly mounted and sealed.
- Mounting Flange: Check the mounting flange for cracks or damage.
- Gaskets: Inspect the carburetor or throttle body gasket for damage or deterioration.
Real-World Examples
Example 1: A car owner experiences a rough idle and poor fuel economy on their Chevy 350-powered truck. After consulting a Chevy 350 intake manifold diagram, they identify a cracked vacuum hose connected to the distributor advance. Replacing the hose resolves the issue.
Example 2: A mechanic is upgrading a Chevy 350 engine for a street rod. They use a diagram to compare different aftermarket aluminum manifolds and choose a dual-plane manifold for improved low-end torque and drivability.
Example 3: During a restoration project, a car enthusiast discovers a coolant leak around the intake manifold of their classic Chevy 350. The diagram helps them identify the correct gaskets and torque specifications for a proper repair.
Conclusion
The Chevy 350 intake manifold is a critical component that significantly impacts engine performance. Understanding the intricacies of a Chevy 350 intake manifold diagram is essential for diagnosing issues, performing repairs, and optimizing engine performance. Whether you're a seasoned mechanic or a passionate car enthusiast, a detailed diagram can be an invaluable tool for working on this legendary engine. From identifying vacuum leaks to choosing the right aftermarket manifold, the information contained within a Chevy 350 intake manifold diagram empowers you to keep your Chevy 350 running smoothly and efficiently for years to come.
