05 Nissan Altima Crank Sensor
The 2005 Nissan Altima, like many modern vehicles, relies heavily on a suite of sensors to ensure optimal engine performance and reliability. One of the unsung heroes in this system is the crankshaft position sensor, often called the crank sensor. Understanding its function, potential issues, and how to diagnose them can be invaluable for any Altima owner or enthusiast.
What is a Crank Sensor and What Does it Do?
Imagine the engine of your Altima as a precisely choreographed dance. The pistons move up and down, the valves open and close, and the spark plugs ignite the air-fuel mixture – all in perfect synchronization. The crank sensor is the conductor of this orchestra, ensuring that the engine control unit (ECU), essentially the car's brain, knows the exact position of the crankshaft. The crankshaft is the main rotating shaft in the engine that converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotational motion, ultimately driving the wheels.
In simpler terms, the crank sensor tells the ECU:
- The rotational speed (RPM) of the engine.
- The exact position of the crankshaft at any given moment.
This information is absolutely critical for several key functions:
- Ignition Timing: The ECU uses the crank sensor data to determine when to fire the spark plugs. Incorrect timing can lead to poor performance, misfires, and even engine damage.
- Fuel Injection Timing: Similarly, the ECU needs to know the crank position to accurately time the fuel injectors, ensuring the correct amount of fuel is injected into the cylinders at the right moment.
- Misfire Detection: By monitoring the crank speed, the ECU can detect subtle variations that indicate a misfire in one or more cylinders.
- Starting the Engine: The ECU needs the crank sensor signal to initiate the starting process. Without a valid signal, the engine may not even attempt to start.
Think of it like this: Imagine trying to play a song on a piano without knowing where the keys are. The crank sensor is the map of the keys for the engine, allowing the ECU to play the engine's "song" correctly.
Types of Crank Sensors
There are primarily two types of crank sensors:
- Magnetic Inductive Sensors: These sensors contain a coil of wire and a magnet. As the crankshaft rotates, a toothed wheel (reluctor ring) passes by the sensor. The teeth interrupt the magnetic field, generating a small AC voltage signal. The frequency and amplitude of this signal change with the engine speed. This type is common across many brands, including older Honda Civics and Toyota Camrys.
- Hall Effect Sensors: These sensors use a semiconductor material that produces a voltage difference when a magnetic field is applied perpendicular to the current flowing through it. A rotating wheel with slots or magnets passes by the sensor, altering the magnetic field and creating a digital signal (on/off). Hall effect sensors are often found in newer vehicles due to their higher accuracy and ability to function at lower speeds. Many modern BMWs and Mercedes-Benz models utilize Hall effect sensors.
The 2005 Nissan Altima typically uses a magnetic inductive crank sensor. It's a robust and reliable design, but it's not immune to failure.
Symptoms of a Failing Crank Sensor
A failing crank sensor can manifest in a variety of ways, ranging from subtle performance issues to a complete engine stall. Recognizing these symptoms early can save you from a more significant headache down the road.
- Engine Stalling: This is one of the most common symptoms. The engine may stall intermittently, especially when hot, or it may refuse to start altogether. Imagine a runner suddenly collapsing mid-race – that's essentially what's happening when the crank sensor fails and the engine stalls.
- Hard Starting: The engine may crank for an extended period before finally starting. This is because the ECU is struggling to determine the correct timing.
- Misfires: A faulty crank sensor can cause the engine to misfire, resulting in rough idling, poor acceleration, and a noticeable decrease in fuel economy. It would be similar to a drummer missing beats in a song, making the rhythm uneven and unpleasant.
- Check Engine Light (CEL): The ECU will often detect a problem with the crank sensor and illuminate the check engine light. Common diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) associated with a crank sensor issue include P0335 (Crankshaft Position Sensor A Circuit Malfunction) and P0336 (Crankshaft Position Sensor A Circuit Range/Performance).
- Poor Fuel Economy: Incorrect timing caused by a failing crank sensor can lead to inefficient combustion, resulting in lower gas mileage.
- Hesitation During Acceleration: The engine may hesitate or stumble when you try to accelerate.
- RPM Fluctuations: The tachometer (RPM gauge) may fluctuate erratically, especially at idle.
It's important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by other issues, such as a faulty camshaft position sensor, a clogged fuel filter, or a vacuum leak. Therefore, a proper diagnosis is crucial before replacing the crank sensor.
Diagnosing a Crank Sensor
Diagnosing a crank sensor typically involves the following steps:
- Check for Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve any stored DTCs. Note down the codes and research their meaning.
- Visual Inspection: Inspect the crank sensor and its wiring for any signs of damage, such as cracks, frayed wires, or corrosion.
- Testing the Sensor: Using a multimeter, you can test the sensor's resistance and voltage output. The specific testing procedure will vary depending on the type of sensor. Consult the service manual for your 2005 Nissan Altima for the correct specifications and procedure.
For a magnetic inductive sensor, you typically measure the resistance across the sensor terminals. An open circuit or a very low resistance indicates a faulty sensor. You can also measure the AC voltage output while cranking the engine. A weak or absent signal suggests a problem.
For a Hall effect sensor, you typically check for a 5V reference voltage and a ground. You then measure the signal voltage while rotating the crankshaft. The voltage should switch between high and low states.
- Checking the Wiring: Use a multimeter to check the continuity of the wiring between the crank sensor and the ECU. Look for any breaks or shorts in the wiring.
- Oscilloscope Testing (Advanced): An oscilloscope can be used to visualize the signal output of the crank sensor. This can help identify subtle issues that may not be apparent with a multimeter.
Safety First! Always disconnect the negative battery terminal before working on any electrical components.
Replacing the Crank Sensor
Replacing the crank sensor is a relatively straightforward procedure, but it's important to follow the correct steps to avoid any issues.
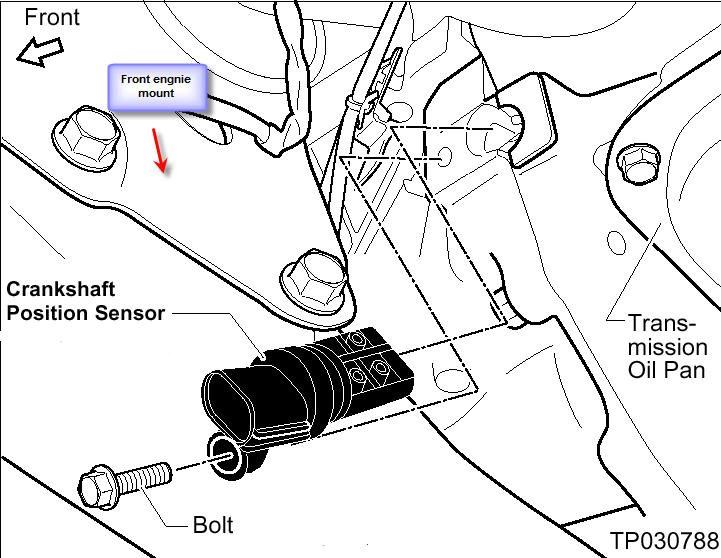
- Locate the Crank Sensor: The crank sensor is typically located near the crankshaft pulley or flywheel. Consult your service manual for the exact location on your 2005 Nissan Altima.
- Disconnect the Wiring Connector: Carefully disconnect the wiring connector from the crank sensor.
- Remove the Old Sensor: Remove the bolt(s) that secure the crank sensor to the engine block. Gently remove the old sensor.
- Install the New Sensor: Install the new crank sensor in the same orientation as the old one. Tighten the bolt(s) to the specified torque.
- Connect the Wiring Connector: Reconnect the wiring connector to the crank sensor.
- Clear Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Use an OBD-II scanner to clear any stored DTCs.
- Start the Engine: Start the engine and verify that it runs smoothly.
Important Considerations:
- Always use a high-quality replacement crank sensor from a reputable manufacturer.
- Ensure that the replacement sensor is compatible with your 2005 Nissan Altima.
- Be careful not to damage the reluctor ring when removing or installing the crank sensor.
- Some vehicles may require a "crankshaft position sensor relearn" procedure after replacing the sensor. This procedure allows the ECU to learn the new sensor's signal characteristics. Consult your service manual for details.
Practical Takeaways
- Know the Symptoms: Be aware of the symptoms of a failing crank sensor and address them promptly. Ignoring these symptoms can lead to more significant engine problems.
- Regular Maintenance: While crank sensors don't require routine maintenance, keeping your engine in good condition overall (oil changes, spark plugs, etc.) can help extend the lifespan of all sensors.
- Proper Diagnosis: Don't assume that a crank sensor is the culprit based on symptoms alone. Perform a thorough diagnosis to rule out other potential issues.
- Use Quality Parts: When replacing the crank sensor, use a high-quality replacement part from a reputable manufacturer. Cheaper aftermarket sensors may not be as reliable.
- Consult a Professional: If you're not comfortable diagnosing or replacing the crank sensor yourself, consult a qualified mechanic.
By understanding the role of the crank sensor and being proactive in addressing any potential issues, you can help keep your 2005 Nissan Altima running smoothly and reliably for years to come.
