2001 Nissan Xterra Speed Sensor Location
The 2001 Nissan Xterra, like many vehicles of its era, relies on speed sensors for a multitude of functions, from accurate speedometer readings to proper transmission shifting and ABS operation. Understanding the location, function, and potential problems associated with these sensors is crucial for both DIY car owners and professional mechanics. This article will delve into the specifics of the 2001 Xterra's speed sensors, providing practical advice on maintenance, troubleshooting, and real-world solutions.
Understanding Speed Sensors on the 2001 Nissan Xterra
The 2001 Xterra primarily utilizes two types of speed sensors: the Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) and the Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) wheel speed sensors. Each plays a distinct, yet interconnected, role in vehicle operation.
Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS)
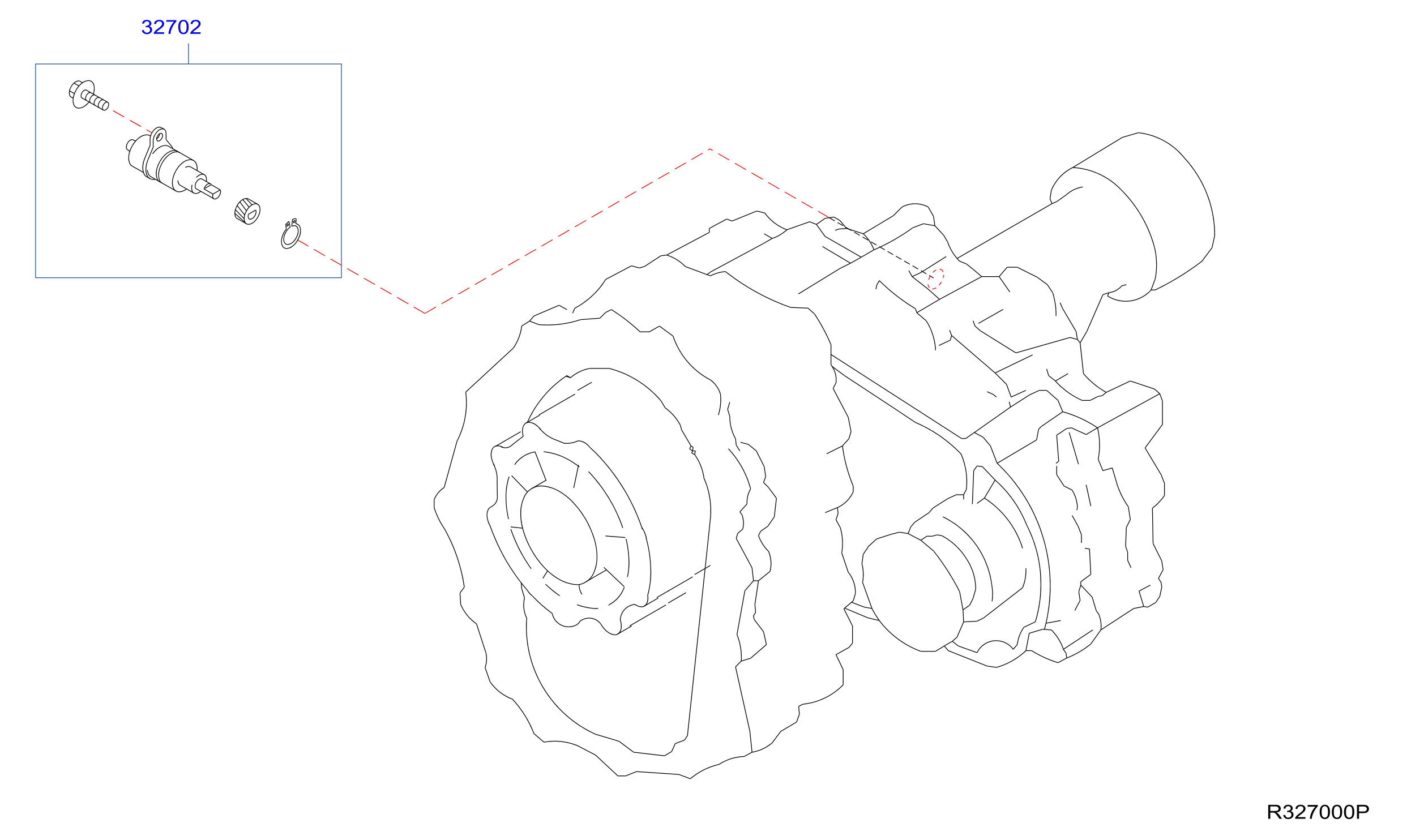
The VSS is typically located on the transmission. Its primary function is to measure the output shaft speed of the transmission and send this information to the Engine Control Unit (ECU) or Powertrain Control Module (PCM). This data is then used for various purposes, including:
- Speedometer operation: The VSS provides the signal that drives the speedometer, displaying the vehicle's current speed.
- Transmission shifting: The PCM uses VSS data to determine the optimal shift points for the automatic transmission, ensuring smooth and efficient gear changes.
- Cruise control function: The VSS signal is essential for the proper operation of the cruise control system.
- Engine management: The PCM uses VSS data to adjust fuel delivery and ignition timing based on vehicle speed.
ABS Wheel Speed Sensors
The ABS wheel speed sensors are located at each wheel hub. They monitor the rotational speed of each wheel individually. This information is crucial for the ABS system to detect and prevent wheel lockup during braking. These sensors are also used by other systems, such as:
- Traction control system (TCS): If equipped, the TCS uses wheel speed data to detect wheel spin and reduce engine power or apply brakes to regain traction.
- Electronic Stability Program (ESP): Also if equipped, ESP uses wheel speed data, along with other sensor inputs, to detect and prevent skidding.
Locating the Speed Sensors on the 2001 Xterra
Finding the speed sensors is the first step in any maintenance or repair procedure. Here's a guide to their locations on the 2001 Nissan Xterra:
- VSS: The VSS is generally found on the transmission housing. You'll typically find it near the rear of the transmission, where the driveshaft connects. It usually has a two- or three-wire connector attached to it. Depending on whether the Xterra is 2WD or 4WD, the exact transmission model will dictate slight variations in its position. Accessing the VSS often requires lifting the vehicle and potentially removing some underbody panels for clear access.
- ABS Wheel Speed Sensors: These sensors are located behind each wheel hub. They are typically mounted to the wheel bearing assembly or knuckle and have a wire running to a connector located in the wheel well. To access these sensors, you will need to remove the wheel.
Troubleshooting Speed Sensor Issues
A faulty speed sensor can cause a variety of problems. Recognizing the symptoms is key to diagnosing the issue correctly.
Common Symptoms of a Faulty VSS
- Erratic or non-functional speedometer: This is one of the most common symptoms. The speedometer may jump around erratically, display an incorrect speed, or stop working altogether.
- Transmission shifting problems: The transmission may shift erratically, shift at the wrong times, or fail to shift at all. This can manifest as harsh shifting, delayed shifting, or getting stuck in a particular gear.
- Cruise control malfunction: The cruise control system may not engage or may disengage unexpectedly.
- Check Engine Light (CEL): A faulty VSS can trigger a CEL and store diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to the VSS or transmission.
- Poor fuel economy: An inaccurate VSS signal can affect the PCM's ability to properly manage fuel delivery, leading to reduced fuel efficiency.
Common Symptoms of Faulty ABS Wheel Speed Sensors
- ABS light illumination: The ABS warning light on the dashboard will illuminate.
- ABS system malfunction: The ABS system may not function properly during braking, leading to longer stopping distances or wheel lockup.
- Traction control/ESP malfunction: If equipped, the traction control or ESP system may not function correctly, potentially causing stability issues.
- Check Engine Light (CEL): A faulty wheel speed sensor can trigger a CEL and store diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to the ABS system.
Diagnosing Speed Sensor Problems
The following steps can help you diagnose speed sensor problems:
- Scan for Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Use an OBD-II scanner to check for any stored DTCs. Common codes related to speed sensors include P0500 (Vehicle Speed Sensor A Malfunction), P0501 (Vehicle Speed Sensor A Range/Performance), C0031 (Left Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit), and C0034 (Right Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit).
- Inspect the Sensors: Visually inspect the sensors and their wiring for any signs of damage, such as broken wires, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Test the Sensor: Use a multimeter to test the sensor's resistance or voltage output. Refer to the vehicle's service manual for the correct testing procedures and specifications.
- Check the Wiring: Inspect the wiring harness and connectors for any signs of damage or corrosion. Use a multimeter to check for continuity and voltage at the connector.
Common Causes of Speed Sensor Failure
Several factors can contribute to speed sensor failure:
- Physical damage: Impacts from road debris, accidents, or improper handling can damage the sensors.
- Contamination: Dirt, grime, and other contaminants can accumulate on the sensor, interfering with its operation.
- Corrosion: Exposure to moisture and road salt can corrode the sensor and its wiring.
- Wiring problems: Broken wires, loose connections, or damaged insulation can disrupt the sensor's signal.
- Sensor wear: Over time, the sensor's internal components can wear out, leading to failure.
Real-World Solutions and Examples
Here are some practical solutions to common speed sensor problems, illustrated with examples:
- Problem: Erratic speedometer reading and DTC P0500.
Solution: Begin by inspecting the VSS connector and wiring. Often, corrosion or a loose connection is the culprit. Clean the connector with electrical contact cleaner and ensure it is securely attached. If the problem persists, test the VSS with a multimeter according to the service manual. If the sensor fails the test, replace it.
- Problem: ABS light on and DTC C0031 (Left Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit).
Solution: Remove the left front wheel and inspect the ABS wheel speed sensor and its wiring. Look for any signs of damage or contamination. Clean the sensor with a brush and mild cleaner. If the wiring is damaged, repair or replace it. If the problem persists, test the sensor's resistance. If the sensor fails the test, replace it.
- Problem: Transmission shifting problems and no speedometer reading.
Solution: In this scenario, the VSS is the likely culprit. Given that both the speedometer and transmission shifting are affected, the sensor is likely completely failed. Replacing the VSS is the best course of action. Remember to clear any stored DTCs after replacing the sensor.
Example from other Nissan models: The speed sensor issues found in the 2001 Xterra are similar to those found in other Nissan vehicles of the same era, such as the Sentra and Altima. For instance, a common issue in early 2000s Nissan Sentras is VSS failure leading to erratic shifting, and this can be diagnosed and resolved using similar techniques as described above. Similarly, ABS sensor failures are frequent in the Altima, often manifesting as an ABS light and compromised braking performance, necessitating sensor replacement.
Maintenance Tips for Keeping Your Xterra in Top Condition
Regular maintenance can help prevent speed sensor problems and extend the life of your vehicle:
- Regular Inspections: Periodically inspect the speed sensors and their wiring for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Cleaning: Keep the sensors clean and free of dirt and debris. Use a brush and mild cleaner to remove any contaminants.
- Wiring Protection: Protect the wiring from damage by using wire loom or electrical tape to secure it to the chassis.
- Proper Installation: When replacing a speed sensor, ensure that it is properly installed and torqued to the correct specification.
- Use Quality Parts: When replacing a speed sensor, use a high-quality replacement part from a reputable manufacturer.
By understanding the function, location, and potential problems associated with the speed sensors on your 2001 Nissan Xterra, you can take proactive steps to maintain your vehicle and prevent costly repairs. Whether you're a seasoned mechanic or a DIY car owner, the information in this article will help you keep your Xterra running smoothly for years to come.
