2005 Nissan Altima 2.5 Crank Sensor Location
The 2005 Nissan Altima, particularly those equipped with the 2.5-liter QR25DE engine, relies heavily on its sensors to maintain optimal performance and fuel efficiency. Among these critical components, the crankshaft position sensor (CKP sensor), often simply called the "crank sensor," plays a pivotal role. Understanding its function, location, and how to access it is crucial for anyone looking to diagnose and potentially repair issues related to engine timing and starting problems. This guide provides a detailed overview of the crank sensor location and access procedure on the 2005 Nissan Altima 2.5.
Understanding the Crankshaft Position Sensor
Before diving into the location, let's briefly recap the sensor's purpose. The crank sensor monitors the position and rotational speed of the crankshaft. This information is relayed to the engine control module (ECM), which uses it to calculate ignition timing, fuel injection timing, and to detect misfires. Without a properly functioning crank sensor, the engine may fail to start, run erratically, or stall altogether. The ECM uses the crank sensor signal to sync with the camshaft position sensor (CMP sensor) signal. These two work in conjunction to inform the engine on the exact position of all valvetrain components.
A typical crank sensor on the QR25DE engine is a magnetic pickup sensor, also known as a variable reluctance sensor. It consists of a coil of wire wrapped around a magnetic core. As the crankshaft rotates, teeth (usually on the crankshaft pulley or flywheel) pass by the sensor tip. This induces a voltage signal in the coil, which the ECM interprets as the crankshaft's position. Variations in the signal strength or pattern can indicate problems with the sensor or the crankshaft's rotational characteristics.
Locating the Crank Sensor on the 2005 Altima 2.5
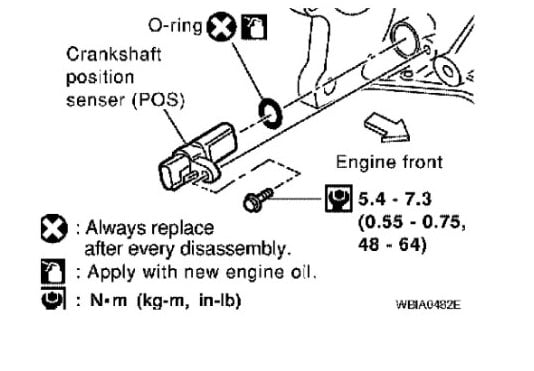
The crank sensor on the 2005 Nissan Altima 2.5 is located at the rear of the engine block, near the transmission bellhousing. Specifically, it's positioned to read the teeth on the flywheel/flexplate. While the general location is consistent, visibility and accessibility can be somewhat challenging due to its placement beneath other components. Let's break down the steps to pinpoint its exact location:
- General Area: Stand on the passenger side of the car. The sensor is positioned towards the rear of the engine, specifically where the engine block meets the transmission. It's crucial to note that you'll be looking down into the engine bay to locate it.
- Visual Obstructions: Several components may obstruct your view. These could include wiring harnesses, coolant hoses, and potentially part of the intake manifold assembly. You may need to carefully move these aside (without disconnecting anything unless absolutely necessary) to improve visibility.
- Sensor Appearance: The crank sensor itself is a relatively small, cylindrical component. It typically has a single electrical connector attached to it. The color may vary, but it is usually dark grey or black. You will see a single bolt holding it onto the engine block.
Accessing the Crank Sensor: A Step-by-Step Guide
Accessing the crank sensor for inspection, testing, or replacement requires some careful preparation and execution. Here's a detailed procedure:
Step 1: Safety First
Before beginning any work on your vehicle, prioritize safety. Disconnect the negative battery terminal to prevent any accidental electrical shorts. Ensure the vehicle is parked on a level surface, the parking brake is engaged, and the wheels are chocked. Wear appropriate safety glasses and gloves.
Step 2: Gather Necessary Tools
You'll need the following tools:
- Socket set (metric sizes)
- Wrench set (metric sizes)
- Screwdrivers (Phillips and flathead)
- Pliers
- Optional: A small inspection mirror and a flashlight or headlamp. These are invaluable for improving visibility in tight spaces.
Step 3: Create Access Space
As mentioned earlier, access can be limited. You may need to carefully move or temporarily remove certain components. Here's a breakdown of potential obstructions and how to address them:
- Wiring Harnesses: Carefully detach any wiring harnesses that are clipped to the engine block in the vicinity of the sensor. Use a small screwdriver or pick to gently release the retaining clips. Do not pull forcefully on the wires.
- Coolant Hoses: Be mindful of coolant hoses that may be routed nearby. Avoid kinking or damaging them. If a hose is directly obstructing access, you may need to carefully detach it. However, be prepared to catch any spilled coolant and top up the system afterward. It is usually not necessary to remove hoses.
- Intake Manifold Components: In some cases, components of the intake manifold assembly may partially block access. Evaluate the situation carefully. Removing these components can be complex and may require specialized knowledge. If you're unsure, it's best to seek professional assistance.
Step 4: Disconnecting the Electrical Connector
Once you have clear access to the sensor, carefully disconnect the electrical connector. The connector typically has a locking mechanism (a clip or tab) that needs to be released before you can pull it off. Do not pull on the wires themselves. Use a small screwdriver to gently depress the locking mechanism and then pull the connector straight off.
Step 5: Removing the Sensor
The crank sensor is typically held in place by a single bolt. Use the appropriate socket or wrench to remove this bolt. Once the bolt is removed, gently wiggle the sensor to loosen it from its mounting hole. Be careful not to damage the sensor or the surrounding components. The sensor should pull straight out. It may be somewhat snug due to age and accumulated grime.
Step 6: Inspection and Replacement
Once the sensor is removed, inspect it for any signs of damage, such as cracks, breaks, or corrosion. Check the electrical connector for damaged pins or corrosion. If the sensor is damaged, it should be replaced with a new one. Before installing the new sensor, clean the mounting surface on the engine block to ensure a good electrical ground. Apply a small amount of dielectric grease to the electrical connector to prevent corrosion and ensure a good connection.
Step 7: Reinstallation
Reinstall the new (or inspected) sensor by reversing the removal procedure. Ensure the sensor is properly seated in its mounting hole and tighten the bolt to the manufacturer's specified torque (if known – otherwise, snug it but don't overtighten). Reconnect the electrical connector, ensuring it locks securely. Reattach any wiring harnesses or components that were moved to gain access. Finally, reconnect the negative battery terminal.
Testing the Crank Sensor
A multimeter can be used to test the crank sensor's resistance. However, resistance values vary between manufacturers and even models. Consulting a repair manual or online database for the correct resistance range for your specific 2005 Nissan Altima 2.5 crank sensor is crucial. An open circuit (infinite resistance) or a short circuit (zero resistance) usually indicates a faulty sensor. Additionally, some advanced diagnostic tools can read the crank sensor's signal while the engine is cranking to verify its output.
Post-Installation Checks
After replacing the crank sensor, start the engine and observe its behavior. If the original problem was related to a faulty crank sensor, the engine should now start and run smoothly. If the problem persists, further diagnosis may be required to identify other potential causes, such as wiring issues, ECM problems, or other sensor failures. Be sure to clear any diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) stored in the ECM using an OBD-II scanner. If the check engine light reappears, investigate the new codes promptly.
Conclusion
While the location of the crank sensor on the 2005 Nissan Altima 2.5 may be somewhat hidden, understanding its function and knowing how to access it is essential for troubleshooting engine-related problems. By following this guide, you can confidently locate, inspect, and potentially replace the crank sensor, saving time and money on repairs. Remember to always prioritize safety and consult a qualified mechanic if you are unsure about any aspect of the procedure.
