2005 Nissan Altima Crank Sensor Location
The 2005 Nissan Altima, a popular mid-size sedan, relies on a network of sensors to ensure its engine operates smoothly and efficiently. Among these crucial components is the crankshaft position sensor (CKP sensor), often simply referred to as the crank sensor. This article delves into the function, location, and significance of the crank sensor in the 2005 Altima, providing a technical overview suitable for both curious readers and aspiring automotive enthusiasts.
Understanding the Crankshaft Position Sensor
The crank sensor plays a vital role in engine management. Its primary function is to monitor the rotational speed and position of the crankshaft. This information is relayed to the engine control module (ECM), also known as the engine control unit (ECU), the car's "brain". The ECM uses this data to precisely control ignition timing and fuel injection. Without accurate crankshaft position information, the engine cannot function correctly, leading to a no-start condition or significant performance issues.
To grasp the importance of the crank sensor, consider the timing of the combustion cycle. The ECM needs to know exactly where each piston is in its stroke – whether it's at the top of the compression stroke, ready for ignition, or at the bottom of the exhaust stroke. The crank sensor provides this critical positional data, allowing the ECM to fire the spark plugs and inject fuel at precisely the right moments.
There are typically two main types of crankshaft position sensors: inductive and Hall-effect. Inductive sensors generate a voltage signal based on changes in a magnetic field as the crankshaft rotates. Hall-effect sensors, on the other hand, use a semiconductor material that generates a voltage when exposed to a magnetic field. While the 2005 Altima may use either type, it's generally a Hall-effect sensor for improved accuracy and reliability.
Locating the Crank Sensor on the 2005 Altima
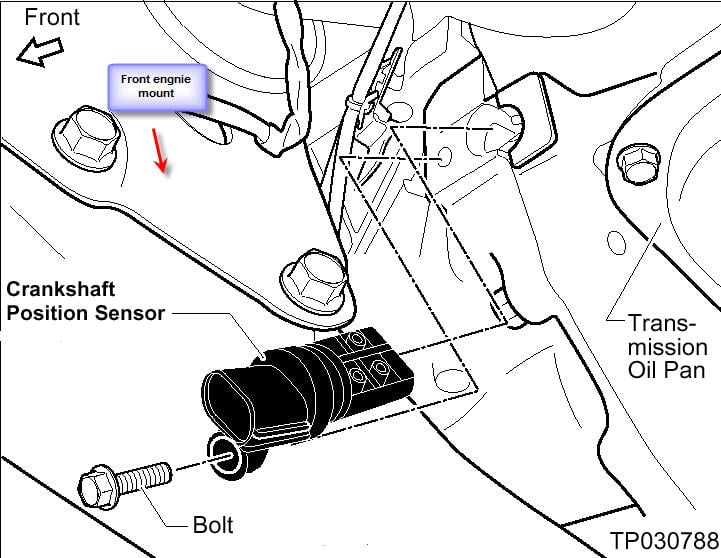
Identifying the precise location of the crank sensor is essential for diagnostics and replacement. On the 2005 Nissan Altima, the crank sensor's location depends on the specific engine equipped in the vehicle. Altima's from this year typically came with one of two engine options:
- 2.5L QR25DE Inline-4 Engine: For Altima's equipped with the 2.5L inline-4 engine, the crank sensor is typically located on the rear of the engine block, near the transmission bellhousing. It is positioned so that it can read a toothed wheel (reluctor ring) attached to the crankshaft. Due to its placement, access can be challenging, often requiring removal of other components for clear visibility and access.
- 3.5L VQ35DE V6 Engine: For Altima's equipped with the 3.5L V6 engine, the crank sensor is also located on the rear of the engine, but it is usually found closer to the side of the engine block than the 2.5L version. Again, it is positioned to read the reluctor ring attached to the crankshaft. Similar to the 2.5L engine, accessing the sensor may require maneuvering around other engine components.
Detailed Inspection and Access
To pinpoint the crank sensor, start by visually inspecting the rear of the engine block near the transmission bellhousing. You might need a flashlight to improve visibility. Look for a small, cylindrical sensor held in place by a bolt. It will have an electrical connector attached to it. Pay close attention to the wire harness leading to the sensor, as damaged or corroded wiring can also cause problems mimicking a faulty sensor.
Access Considerations: The location can be quite cramped, and access can be obstructed by exhaust components, hoses, and other engine bay elements. Depending on your skill level and available tools, you may need to remove air intake components or other nearby parts to gain sufficient access. Disconnecting the battery is always recommended before working on any electrical component.
Visual Aids and Resources
Due to the sometimes-obstructed location, consulting repair manuals or online resources with diagrams or videos can be incredibly helpful. Websites like YouTube often feature videos demonstrating the crank sensor replacement procedure for the 2005 Altima, providing visual guidance that complements written instructions. Online parts catalogs, such as those offered by auto parts stores, may also provide exploded views of the engine that indicate the sensor's location.
Symptoms of a Failing Crank Sensor
A failing crank sensor can manifest in a range of symptoms, some more subtle than others. Recognizing these signs early can help prevent a complete engine shutdown.
- Engine Stalling: One of the most common symptoms is unexpected engine stalling, particularly when the engine is warm. The engine might start fine initially, but then stall after running for a while.
- No-Start Condition: In more severe cases, a completely failed crank sensor will prevent the engine from starting at all. The ECM relies on the crank sensor signal to initiate fuel injection and spark, so without it, the engine simply won't fire.
- Check Engine Light: A faulty crank sensor will typically trigger the check engine light. The diagnostic trouble code (DTC) stored in the ECM will often point to a problem with the crank sensor circuit. Common codes include P0335 (Crankshaft Position Sensor "A" Circuit) and related codes.
- Rough Running or Misfires: Intermittent signal loss from the crank sensor can lead to rough engine running, misfires, and decreased fuel efficiency. The engine might hesitate or stumble during acceleration.
- Difficulty Starting: Even if the engine eventually starts, a failing crank sensor can make the starting process more difficult, requiring extended cranking.
Diagnosis and Testing
If you suspect a problem with the crank sensor, proper diagnosis is crucial before replacing it. A simple visual inspection of the sensor and its wiring can sometimes reveal obvious damage, such as frayed wires or a cracked sensor body. However, a more thorough diagnosis typically requires the use of a multimeter or an oscilloscope.
Multimeter Testing: A multimeter can be used to check the sensor's resistance and voltage output. Consult the vehicle's repair manual for the correct resistance values. If the resistance is outside the specified range, the sensor is likely faulty.
Oscilloscope Testing: An oscilloscope provides a more detailed view of the sensor's signal waveform. By observing the waveform as the engine cranks, you can identify signal dropouts, irregularities, or a complete lack of signal. This is the preferred method for definitively diagnosing a faulty crank sensor.
Important Note: Before replacing the crank sensor, it's essential to rule out other potential causes of the symptoms, such as a faulty camshaft position sensor (CMP sensor), wiring issues, or problems with the ECM itself. The CMP sensor works in conjunction with the CKP sensor to provide precise engine timing information, and a problem with the CMP sensor can sometimes mimic the symptoms of a faulty CKP sensor.
Replacement Considerations
If the diagnosis confirms that the crank sensor is indeed faulty, replacement is the next step. When purchasing a replacement sensor, it's crucial to choose a high-quality part from a reputable brand. Using a cheap or generic sensor can lead to premature failure and continued performance issues.
Installation: Follow the vehicle's repair manual for the specific installation procedure. Typically, this involves disconnecting the battery, disconnecting the electrical connector from the sensor, removing the mounting bolt, and carefully removing the old sensor. Install the new sensor in the reverse order, ensuring that the mounting bolt is tightened to the specified torque. Be sure to reconnect the electrical connector securely. After replacing the sensor, clear any diagnostic trouble codes from the ECM using a scan tool. Test drive the vehicle to verify that the problem has been resolved and that the engine is running smoothly.
Professional Assistance: If you are not comfortable performing the diagnosis or replacement yourself, it's best to seek the assistance of a qualified mechanic. They have the expertise, tools, and diagnostic equipment necessary to accurately diagnose the problem and perform the repair correctly.
Conclusion
The crankshaft position sensor is a critical component in the 2005 Nissan Altima's engine management system. Understanding its function, location, and potential failure symptoms is essential for maintaining the vehicle's performance and reliability. While accessing the sensor can be challenging due to its location on the rear of the engine block, proper diagnosis and replacement can restore proper engine operation. Remember to consult repair manuals, utilize visual aids, and seek professional assistance when needed to ensure a successful repair.
