2012 Nissan Sentra Step Motor
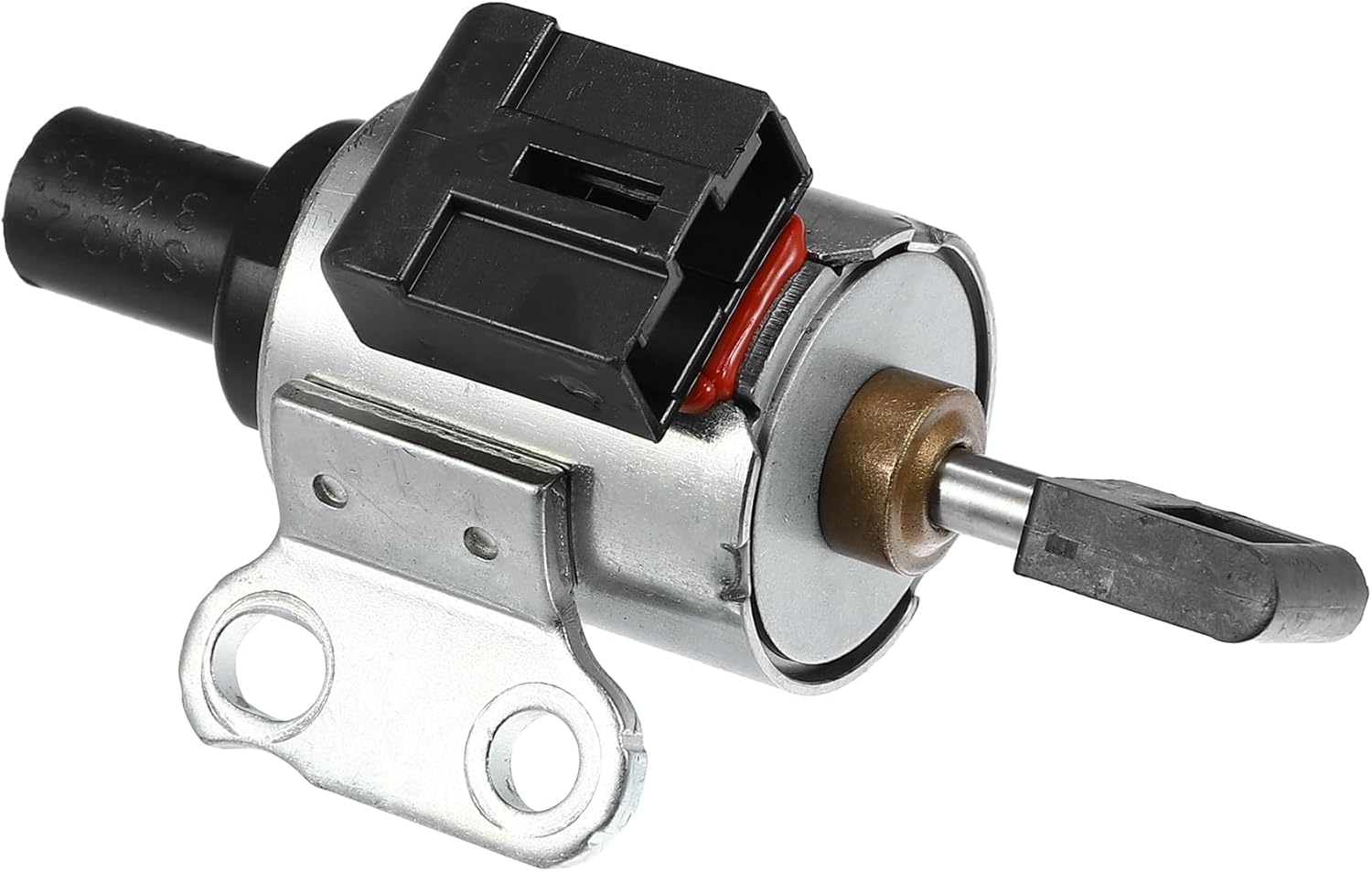
The 2012 Nissan Sentra, like many modern vehicles, relies on a sophisticated electronic control system to optimize engine performance and emissions. A critical component within this system is the step motor, also known as a stepper motor. This article will delve into the workings of the 2012 Sentra's step motor, exploring its function, construction, operation, and common issues.
What is a Step Motor and Why is it Used?
A step motor is a type of brushless DC electric motor that divides a full rotation into a number of equal steps. Unlike a traditional DC motor, which spins continuously when power is applied, a step motor rotates in discrete increments. This precise positioning capability makes it ideal for applications requiring accurate control, such as throttle body actuation, idle speed control, and even in some variable valve timing (VVT) systems. In the 2012 Sentra, the step motor is primarily used to control the idle air control (IAC) valve, ensuring a smooth and stable idle speed regardless of engine load or temperature.
The precision afforded by step motors makes them invaluable in systems demanding accurate positioning and control.
Before the widespread adoption of electronic throttle control (ETC), where the throttle plate is directly controlled by the ECU via a motor, IAC valves controlled idle speed. Even with ETC, a step motor might still be present in the system for other auxiliary functions.
Construction of the 2012 Sentra's Step Motor
While specific designs may vary, the step motor found in a 2012 Nissan Sentra typically consists of the following key components:
- Rotor: The rotating part of the motor. It's typically a permanent magnet or a variable reluctance rotor. In many IAC applications, the rotor is connected to a valve or plunger that regulates the airflow.
- Stator: The stationary part of the motor, containing multiple electromagnetic coils or windings. These coils, when energized in a specific sequence, create a magnetic field that pulls the rotor around.
- Bearings: These allow the rotor to rotate freely within the stator. Proper lubrication and maintenance are crucial for the motor's longevity.
- Housing: A protective casing that encloses the motor components and provides a mounting point.
- Electrical Connector: A connector for receiving electrical signals from the engine control unit (ECU). The number of pins varies depending on the specific motor design.
- Plunger/Valve (IAC specific): When used in an IAC valve application, the rotor will be connected to a plunger or valve, allowing the rotor rotation to influence air-flow rates.
The motor itself will be relatively small, often integrated directly into the IAC valve housing or the throttle body assembly, depending on the specific design used on the 2012 Sentra. Disassembling the step motor can be challenging and is often not recommended unless you possess specialized tools and knowledge, as it involves delicate components and precise alignments.
How the Step Motor Operates
The operation of a step motor relies on the precise sequencing of electrical pulses to the stator windings. The ECU sends these pulses, energizing different coils in a specific order. This creates a rotating magnetic field that attracts the rotor, causing it to move a defined step angle. By continuously energizing the coils in a controlled sequence, the rotor can be rotated in precise increments.
Here's a simplified breakdown of the process:
- ECU Input: The ECU monitors various engine parameters, such as engine speed (RPM), coolant temperature, throttle position, and manifold absolute pressure (MAP). Based on these inputs, the ECU determines the optimal idle air volume.
- Signal Transmission: The ECU sends a series of precisely timed electrical pulses to the step motor.
- Coil Energization: Each pulse energizes a specific coil in the stator.
- Rotor Movement: The energized coil creates a magnetic field that pulls the rotor, causing it to move one step.
- IAC Valve Adjustment: The rotor's movement is translated into a corresponding adjustment of the IAC valve, allowing more or less air to bypass the throttle plate and enter the engine.
- Idle Speed Regulation: By precisely controlling the amount of bypass air, the ECU maintains the desired idle speed.
The step angle is a crucial parameter that determines the resolution of the motor. A smaller step angle allows for finer control over the IAC valve position, leading to more precise idle speed regulation.
Different Driving Modes
Step motors can be driven in different modes, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
- Full-Step Drive: In this mode, two adjacent stator coils are energized simultaneously. This provides high torque but can result in lower resolution.
- Half-Step Drive: In this mode, either one or two coils are energized alternately. This doubles the resolution compared to full-step drive but reduces torque.
- Microstepping: This advanced technique involves varying the current in the coils to create intermediate positions between full steps. This results in very high resolution and smoother operation but requires more complex control circuitry.
The specific driving mode used in the 2012 Sentra's IAC step motor will depend on the specific design and control strategy employed by Nissan.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Like any mechanical and electrical component, the step motor in a 2012 Sentra is susceptible to wear and tear, and can develop faults. Here are some common issues:
- Sticking or Binding: Dirt, debris, or corrosion can cause the rotor or IAC valve to stick or bind, preventing smooth movement.
- Coil Failure: One or more of the stator coils may fail due to overheating or electrical damage.
- Wiring Problems: Damaged or corroded wiring can disrupt the electrical signals from the ECU to the motor.
- ECU Malfunction: In rare cases, the ECU itself may be the source of the problem, sending incorrect signals to the step motor.
- Vacuum Leaks: Vacuum leaks in the intake system can confuse the ECU and cause it to misadjust the IAC valve, leading to idle problems.
Symptoms of a faulty step motor can include:
- Rough Idle: Unstable or fluctuating idle speed.
- Stalling: The engine may stall, especially when coming to a stop or when the air conditioner is turned on.
- High Idle: The engine may idle at an excessively high RPM.
- Check Engine Light (CEL): A diagnostic trouble code (DTC) related to the IAC system may be stored in the ECU's memory, triggering the CEL.
Troubleshooting a suspected step motor issue typically involves the following steps:
- Check for DTCs: Use a scan tool to retrieve any stored DTCs from the ECU. Common codes related to the IAC system include P0505 (IAC System Malfunction), P0506 (IAC System RPM Lower Than Expected), and P0507 (IAC System RPM Higher Than Expected).
- Inspect Wiring and Connectors: Carefully inspect the wiring and connectors leading to the step motor and IAC valve for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Clean the IAC Valve: If the valve is accessible, try cleaning it with a throttle body cleaner to remove any dirt or debris. Be careful not to damage any delicate components.
- Test the Step Motor: Use a multimeter to check the resistance of the stator coils. Compare the readings to the manufacturer's specifications. An open or shorted coil indicates a faulty motor. Advanced diagnostics may involve using an oscilloscope to observe the waveforms of the control signals sent by the ECU.
- Scan Tool Actuation: Some scan tools offer the ability to command the IAC motor to move. Observe if the motor responds and if the idle speed changes accordingly.
If the step motor is found to be faulty, replacement is typically the best course of action. After replacing the motor, it may be necessary to perform an idle learn procedure to ensure proper operation. This procedure allows the ECU to learn the new motor's characteristics and adjust its control strategy accordingly.
Conclusion
The step motor plays a vital role in maintaining stable and efficient idle speed in the 2012 Nissan Sentra. Understanding its construction, operation, and common issues can help diagnose and resolve idle-related problems. While some troubleshooting steps can be performed by DIY enthusiasts, complex diagnostics and repairs may require the expertise of a qualified automotive technician. Regular maintenance and prompt attention to any symptoms of a faulty step motor can help ensure the smooth and reliable operation of your vehicle.
