2014 Nissan Maxima Valve Body
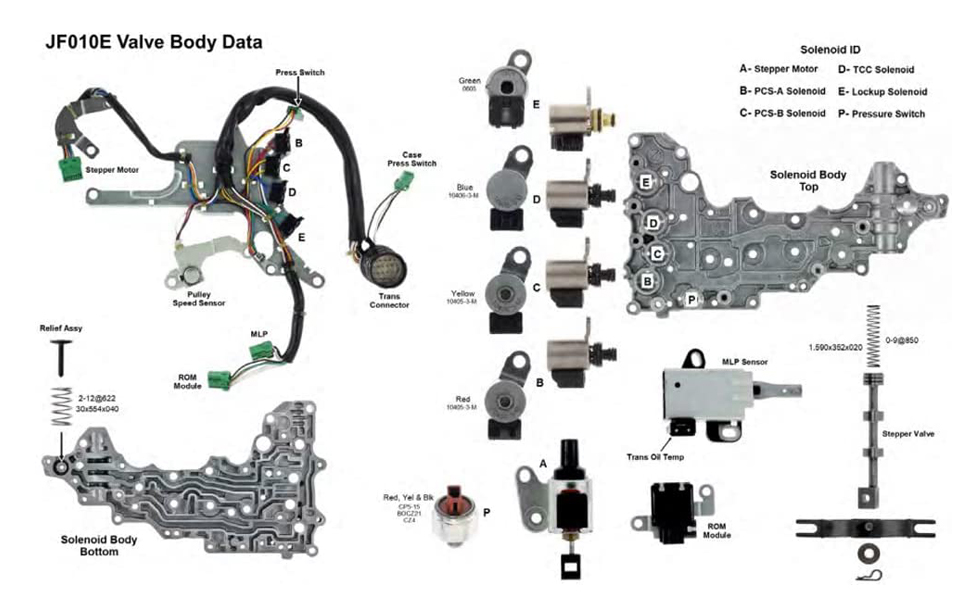
The 2014 Nissan Maxima, known for its sporty performance and near-luxury features, often sees issues related to its automatic transmission. A common culprit behind these problems is the valve body. This article dives deep into the 2014 Maxima's valve body, focusing on maintenance, troubleshooting, common issues, and practical solutions for both car owners and mechanics.
Understanding the Valve Body
The valve body is the hydraulic control center of an automatic transmission. Think of it as the transmission's brain, directing pressurized transmission fluid to various clutches and bands to engage the correct gears. It contains a network of channels, valves, and solenoids that work together to manage gear shifts. When the valve body malfunctions, it can lead to a variety of transmission problems.
Common Symptoms of a Failing 2014 Maxima Valve Body
Recognizing the symptoms early can save you from costly repairs. Here are some typical signs of a failing valve body in a 2014 Nissan Maxima:
- Rough or harsh shifting: This is often one of the first signs. You might feel a noticeable jolt or hesitation when the transmission shifts gears.
- Delayed engagement: When you shift into drive or reverse, there might be a delay before the transmission engages.
- Slipping gears: The transmission might momentarily lose power or feel like it's "slipping" out of gear while driving.
- Erratic shifting: The transmission might shift inappropriately, such as shifting into a higher gear too soon or shifting down unexpectedly.
- Stuck in gear: The transmission might become stuck in a particular gear, preventing you from shifting up or down.
- Check Engine Light: A failing valve body can trigger the check engine light. Diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to the transmission, such as P0775 (Pressure Control Solenoid 'B' Malfunction), P0744 (Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Intermittent), and others, may be stored.
- Transmission noise: Unusual whining or clunking noises coming from the transmission can sometimes indicate a valve body problem.
- Complete transmission failure: In severe cases, a severely damaged valve body can lead to complete transmission failure, rendering the vehicle undrivable.
Troubleshooting the 2014 Maxima Valve Body
When diagnosing transmission problems in a 2014 Maxima, it's essential to follow a systematic approach:
1. Scan for Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve any stored DTCs. Pay close attention to codes related to the transmission, solenoids, or pressure sensors. Important: A DTC related to the valve body doesn't automatically mean the valve body is bad. Further testing is needed.
Example: If you find a code like P0775, it points to a potential issue with the Pressure Control Solenoid 'B'. This could be a faulty solenoid, wiring problem, or a problem within the valve body itself.
2. Check Transmission Fluid Level and Condition
Inspect the transmission fluid level and condition. Low fluid levels can cause shifting problems. The fluid should be bright red and free of debris. Dark, burnt-smelling fluid indicates overheating and potential internal damage.
Contaminated fluid is a major contributor to valve body failures.
Problem: Low transmission fluid.
Solution: Check for leaks. Common leak points include the transmission pan gasket, seals, and cooler lines. Add the correct type of transmission fluid (Nissan Matic-S or equivalent) to the proper level.
Problem: Dark, burnt transmission fluid.
Solution: This indicates significant wear or overheating. A transmission fluid flush may help in some cases, but often it's a sign of more serious internal damage requiring a transmission rebuild or replacement. Address the cause of the overheating (e.g., a faulty cooler).
3. Inspect Wiring and Connectors
Check the wiring and connectors leading to the valve body for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Use a multimeter to test for voltage and continuity to the solenoids.
Problem: Corroded or damaged wiring.
Solution: Clean corroded connectors with electrical contact cleaner. Repair or replace damaged wiring. Ensure proper connections are made.
4. Valve Body Solenoid Testing
Each solenoid within the valve body controls a specific function. You can test the solenoids using a multimeter to measure their resistance. Consult the 2014 Maxima service manual for the correct resistance values.
Problem: A solenoid has an incorrect resistance reading or is open circuit.
Solution: Replace the faulty solenoid. Many valve body issues stem from failing solenoids. You can often purchase individual solenoids without replacing the entire valve body.
5. Pressure Testing
A professional mechanic can perform pressure tests to check the hydraulic pressure within the transmission. Low pressure can indicate a valve body problem or other internal transmission issues.
Problem: Low transmission pressure.
Solution: This often points to internal transmission wear, valve body issues, or a failing transmission pump. Further diagnosis is needed to pinpoint the exact cause.
Real-World Issues and Solutions
Here are some specific issues encountered with the 2014 Nissan Maxima valve body and their solutions:
Issue 1: Harsh 1-2 Shift
Symptom: A noticeable jolt or hard shift when the transmission shifts from first to second gear.
Possible Causes: Sticking valves in the valve body, a faulty 1-2 shift solenoid, or worn clutch packs.
Solution: Start by checking the transmission fluid condition. If it's dark or burnt, a fluid flush (and filter change) might help, but be aware of the risks. If the fluid is okay, consider replacing the 1-2 shift solenoid. If the problem persists, the valve body might need to be removed, cleaned, and rebuilt or replaced. In some cases, the clutch packs are damaged and transmission overhaul is required.
Issue 2: Torque Converter Lockup Problems
Symptom: The torque converter clutch (TCC) fails to lock up at highway speeds, or it locks and unlocks erratically. This can cause surging and reduced fuel economy.
Possible Causes: A faulty TCC solenoid, a problem with the TCC valve in the valve body, or a malfunctioning torque converter.
Solution: Check the TCC solenoid for proper operation. If it's faulty, replace it. If the solenoid is good, the valve body might need to be inspected and cleaned. In severe cases, the torque converter itself may need to be replaced.
Issue 3: No Reverse Gear
Symptom: The transmission will not engage reverse gear.
Possible Causes: A faulty reverse solenoid, a problem with the reverse valve in the valve body, or damaged reverse clutches or bands.
Solution: Check the reverse solenoid. If it's good, the valve body may need to be inspected and possibly rebuilt or replaced. In some cases, the internal clutches/bands related to reverse are damaged, requiring transmission overhaul.
Valve Body Replacement or Rebuild?
When a valve body is diagnosed as faulty, you have two main options: replacement or rebuild.
- Replacement: This involves installing a new or remanufactured valve body. It's generally the quicker and more straightforward option. Remanufactured valve bodies are often tested and come with a warranty.
- Rebuild: This involves disassembling the valve body, cleaning all the components, replacing worn or damaged parts (solenoids, valves, etc.), and reassembling it. This requires specialized knowledge and tools. It can be a more cost-effective option, but it's also more labor-intensive.
Recommendation: For most DIYers, replacing the valve body with a remanufactured unit is the preferred option. For experienced mechanics, rebuilding the valve body can be a viable alternative.
Preventative Maintenance
The best way to avoid valve body problems is to perform regular preventative maintenance:
- Regular Transmission Fluid Changes: Follow the manufacturer's recommended service interval for transmission fluid changes. This is crucial for maintaining proper lubrication and preventing debris buildup in the valve body.
Consider shortening the interval if you frequently drive in severe conditions (e.g., towing, stop-and-go traffic).
- Use the Correct Transmission Fluid: Always use the correct type of transmission fluid specified for your 2014 Nissan Maxima (Nissan Matic-S or equivalent). Using the wrong fluid can damage the transmission.
- Address Transmission Leaks Promptly: Fix any transmission leaks as soon as they are detected. Low fluid levels can cause serious transmission problems.
- Avoid Harsh Driving Habits: Avoid aggressive acceleration and hard braking, as these can put excessive stress on the transmission.
Examples from Other Popular Car Models
Valve body issues aren't exclusive to the Nissan Maxima. Many other vehicles with automatic transmissions experience similar problems. For instance:
- Honda Accord (2003-2007): These models were known for transmission issues, often related to valve body wear. Symptoms included harsh shifting and slipping gears.
- Ford Explorer (2002-2010): Some Explorer models experienced problems with the 5R55S transmission, often due to valve body malfunctions.
- BMW 3 Series (E46): Certain BMW models with GM transmissions also faced valve body issues, resulting in shifting problems.
Keeping Your Car in Top Condition
Maintaining your 2014 Nissan Maxima, or any vehicle, requires a proactive approach. Besides transmission care, consider these points:
- Regular Oil Changes: Keep the engine properly lubricated. Follow the manufacturer's recommended oil change intervals.
- Brake System Maintenance: Inspect brake pads, rotors, and brake fluid regularly. Replace worn components as needed.
- Cooling System Service: Maintain the cooling system to prevent overheating. Flush the coolant and inspect hoses and belts periodically.
- Tire Maintenance: Check tire pressure regularly and rotate tires to ensure even wear.
- Regular Inspections: Have your vehicle inspected by a qualified mechanic regularly to identify potential problems early on.
By understanding the potential issues with the 2014 Maxima's valve body and following a consistent maintenance schedule, car owners and mechanics can work together to keep these vehicles running smoothly for years to come. Ignoring the symptoms of a failing valve body can lead to more expensive and extensive repairs down the road. Early detection and prompt action are key to preserving the life of your transmission.
