2016 Nissan Altima Valve Body
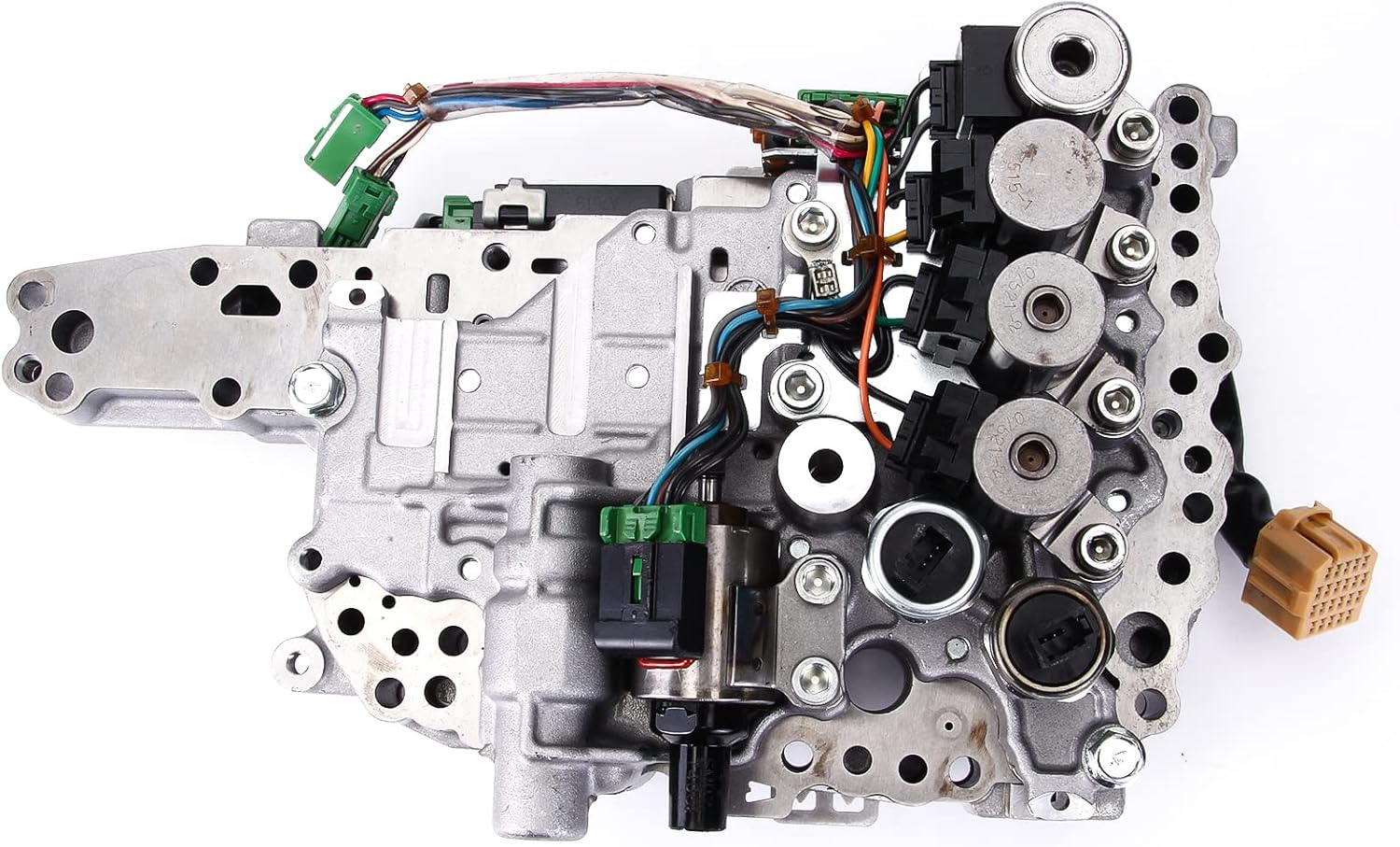
The 2016 Nissan Altima, like many vehicles using continuously variable transmissions (CVTs), can experience issues with its valve body. Understanding the function of the valve body, common problems, and appropriate maintenance strategies is crucial for both car owners and mechanics to ensure the longevity and performance of the vehicle. This article will delve into the intricacies of the Altima's valve body, offering practical advice on troubleshooting, maintenance, and real-world solutions.
Understanding the Valve Body in the 2016 Altima's CVT
The valve body is the hydraulic control center of an automatic transmission. In the 2016 Nissan Altima's CVT, it plays a critical role in managing the flow of transmission fluid to various parts of the transmission. It contains a complex network of solenoids, valves, and channels that regulate pressure and direct fluid to engage different gear ratios within the CVT belt and pulley system. Essentially, it's the brain of the transmission, translating electronic signals from the transmission control module (TCM) into physical actions.
A properly functioning valve body ensures smooth gear transitions, optimal fuel efficiency, and overall driving comfort. Conversely, a malfunctioning valve body can lead to a range of performance issues, potentially causing significant damage to the CVT if left unaddressed.
Common Symptoms of a Failing Valve Body
Recognizing the symptoms of a failing valve body is the first step in diagnosing and addressing the problem. Several telltale signs indicate potential issues:
- Rough or Erratic Shifting: The most common symptom. Instead of smooth transitions, you might experience harsh jerks, hesitations, or unexpected shifts.
- Slipping Gears: The engine revs up without a corresponding increase in speed. This can occur intermittently or consistently.
- Delayed Engagement: When shifting from Park to Drive or Reverse, there's a noticeable delay before the transmission engages.
- Transmission Limp Mode: The vehicle enters a safety mode, limiting speed and performance. The check engine light will usually illuminate.
- Check Engine Light: A faulty valve body can trigger diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to transmission performance, such as P0776, P0777, P0778, P0779 (Pressure Control Solenoid "B" Performance/Stuck Off/Electrical/Stuck On), and others.
- Unusual Noises: Whining, clunking, or humming sounds emanating from the transmission area.
- Decreased Fuel Efficiency: The transmission struggles to operate efficiently, leading to increased fuel consumption.
Consider these symptoms similar to those seen in other CVT-equipped vehicles, such as certain Honda models or Subaru vehicles with their Lineartronic CVT. The underlying issues and diagnostic approach are often comparable.
Causes of Valve Body Failure
Several factors can contribute to valve body failure in the 2016 Nissan Altima:
- Contaminated Transmission Fluid: Dirty or degraded transmission fluid is a primary culprit. Over time, friction material from the CVT belt wears down, creating microscopic particles that circulate within the fluid. These particles can clog the narrow passages within the valve body, hindering proper valve operation.
- Overheating: Excessive heat can damage the solenoids and seals within the valve body. Overheating often results from towing heavy loads, aggressive driving habits, or insufficient cooling system maintenance.
- Normal Wear and Tear: Over time, the mechanical components within the valve body, such as valves and solenoids, can wear out due to constant use.
- Electrical Issues: Faulty wiring, damaged connectors, or malfunctioning solenoids can disrupt the electrical signals controlling the valve body.
- Infrequent Transmission Fluid Changes: Neglecting regular transmission fluid changes allows contaminants to accumulate, accelerating wear and tear on the valve body.
Think of it this way: just as neglecting oil changes in your engine can lead to sludge buildup and engine damage, neglecting transmission fluid changes leads to similar issues within the valve body and CVT system.
Troubleshooting the Valve Body
Diagnosing a valve body issue requires a systematic approach:
- Scan for Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve any stored DTCs related to the transmission. These codes provide valuable clues about the nature and location of the problem. Pay close attention to codes related to pressure control solenoids or overall transmission performance.
- Inspect Transmission Fluid: Check the fluid level and condition. Low fluid level can indicate a leak. Dark, burnt-smelling fluid suggests overheating and contamination. If the fluid contains visible metal shavings, it's a sign of serious internal damage within the CVT.
- Perform a Visual Inspection: Inspect the valve body for any signs of external damage, such as cracks, leaks, or corrosion. Also, check the wiring harness and connectors for any loose connections or damaged wires.
- Solenoid Testing: Use a multimeter to test the resistance of individual solenoids. Compare the readings to the manufacturer's specifications. An out-of-range reading indicates a faulty solenoid.
- Pressure Testing: Connect a pressure gauge to the transmission test ports and monitor the pressure readings while the engine is running. Abnormal pressure readings can indicate a faulty valve body or other transmission issues. This test is often performed by experienced mechanics.
- Data Logging: Use a scan tool capable of data logging to monitor transmission parameters, such as fluid temperature, solenoid duty cycles, and gear ratios, while driving. This can help identify intermittent problems or abnormal operating conditions.
For example, if you find DTC P0777 (Pressure Control Solenoid "B" Stuck On), combined with rough shifting and dark transmission fluid, it strongly suggests a problem with that specific solenoid and overall fluid contamination. This points towards a need for valve body service and a fluid flush.
Solutions and Repairs
Depending on the severity of the problem, there are several possible solutions:
- Transmission Fluid Change and Filter Replacement: If the problem is caught early and the fluid is only mildly contaminated, a simple fluid change and filter replacement might be sufficient. Use the correct Nissan CVT fluid specified for the 2016 Altima. This is crucial! Do not use generic transmission fluid.
- Valve Body Cleaning or Reconditioning: In some cases, the valve body can be removed and cleaned to remove debris and restore proper function. Specialized transmission shops may offer valve body reconditioning services, which involve replacing worn or damaged components. This is often a more cost-effective solution than replacing the entire valve body.
- Solenoid Replacement: If a specific solenoid is identified as faulty, it can be replaced individually. Ensure you use a high-quality replacement solenoid from a reputable supplier.
- Valve Body Replacement: If the valve body is severely damaged or beyond repair, it may need to be replaced with a new or remanufactured unit. This is the most expensive option, but it ensures that all components are functioning properly.
- CVT Replacement: In the worst-case scenario, where the CVT has suffered significant internal damage due to a prolonged valve body issue, the entire transmission may need to be replaced.
Important Note: After performing any repairs on the valve body or transmission, it's essential to reset the transmission control module (TCM) to allow it to learn the new operating parameters. This often involves using a specialized scan tool to perform a transmission adaptation reset.
Consider this scenario: A 2016 Altima owner experiences delayed engagement and harsh shifting, along with DTC P0776. Upon inspection, the mechanic finds severely degraded transmission fluid. They opt for a valve body cleaning, solenoid replacement (for the solenoid associated with P0776), and a complete fluid flush. After the repair, the TCM is reset. The result? Smooth shifting and restored transmission performance.
Real-World Issues and Considerations
Several real-world issues often complicate valve body repairs:
- Availability of Parts: Finding genuine Nissan parts, especially for older CVT models, can sometimes be challenging. Consider using reputable aftermarket suppliers, but always ensure the parts meet or exceed OEM specifications.
- Complexity of CVT Systems: CVTs are complex systems, and diagnosing and repairing them requires specialized knowledge and tools. It's often best left to experienced technicians with expertise in CVT transmissions.
- Programming Requirements: Some valve bodies require programming or calibration after installation. Ensure your mechanic has the necessary equipment and software to perform this task.
- Cost of Repairs: Valve body repairs can be expensive, especially if replacement is required. Get multiple quotes from different shops and carefully consider the warranty offered on the repairs.
For instance, many independent mechanics may hesitate to work on CVTs due to their complexity, pushing owners towards dealerships, which often have higher labor costs. This highlights the importance of finding a trusted and knowledgeable mechanic who specializes in CVT transmissions.
Preventative Maintenance: Keeping Your Altima's CVT Healthy
The best way to avoid valve body problems is through preventative maintenance:
- Regular Transmission Fluid Changes: Follow the manufacturer's recommended maintenance schedule for transmission fluid changes. Nissan typically recommends changing the CVT fluid every 30,000 to 60,000 miles, depending on driving conditions. Consider shortening the interval if you frequently tow heavy loads or drive in stop-and-go traffic.
- Use the Correct Transmission Fluid: Always use the specified Nissan CVT fluid. Using the wrong fluid can damage the transmission.
- Avoid Aggressive Driving: Aggressive driving habits, such as frequent hard acceleration and braking, can put excessive stress on the transmission, leading to premature wear and tear.
- Monitor Transmission Temperature: If you frequently tow heavy loads or drive in hot climates, consider installing a transmission temperature gauge to monitor the fluid temperature. Excessive heat can damage the valve body and other transmission components.
- Address Issues Promptly: Don't ignore any signs of transmission problems. Addressing minor issues promptly can prevent them from escalating into more serious and expensive repairs.
By adhering to a proactive maintenance schedule and addressing potential problems early, you can significantly extend the life of your 2016 Nissan Altima's CVT and avoid costly valve body repairs.
In conclusion, understanding the function of the valve body, recognizing the symptoms of a failing unit, and implementing preventative maintenance strategies are crucial for maintaining the health and performance of your 2016 Nissan Altima's CVT. By following the advice outlined in this article, car owners and mechanics can work together to ensure the longevity and reliability of this important component.
