2017 Nissan Altima Transmission Problems
The 2017 Nissan Altima, a mid-size sedan known for its fuel efficiency and comfortable ride, gained considerable popularity. However, like many vehicles, it's not immune to potential issues. A recurring concern reported by owners centers around the continuously variable transmission, or CVT. This article delves into the specific transmission problems experienced with the 2017 Altima, offering a technical overview and exploring the underlying causes.
Understanding the CVT in the 2017 Altima
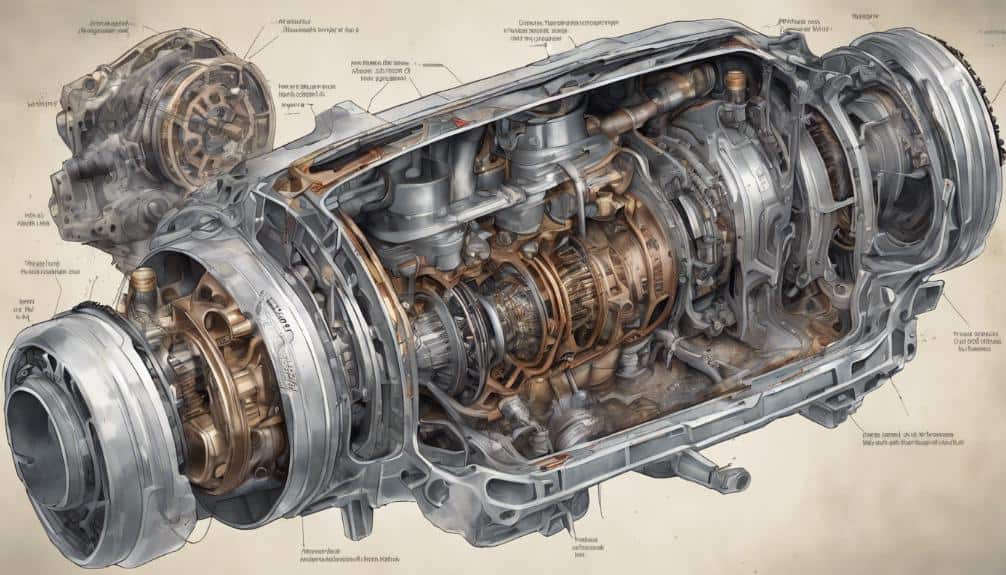
Before addressing the specific problems, it's crucial to understand the function of a CVT. Unlike traditional automatic transmissions with fixed gears, a CVT utilizes a system of pulleys and a belt or chain to provide a theoretically infinite number of gear ratios within its range. This allows the engine to operate at its most efficient RPM, leading to better fuel economy and smoother acceleration. In the 2017 Altima, Nissan employed a Jatco-sourced CVT, specifically the JF017E/RE0F10D variant depending on the engine option. This CVT model is found in various Nissan and other manufacturer vehicles.
Key Components and Operation
The JF017E/RE0F10D CVT comprises several key components:
- Input Pulley: Connected to the engine's crankshaft, it receives engine power.
- Output Pulley: Connected to the drive axles, it transmits power to the wheels.
- Steel Belt or Chain: Connects the input and output pulleys, transferring torque. The JF017E/RE0F10D typically uses a pushbelt design where multiple steel elements push against each other to transmit torque.
- Hydraulic Control System: Regulates the pressure applied to the pulleys, changing their effective diameters and thus the gear ratio. This system relies on solenoids, valves, and sensors to precisely control the transmission's behavior.
- Transmission Control Module (TCM): The brain of the CVT, the TCM receives input from various sensors (vehicle speed, engine speed, throttle position, etc.) and controls the hydraulic system to achieve the desired gear ratio.
The CVT operates by varying the diameters of the input and output pulleys. When the input pulley is small and the output pulley is large, the transmission is in a low gear ratio, providing high torque for acceleration. Conversely, when the input pulley is large and the output pulley is small, the transmission is in a high gear ratio, optimizing fuel efficiency at cruising speeds. The TCM constantly adjusts these pulley diameters based on driving conditions.
Common Transmission Problems in the 2017 Altima
Despite the benefits of CVTs, the 2017 Altima has been associated with several transmission-related problems. These issues can range from minor annoyances to major failures requiring costly repairs or replacements.
1. Slipping and Hesitation
One of the most frequently reported problems is transmission slippage or hesitation during acceleration. This manifests as a delay in response when the accelerator pedal is pressed, followed by a sudden surge in power or a lack of smooth power delivery. This can be attributed to several factors:
- Worn Belt/Chain: Over time, the steel belt or chain can wear down, losing its grip on the pulleys. This leads to slippage, especially under heavy load.
- Low Transmission Fluid Level: Insufficient fluid can reduce hydraulic pressure, hindering the ability of the pulleys to maintain proper contact with the belt/chain.
- Contaminated Transmission Fluid: Dirty or degraded fluid can clog the hydraulic system, preventing it from functioning correctly. Metal particles from wear and tear act as abrasives, further accelerating wear on internal components.
- Faulty Solenoids: Solenoids control the flow of hydraulic fluid to the pulleys. If a solenoid malfunctions, it can disrupt the gear ratio adjustments, leading to slippage or erratic shifting.
- TCM Issues: A malfunctioning TCM can send incorrect signals to the hydraulic system, resulting in improper gear ratios.
2. Jerky or Erratic Shifting
Some owners have reported experiencing jerky or erratic shifting, even though CVTs are designed for smooth, seamless gear ratio changes. This can feel like a traditional automatic transmission shifting harshly between gears. This is often related to:
- Valve Body Problems: The valve body contains numerous valves that control the flow of hydraulic fluid. If these valves become stuck or clogged, it can cause erratic shifting.
- Sensor Malfunctions: Sensors provide the TCM with information about vehicle speed, engine speed, and throttle position. If a sensor fails or provides inaccurate data, the TCM may make incorrect gear ratio adjustments.
- Internal Component Wear: Excessive wear on internal components, such as bearings or seals, can also contribute to jerky shifting.
3. Overheating
CVTs can generate significant heat, especially under demanding driving conditions. Overheating can damage internal components and lead to premature failure. Contributing factors include:
- Heavy Towing: Towing heavy loads places excessive strain on the transmission, generating more heat. The 2017 Altima is not designed for heavy towing.
- Aggressive Driving: Frequent hard acceleration and deceleration can also increase heat generation.
- Clogged Transmission Cooler: The transmission cooler helps dissipate heat. If it becomes clogged with debris, it reduces its efficiency, leading to overheating.
- Low Transmission Fluid Level: Insufficient fluid reduces the transmission's ability to dissipate heat effectively.
4. Complete Transmission Failure
In some cases, the aforementioned problems can escalate to complete transmission failure, requiring a replacement. This is often preceded by warning signs such as loud noises (whining, grinding), severe slippage, or a complete loss of power. This can occur when:
- Neglecting Maintenance: Infrequent transmission fluid changes can lead to excessive wear and eventual failure.
- Ignoring Early Warning Signs: Delaying repairs when problems first appear can allow them to worsen, leading to catastrophic failure.
- Pre-existing Manufacturing Defects: Though less common, some transmissions may have underlying manufacturing defects that contribute to premature failure.
Diagnosing and Addressing Transmission Problems
Proper diagnosis is essential for addressing transmission problems effectively. A qualified mechanic can use specialized diagnostic tools to identify the root cause of the issue. These tools can read fault codes stored in the TCM, monitor sensor data, and perform tests to assess the transmission's performance. Here are some diagnostic steps:
- Visual Inspection: Check for any signs of leaks or damage to the transmission.
- Fluid Level and Condition Check: Verify the transmission fluid level and examine its condition. Dark, burnt, or contaminated fluid indicates a problem.
- Scan for Fault Codes: Use a scan tool to retrieve any stored fault codes from the TCM. These codes can provide valuable clues about the nature of the problem.
- Sensor Data Analysis: Monitor sensor data (vehicle speed, engine speed, throttle position, etc.) to identify any inconsistencies or malfunctions.
- Pressure Testing: Perform pressure tests to assess the hydraulic system's performance.
- Road Test: Observe the transmission's behavior during a road test to identify any symptoms such as slipping, hesitation, or jerky shifting.
Once the problem has been diagnosed, appropriate repairs can be performed. These may include:
- Transmission Fluid Change: Replacing the transmission fluid with the correct type of fluid is crucial for maintaining optimal performance. Nissan recommends using its specified CVT fluid (NS-3) for the JF017E/RE0F10D.
- Solenoid Replacement: Replacing faulty solenoids can restore proper hydraulic control.
- Valve Body Repair or Replacement: Cleaning, repairing, or replacing the valve body can address issues related to jerky shifting.
- Transmission Cooler Cleaning or Replacement: Cleaning or replacing the transmission cooler can improve its efficiency and prevent overheating.
- Transmission Rebuild or Replacement: In severe cases, a complete transmission rebuild or replacement may be necessary.
Preventive Maintenance
Proper preventive maintenance is crucial for extending the lifespan of the CVT and preventing costly repairs. Here are some key maintenance recommendations:
- Regular Transmission Fluid Changes: Follow Nissan's recommended maintenance schedule for transmission fluid changes. While some sources suggest longer intervals, more frequent changes (e.g., every 30,000 miles) are often recommended, especially under demanding driving conditions.
- Avoid Heavy Towing: The 2017 Altima is not designed for heavy towing. Avoid towing altogether or limit it to light loads.
- Drive Conservatively: Avoid frequent hard acceleration and deceleration, as this can increase heat generation and stress the transmission.
- Monitor for Warning Signs: Pay attention to any unusual noises, vibrations, or shifting problems. Address these issues promptly to prevent them from worsening.
In conclusion, while the 2017 Nissan Altima offers several advantages, its CVT transmission has been a source of concern for some owners. Understanding the underlying causes of these problems and performing regular maintenance can help minimize the risk of transmission issues and ensure the long-term reliability of the vehicle. If you suspect a problem with your Altima's transmission, it's imperative to seek professional diagnosis and repair from a qualified mechanic experienced with CVTs.
