2017 Nissan Pathfinder Timing Chain Recall
The 2017 Nissan Pathfinder, a popular choice for families seeking a versatile and capable SUV, faced a significant challenge with a widespread timing chain recall. This article delves into the specifics of the recall, the underlying engineering choices that contributed to the problem, comparisons with alternative designs, and offers insights for automotive professionals regarding diagnostics, repair, and future preventative measures.
The 2017 Nissan Pathfinder Timing Chain Recall: An Overview
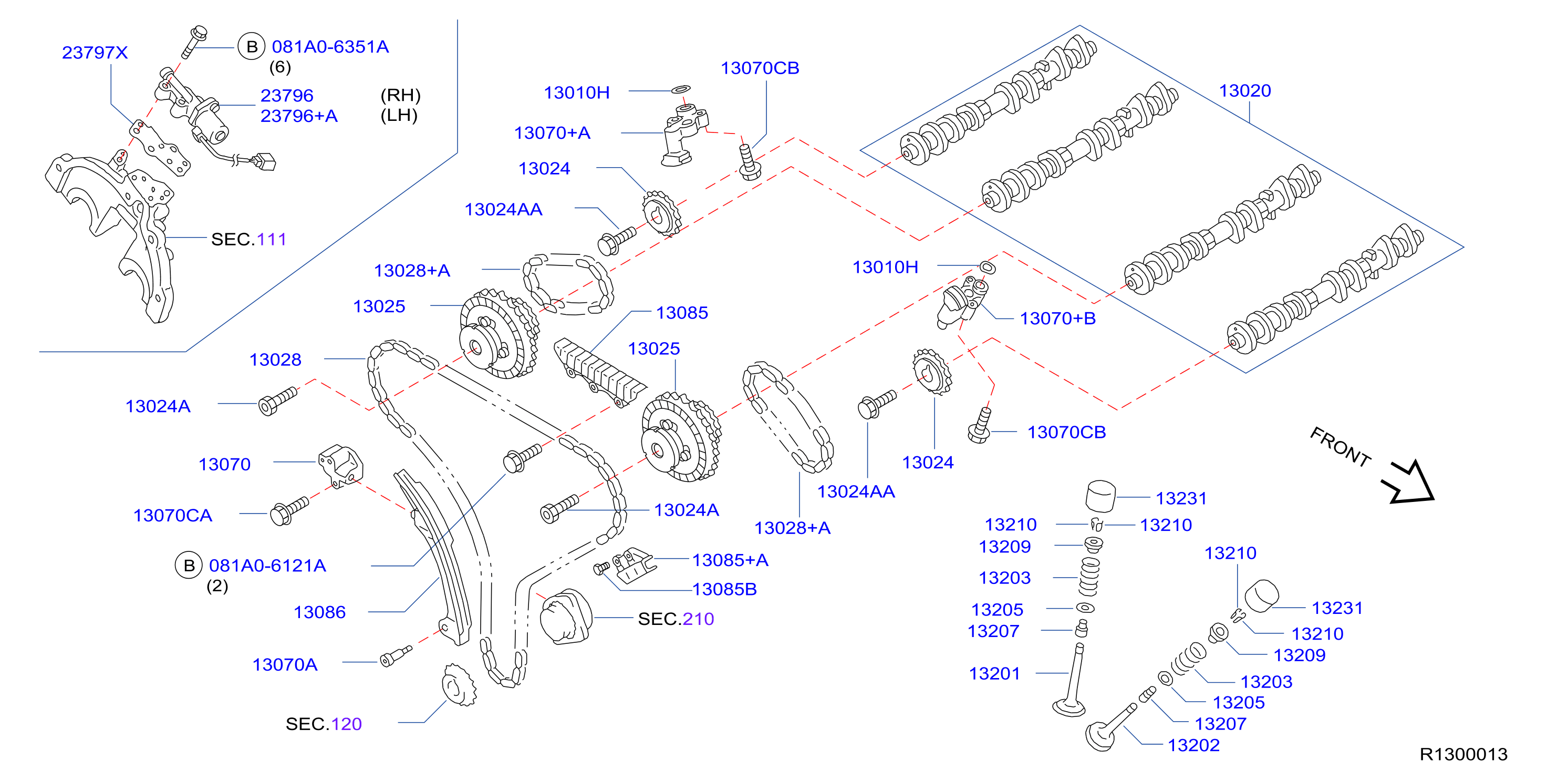
The recall, officially affecting certain 2017 Nissan Pathfinders (and, significantly, other Nissan and Infiniti models equipped with the VQ35DD engine), centered around a faulty timing chain tensioner. The timing chain, a critical component responsible for synchronizing the crankshaft and camshafts, relies on the tensioner to maintain proper tension and prevent slack. Insufficient tension can lead to chain slippage, impacting engine timing. In severe cases, this can result in engine damage, stalling, or failure to start. The NHTSA campaign number related to this recall is important for technicians to keep in mind.
Technical Specifications and Engineering Choices
The 2017 Pathfinder utilized the VQ35DD engine, a 3.5-liter V6 featuring direct injection. This engine was designed for improved fuel efficiency and power output compared to its predecessors. Direct injection, while offering advantages, also places greater stress on certain engine components due to the higher combustion pressures. The timing chain system within the VQ35DD employed a chain-driven design, common in many modern engines, but the choice of materials and design of the tensioner proved to be a critical weakness.
The problematic tensioner in question used a spring-loaded ratchet mechanism to maintain tension. The plastic components within this ratchet mechanism were prone to premature wear and degradation, especially under the demanding conditions of stop-and-go driving and high engine temperatures. This degradation resulted in reduced spring force and ultimately, insufficient tension on the timing chain. It's important to note that Nissan had been using variations of the VQ engine for many years prior, and while there were minor timing chain issues reported over the years, the 2017 timeframe saw a significant increase in failures. The direct injection system's contribution to increased cylinder pressures, combined with a potentially cost-reduced or redesigned tensioner, likely played a role.
Real-World Performance and Symptoms
The real-world manifestation of the timing chain issue presented in several ways:
- Rattling Noise: A distinctive rattling or whining noise from the engine, particularly during startup or acceleration, was a common symptom. This noise indicated slack in the timing chain.
- Check Engine Light: Illumination of the check engine light, often accompanied by diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to camshaft or crankshaft position sensor correlation, was another indicator. P0011, P0012, P0016, and P0017 were frequently reported DTCs.
- Rough Idling: Unstable or rough idling, potentially accompanied by stalling, occurred as the timing drifted out of optimal range.
- Reduced Performance: A noticeable decrease in engine power and fuel economy could result from improper valve timing.
- Engine Stalling: In severe cases, the timing chain could slip significantly, leading to engine stalling and potentially catastrophic engine damage.
Owners reported these issues at varying mileages, some experiencing problems well before the expected lifespan of a timing chain system. This variability underscored the unpredictable nature of the failure and the potential for significant inconvenience and repair costs.
Alternatives and Comparisons
While chain-driven timing systems are prevalent, alternative designs exist. A notable alternative is the use of a timing belt. Here's a comparison:
Timing Chain vs. Timing Belt: Pros and Cons
Timing Chain:
- Pros: Generally longer lifespan, theoretically lasting the life of the engine with proper maintenance. More durable and resistant to wear and tear compared to belts. Less susceptible to damage from oil contamination.
- Cons: Can be noisier than timing belts. More complex and expensive to repair. Requires a robust lubrication system. As evidenced by the Pathfinder recall, even chain systems can fail prematurely due to tensioner issues or chain stretch.
Timing Belt:
- Pros: Quieter operation. Generally less expensive to replace.
- Cons: Requires periodic replacement at specified intervals (typically every 60,000-100,000 miles). Susceptible to damage from oil contamination and extreme temperatures. Failure can lead to catastrophic engine damage if not replaced on time.
Some manufacturers are also exploring more advanced variable valve timing systems that can influence timing chain tension and stress. However, these systems introduce their own complexities and potential failure points.
Reliability Aspects and Maintenance Tips
The 2017 Pathfinder timing chain recall highlighted the importance of preventative maintenance and early detection. For automotive professionals working on vehicles with the VQ35DD engine (or similar direct-injection V6 engines):
- Regular Oil Changes: Using the recommended oil viscosity and adhering to the manufacturer's recommended oil change intervals is critical. Clean oil lubricates the timing chain and tensioner, minimizing wear. Consider recommending shorter intervals for vehicles subjected to frequent stop-and-go driving or extreme operating conditions.
- Listen for Unusual Noises: Train your ear to recognize the telltale rattling or whining noise associated with a worn timing chain or tensioner. This is especially important during cold starts.
- Inspect for Oil Leaks: Check for oil leaks around the timing chain cover. Leaks can indicate failing seals and potential oil contamination of the timing chain.
- OBD-II Scanning: Regularly scan the vehicle's onboard diagnostic system for any relevant DTCs, even if the check engine light is not illuminated. Pending codes can provide early warnings.
- Inspect Chain Slack: During engine servicing (valve cover removal, etc.), visually inspect the timing chain for excessive slack or wear. This can be difficult without specific tools and experience, but an experienced technician can often detect subtle signs of impending failure.
- Use Genuine Parts: When replacing timing chain components, using genuine Nissan parts or reputable aftermarket brands is recommended. Lower-quality aftermarket parts may not meet the required specifications and could fail prematurely.
- Updated Tensioner Design: When performing the recall or replacing the timing chain components, ensure the replacement parts incorporate any design improvements or revisions made by Nissan to address the original defect.
Future Trends and Forward-Looking Notes
The automotive industry is constantly evolving, with a focus on improving engine efficiency, reducing emissions, and enhancing reliability. Future trends related to timing systems include:
- Improved Materials: Manufacturers are exploring the use of more durable and wear-resistant materials for timing chains and tensioners. This includes advanced alloys and coatings.
- Optimized Designs: Research is underway to optimize the design of timing chain systems to reduce friction and stress, thereby extending their lifespan.
- Sensor Integration: Integrating sensors into the timing chain system to monitor tension and wear in real-time could provide early warnings of potential failures.
- Electrification: The increasing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) eliminates the need for traditional timing systems altogether. As EVs gain market share, the demand for internal combustion engine (ICE) components, including timing chains, will gradually decline.
The 2017 Nissan Pathfinder timing chain recall serves as a valuable lesson for both manufacturers and automotive professionals. It underscores the importance of robust engineering design, rigorous testing, and proactive maintenance. As the automotive industry continues to innovate, a focus on reliability and preventative measures will remain crucial to ensuring customer satisfaction and minimizing costly repairs. The push towards electrification and alternative powertrain designs represents a significant shift, but ICE vehicles will remain a vital part of the automotive landscape for years to come, demanding continued expertise and attention to detail from automotive technicians.
The incident also highlights the increasing complexity of modern engines and the importance of staying up-to-date with the latest technical information and diagnostic techniques. Continuous training and investment in specialized tools are essential for automotive professionals to effectively diagnose and repair these systems. Furthermore, the recall emphasizes the need for clear communication with customers regarding potential maintenance requirements and the importance of addressing any warning signs promptly to prevent more serious and expensive engine damage. This recall is a critical case study for understanding the long-term implications of design choices in modern automotive engineering.
Finally, the trend towards longer warranty periods and extended service intervals places a greater burden on manufacturers to ensure the reliability of their components over the long term. The 2017 Pathfinder recall serves as a reminder that even seemingly minor design flaws can have significant consequences, impacting brand reputation and customer loyalty. Proactive preventative maintenance and the use of high-quality replacement parts are the best defense against premature timing chain failure.
