240sx Starter Relay Location
The Nissan 240SX, a beloved platform for drifting, modification, and general automotive enthusiasm, often presents unique challenges to automotive professionals, particularly regarding electrical components. Among these, the starter relay stands out as a frequent point of inspection and troubleshooting. This article delves into the specifics of the 240SX starter relay location, its function, alternative systems, maintenance, and the broader implications for the automotive industry.
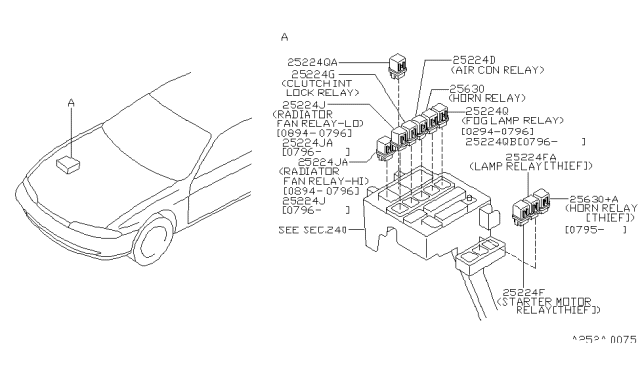
Location and Function of the 240SX Starter Relay
The starter relay in a 240SX, typically found in models from 1989-1998 (S13 and S14 chassis), is generally located within the engine bay's fuse box. Specifically, it's often in the fuse box near the battery, though the exact positioning can vary slightly based on the specific year and trim. Always consult the factory service manual for the precise diagram relevant to the vehicle in question. It is essential to disconnect the negative battery terminal before working on any electrical components to prevent shorts or damage.
The starter relay’s primary function is to act as an intermediary switch between the ignition switch and the starter solenoid. The ignition switch carries a relatively low current signal. This low current is insufficient to directly activate the high-current solenoid needed to engage the starter motor. The relay allows a small current to control a larger current, protecting the ignition switch from potential overload and allowing for a more efficient starting process. When the ignition switch is turned to the 'start' position, it sends a signal to the starter relay. The relay then closes, completing a circuit that sends a high-current flow to the starter solenoid. The solenoid then pushes the starter motor's pinion gear into the flywheel, allowing the engine to crank.
Technical Specifications and Engineering Choices
The starter relay in the 240SX is usually a standard automotive relay, commonly a 4- or 5-pin type. Key specifications include its coil voltage (typically 12V DC), its contact rating (usually around 30-40 amps), and its operating temperature range. The choice of a relay for this function is a direct result of engineering considerations. Relays are robust, reliable, and relatively inexpensive, making them a practical solution for controlling high-current circuits with low-current inputs. The internal mechanism of the relay consists of an electromagnet that, when energized, pulls a contact arm closed, bridging the high-current circuit. This simple design makes it easy to diagnose and replace.
Common Problems and Troubleshooting
A failing starter relay can manifest in several ways, including a no-start condition, intermittent starting issues, or a clicking sound from the relay itself. It's crucial to differentiate a relay problem from other starting issues such as a faulty starter motor, a discharged battery, or a problem with the ignition switch. Troubleshooting involves several steps:
- Visual Inspection: Check the relay for any signs of physical damage, corrosion, or melting.
- Relay Swapping: If possible, swap the starter relay with another identical relay in the fuse box (e.g., a horn relay). If the problem moves with the relay, the relay is faulty.
- Voltage Testing: Use a multimeter to check for voltage at the relay terminals when the ignition switch is in the 'start' position. There should be 12V present at the coil terminal. Also, check for continuity between the relay's output terminals when the relay is activated.
- Bypass Test: A bypass test involves manually jumping the relay's power and output terminals with a jumper wire. This test should only be performed by experienced technicians and with extreme caution. If the engine starts when the relay is bypassed, the relay is the likely culprit.
Comparison with Alternatives and Performance
While relays are the standard solution for starter control in the 240SX and many other vehicles, alternative systems exist. Solid-state relays (SSRs) offer several advantages over traditional electromechanical relays. SSRs use semiconductor devices to switch the circuit, eliminating the mechanical contacts prone to wear and tear. This leads to increased reliability and a longer lifespan. However, SSRs are generally more expensive and can generate more heat, requiring proper heat sinking. Another, albeit less common, alternative is a direct high-current ignition switch. This is usually only employed in very basic, low-power applications due to the higher current requirements and potential for damage to the switch over time.
In terms of real-world performance, the traditional relay system in the 240SX has proven to be adequate, but not without its drawbacks. The electromechanical nature of the relay makes it susceptible to wear, corrosion, and contact degradation, particularly in harsh environments or vehicles with poor electrical maintenance. SSRs, while offering superior reliability, might not be a direct drop-in replacement without modifications to the wiring harness and consideration for heat dissipation.
Pros and Cons of Relay vs. SSR
Relay (Electromechanical):
- Pros: Inexpensive, readily available, easy to diagnose, relatively simple to replace.
- Cons: Prone to wear and tear, susceptible to corrosion, slower switching speed compared to SSRs, audible clicking noise can be annoying.
SSR (Solid-State Relay):
- Pros: Higher reliability, longer lifespan, faster switching speed, silent operation.
- Cons: More expensive, can generate more heat, potentially requires wiring modifications, more complex to diagnose.
Reliability Aspects and Maintenance Tips
The reliability of the starter relay in a 240SX is directly related to the overall condition of the vehicle's electrical system. Corrosion, loose connections, and voltage drops can all contribute to premature relay failure. Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the relay's longevity. This includes:
- Visual Inspection: Periodically inspect the fuse box and relay for signs of corrosion or damage.
- Terminal Cleaning: Clean the relay terminals and the corresponding sockets in the fuse box to ensure good electrical contact. Use a contact cleaner specifically designed for electronics.
- Voltage Testing: Regularly check the battery voltage and charging system to ensure that the relay is receiving the correct voltage.
- Relay Replacement: Consider replacing the starter relay as part of routine maintenance, especially on older vehicles. A new relay is an inexpensive insurance policy against potential starting problems.
Furthermore, proper wiring and grounding are critical. Ensure that all ground connections in the engine bay are clean and secure. A poor ground can cause voltage drops and increase the likelihood of relay failure. Consider using dielectric grease on electrical connections to prevent corrosion.
Future Trends
The automotive industry is rapidly evolving, with a growing emphasis on electric vehicles (EVs) and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). While the 240SX, being an older platform, doesn't directly benefit from these advancements, the principles of electrical control remain relevant. In modern vehicles, relays are gradually being replaced by solid-state devices and integrated electronic control units (ECUs). These ECUs offer more precise control, diagnostic capabilities, and integration with other vehicle systems.
However, even in EVs, relays still play a crucial role in high-voltage circuits, such as battery disconnects and charging systems. As battery technology advances and voltage levels increase, the demands on these relays become more stringent, requiring robust designs and advanced materials. Furthermore, the increasing complexity of automotive electrical systems necessitates more sophisticated diagnostic tools and training for automotive technicians.
Conclusion
Understanding the location, function, and potential issues of the starter relay in a Nissan 240SX is essential for automotive professionals working on this platform. While the relay itself is a relatively simple component, its role in the starting system is critical. By following proper troubleshooting procedures, implementing preventative maintenance, and staying informed about advancements in electrical control systems, technicians can effectively diagnose and resolve starting problems, ensuring the continued reliability of these iconic vehicles. As the automotive industry moves towards electrification and advanced electronics, a strong foundation in basic electrical principles will remain essential for success.
