Car Steering Rack And Pinion
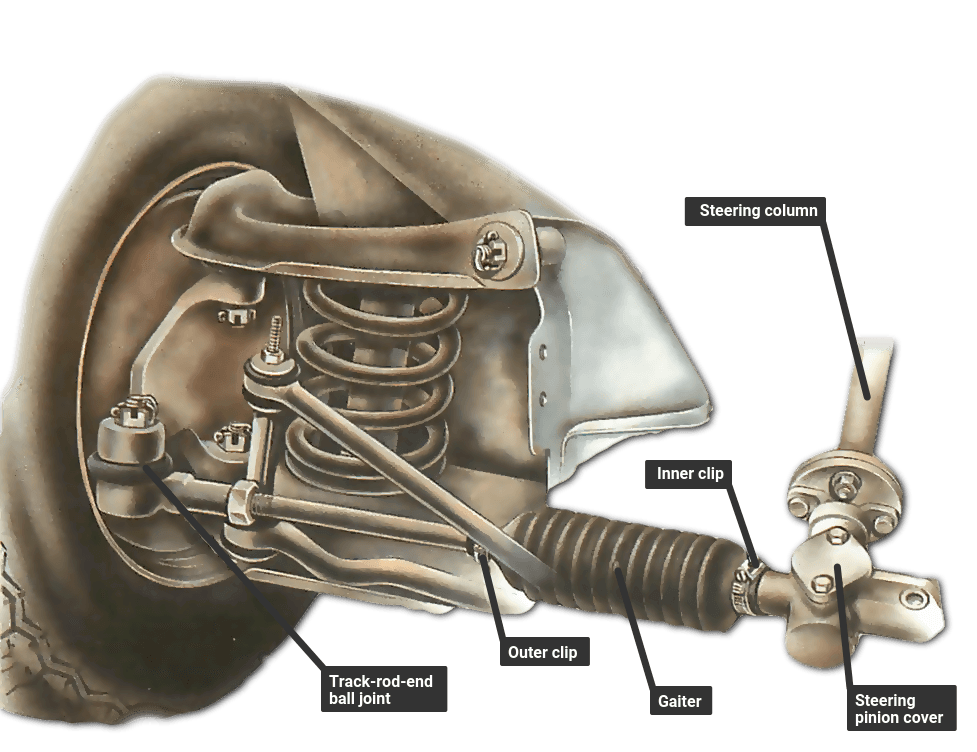
The steering rack and pinion is a critical component in most modern cars, responsible for translating the rotation of your steering wheel into the lateral movement that steers your vehicle. It's a robust system, but understanding its workings, common issues, and maintenance can help you keep your car handling smoothly and safely.
How It Works: A Simplified Explanation
Imagine you're turning a doorknob. The doorknob is your steering wheel, and the mechanism that opens and closes the latch is analogous to the rack and pinion. In simple terms, the rack and pinion system consists of two primary parts:
* The Pinion: This is a small, circular gear connected to the steering column. When you turn the steering wheel, you're directly rotating the pinion. * The Rack: This is a long, toothed bar that runs horizontally across the front (or sometimes rear) of the car. The pinion gear meshes with the teeth of the rack.As the pinion rotates, its teeth push against the rack's teeth, causing the rack to move either left or right. This linear motion of the rack is then transferred to the wheels via tie rods. The tie rods connect to the steering knuckles, which pivot the wheels, allowing you to steer. It's a mechanical marvel of efficiency and relative simplicity.
The Role of Power Steering
While the basic rack and pinion system is relatively straightforward, most modern vehicles incorporate power steering to reduce the effort required to turn the wheel. Power steering assists the driver by using hydraulic or electric pressure to augment the force applied to the rack. The pump (hydraulic) or electric motor (electric) provide a supplemental force in the same direction the driver is turning the wheel. This allows for lighter, easier steering, especially at low speeds.
A typical hydraulic power steering system uses a pump, driven by the engine via a belt, to create hydraulic pressure. This pressure is directed to either side of the rack via a control valve. When you turn the wheel, the control valve directs the pressurized fluid to the appropriate side of the rack, helping it move more easily. Think of it as having a powerful assistant helping you push the rack.
Electric power steering (EPS) systems, increasingly common in newer vehicles like the Toyota Prius or the Honda Civic, use an electric motor to provide the assistance. This motor can be mounted on the steering column or directly on the rack itself. EPS systems are often more efficient than hydraulic systems because they only draw power when steering assistance is needed. They also allow for more sophisticated features like variable assist, where the amount of assistance changes based on speed and driving conditions. For example, a BMW M3 might have heavier steering at high speeds for better stability and lighter steering at low speeds for easier maneuvering.
Rack and Pinion in Action: Real-World Examples
The rack and pinion system is widely used across a diverse range of vehicles. Here are a few examples:
* Ford Mustang: Traditionally, Mustangs have used rack and pinion steering for a sporty and responsive feel. Earlier models often used hydraulic power steering, while newer models have transitioned to EPS for improved efficiency and control. * Honda Accord: The Accord, known for its reliability and practicality, has long utilized rack and pinion steering. Its system is typically calibrated for a balance of comfort and responsiveness, suitable for everyday driving. * Chevrolet Silverado: Even large trucks like the Silverado employ rack and pinion steering in some configurations, particularly in newer models. Due to the weight of the vehicle, these systems are typically robust and feature heavy-duty components. In earlier models, recirculating ball steering was more common due to its high load capacity. * Mazda MX-5 Miata: The Miata is a prime example of a car where steering feel is paramount. Its rack and pinion system is carefully tuned to provide direct and precise feedback to the driver, enhancing the driving experience.Common Rack and Pinion Problems
While the rack and pinion system is generally reliable, it's not immune to problems. Here are some common issues:
* Leaks: Hydraulic power steering systems are prone to leaks. These leaks can occur in the hoses, the pump, or the rack itself. Low power steering fluid can lead to noisy operation, stiff steering, and eventually, pump failure. You might notice a red or brown fluid leaking under the car. * Worn Tie Rods: Tie rod ends connect the rack to the steering knuckles. These joints are subject to wear and tear, leading to loose steering and vibrations. A clunking sound when turning the wheel is a common symptom. * Internal Wear: Over time, the rack and pinion gears can wear out, leading to excessive play and sloppy steering. This is more common in older vehicles or those with high mileage. * Contamination: Dirt and debris can contaminate the power steering fluid, causing damage to the pump and rack. Regular power steering fluid flushes can help prevent this. * Noisy Operation: A whining or groaning noise when turning the wheel can indicate a problem with the power steering pump. This could be due to low fluid, a failing pump, or a blockage in the system. * Uneven Tire Wear: Problems within the rack and pinion, like worn tie rod ends, can lead to misalignment and cause uneven tire wear.Diagnosing Rack and Pinion Issues
Diagnosing rack and pinion problems can sometimes be tricky, as many symptoms can be attributed to other suspension components. However, here are some steps you can take:
1. Visual Inspection: Check for leaks around the rack and pinion unit, power steering pump, and hoses. Look for any signs of damage or corrosion. 2. Steering Feel: Pay attention to how the steering feels. Is it stiff, loose, or noisy? Does the car wander or pull to one side? 3. Listen for Noises: Listen for any unusual noises when turning the wheel, such as clunking, groaning, or whining. 4. Check Tie Rods: Jack up the front of the car and check for play in the tie rod ends. Grab the tie rod and try to move it up and down or side to side. Excessive play indicates wear. 5. Power Steering Fluid: Check the power steering fluid level and condition. Low fluid or dirty fluid can indicate a problem. 6. Professional Inspection: If you suspect a rack and pinion problem, it's always best to have a qualified mechanic inspect the system. They have the tools and expertise to diagnose the problem accurately.Maintenance and Prevention
Proper maintenance can help extend the life of your rack and pinion system. Here are some tips:
* Regular Power Steering Fluid Flushes: Follow your vehicle manufacturer's recommendations for power steering fluid flushes. This helps remove contaminants and keeps the system operating smoothly. * Check Fluid Level Regularly: Keep an eye on the power steering fluid level and top it off as needed. Use the correct type of fluid specified in your owner's manual. * Avoid "Lock to Lock" Steering: Avoid holding the steering wheel at full lock for extended periods, as this can put excessive strain on the power steering pump. * Inspect Suspension Components: Regularly inspect the suspension components, including tie rod ends, ball joints, and control arm bushings. Worn suspension parts can put extra stress on the rack and pinion. * Address Problems Promptly: If you notice any signs of a rack and pinion problem, such as leaks, noises, or loose steering, have it addressed promptly. Ignoring the problem can lead to more extensive and costly repairs.Practical Takeaways
Understanding the rack and pinion system empowers you to better maintain your vehicle and diagnose potential issues. Here are some key takeaways:
* Recognize the Symptoms: Be aware of the common symptoms of rack and pinion problems, such as leaks, noises, and loose steering. Early detection can prevent more serious damage. * Perform Basic Maintenance: Regularly check the power steering fluid level and condition, and follow the manufacturer's recommendations for fluid flushes. * Inspect for Leaks: Visually inspect the rack and pinion area for leaks. Address any leaks promptly to prevent further damage. * Don't Ignore Noises: Pay attention to any unusual noises when turning the wheel. These noises can be a sign of a problem with the power steering pump or rack. * Seek Professional Help: If you suspect a rack and pinion problem, don't hesitate to seek professional help. A qualified mechanic can accurately diagnose the problem and recommend the appropriate repairs. * Consider EPS Advantages: When purchasing a new vehicle, consider the advantages of electric power steering (EPS), such as improved efficiency and customizable steering feel.By understanding the rack and pinion system and following these practical tips, you can keep your car steering smoothly and safely for years to come. Remember that preventative maintenance is key to avoiding costly repairs and ensuring a comfortable and enjoyable driving experience.
