Coil Pack Nissan Altima 2005
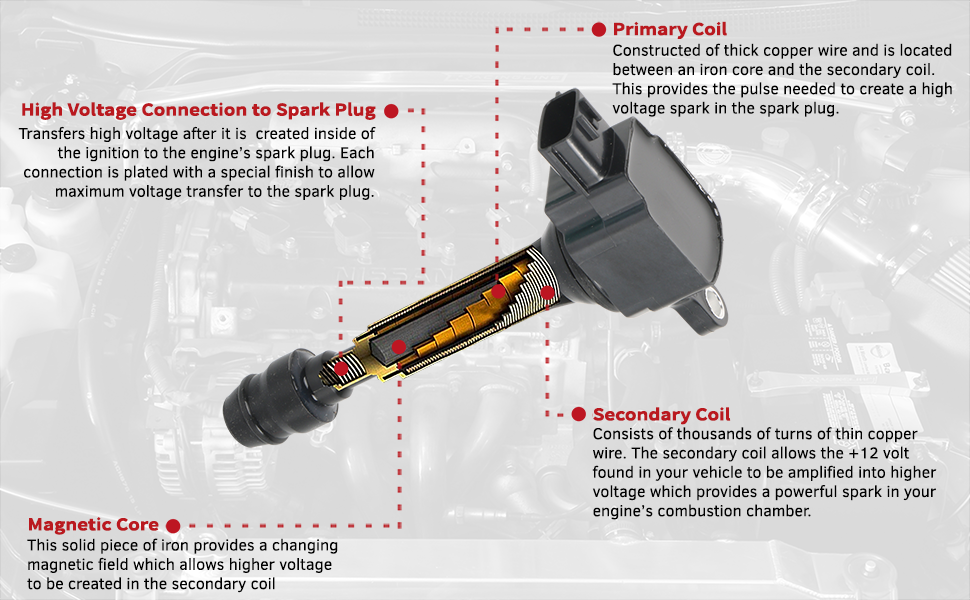
The 2005 Nissan Altima, like many vehicles of its era, relies on coil packs for its ignition system. These seemingly simple components are crucial for reliable engine performance. However, coil packs can fail, leading to a variety of drivability issues. This article will delve into the world of coil packs in the 2005 Altima, covering maintenance, troubleshooting, and real-world problems encountered by owners and mechanics alike.
Understanding Coil Packs
A coil pack is essentially an ignition coil, but instead of a single coil distributing spark to all cylinders via a distributor, each coil pack typically serves one or two cylinders directly. This design offers improved efficiency and reliability compared to older distributor-based systems. In the 2005 Altima, specifically, you'll find individual coil packs sitting directly atop each spark plug, often referred to as "coil-on-plug" (COP) ignition.
Common Symptoms of a Failing Coil Pack
Recognizing the symptoms of a failing coil pack is the first step in diagnosing the problem. Here are some of the most common signs:
- Misfiring: This is perhaps the most frequent symptom. A misfire occurs when one or more cylinders fail to fire correctly, resulting in a rough-running engine. You might feel vibrations, jerking, or a generally unstable idle.
- Check Engine Light (CEL): A misfire will almost certainly trigger the CEL. Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) related to misfires (e.g., P0300, P0301, P0302, etc.) will be stored in the vehicle's computer. A generic OBD-II scanner can retrieve these codes.
- Reduced Engine Power: If a coil pack fails, the engine will lose power. This is especially noticeable during acceleration or when climbing hills. The car may feel sluggish and unresponsive.
- Poor Fuel Economy: Misfires cause incomplete combustion, leading to wasted fuel and decreased fuel economy. You might notice that you're filling up your tank more often.
- Rough Idle: The engine may idle unevenly or stall, particularly when cold. This is due to the misfiring cylinder not contributing to the engine's overall stability.
- Engine Stalling: In severe cases, a failing coil pack can cause the engine to stall completely. This is a serious safety concern, especially while driving.
Troubleshooting Coil Pack Issues
Once you suspect a coil pack issue, a systematic troubleshooting approach is essential.
Step 1: Retrieve Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve any stored DTCs. Pay close attention to misfire codes (P0300-P0306) and codes specifically related to individual cylinders. For example, P0302 indicates a misfire in cylinder #2.
Step 2: Visual Inspection
Carefully inspect each coil pack for any signs of physical damage, such as cracks, melting, or corrosion. Also, check the wiring harness and connectors for any loose connections or damaged wires. Look for signs of arcing, which may appear as burn marks on the coil pack or surrounding components.
Step 3: Swapping Coil Packs
This is a classic troubleshooting technique. If you have a specific cylinder misfiring (e.g., P0302), swap the coil pack from that cylinder with a known good coil pack from another cylinder (e.g., cylinder #1). Clear the DTCs and start the engine. If the misfire follows the coil pack to the new cylinder (now P0301), then the coil pack is likely the problem. Important: Disconnect the battery before performing this step to avoid electrical shorts.
Step 4: Testing with a Multimeter
A multimeter can be used to check the primary and secondary resistance of the coil pack. Consult the vehicle's service manual for the correct resistance values. A significant deviation from the specified values indicates a faulty coil pack. Testing the input voltage at the coil pack connector can also reveal issues with the wiring harness or the Engine Control Module (ECM).
Step 5: Spark Plug Inspection
While troubleshooting coil packs, it's also essential to inspect the spark plugs. A fouled or damaged spark plug can overload the coil pack, leading to premature failure. Replace the spark plugs if they are worn, damaged, or have excessive carbon buildup.
Common Causes of Coil Pack Failure
Understanding the root causes of coil pack failure can help prevent future problems.
- Age and Wear: Like any mechanical component, coil packs have a limited lifespan. Over time, the internal windings can degrade due to heat, vibration, and electrical stress.
- Overheating: Excessive engine heat can damage the coil pack's insulation, leading to short circuits and failure.
- Spark Plug Issues: Worn or improperly gapped spark plugs can put extra strain on the coil pack, shortening its lifespan.
- Loose Connections: Loose or corroded electrical connections can cause voltage drops and intermittent misfires, eventually damaging the coil pack.
- Oil Leaks: Oil leaks from valve cover gaskets or other engine seals can contaminate the coil pack, causing it to fail.
- Moisture: Exposure to moisture can corrode the coil pack's internal components.
- Voltage Spikes: Voltage spikes in the electrical system can damage the coil pack.
Real-World Issues and Solutions
Here are some specific issues related to coil packs in the 2005 Nissan Altima, along with potential solutions:
Problem: Intermittent misfire, especially in humid weather.
Possible Cause: Moisture intrusion into the coil pack connector or hairline cracks in the coil pack insulation. Solution: Thoroughly clean the coil pack connectors with electrical contact cleaner. Inspect the coil packs for cracks and replace any that are damaged. Consider using dielectric grease on the connectors to prevent future moisture intrusion. For example, I've seen this on 2007-2012 Toyota Camrys where the coil packs near the firewall are exposed to more heat and moisture.
Problem: Recurring coil pack failure on the same cylinder.
Possible Cause: An underlying issue with the spark plug, fuel injector, or engine compression in that cylinder. Solution: Perform a compression test on the affected cylinder to rule out any mechanical issues. Inspect the fuel injector for proper operation and replace it if necessary. Ensure that the spark plug is properly gapped and in good condition. I've seen this on a 2003 Honda Accord, where a slightly bent valve caused repeated misfires on one cylinder.
Problem: Check Engine Light (CEL) with multiple misfire codes (P0300, P0301, P0302, etc.).
Possible Cause: A vacuum leak, a faulty mass airflow sensor (MAF), or a clogged catalytic converter. While coil packs could be involved, the widespread nature suggests a more systemic issue. Solution: Inspect the vacuum hoses for cracks or leaks. Clean or replace the MAF sensor. Check the catalytic converter for restrictions. These issues can cause a lean fuel mixture, leading to misfires across multiple cylinders. A similar issue is commonly seen in older Subaru Outbacks, where a vacuum leak can mimic coil pack problems.
Problem: Rough idle and stalling, particularly when the engine is cold.
Possible Cause: A failing coil pack combined with a dirty throttle body. The combined effect is exacerbated when the engine is cold. Solution: Replace the faulty coil pack. Clean the throttle body to ensure smooth airflow. A dirty throttle body can restrict airflow, especially at idle, making the engine more sensitive to misfires. This is especially true in Nissan Altimas with over 100,000 miles.
Maintenance Tips for Extending Coil Pack Life
Proper maintenance can significantly extend the life of your coil packs and prevent costly repairs.
- Replace Spark Plugs Regularly: Follow the manufacturer's recommended maintenance schedule for spark plug replacement. Using the correct spark plug type and gap is crucial.
- Inspect Coil Packs Periodically: During routine maintenance, visually inspect the coil packs for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Keep the Engine Clean: Clean any oil leaks or spills that could contaminate the coil packs.
- Use Dielectric Grease: Apply dielectric grease to the coil pack connectors to prevent moisture intrusion and corrosion.
- Avoid "Lugging" the Engine: Avoid driving in too high a gear at low speeds, as this can put extra stress on the ignition system.
- Monitor Engine Performance: Pay attention to any changes in engine performance, such as rough idle, misfires, or reduced power. Address these issues promptly to prevent further damage.
Choosing Replacement Coil Packs
When replacing coil packs, it's essential to choose high-quality replacements. While aftermarket options are available, it's generally recommended to stick with OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) or reputable aftermarket brands. Avoid extremely cheap coil packs, as they may be unreliable and short-lived.
Example of a bad decision: buying the cheapest no-name brand on an online retailer. These coils often have incorrect resistance values and fail prematurely.
Example of a good decision: sticking with a known brand such as Delphi, Denso, or NGK, even if they cost a bit more.
Keeping Your Car in Top Condition
Maintaining your 2005 Nissan Altima, or any vehicle, in top condition involves more than just addressing coil pack issues. Regular oil changes, air filter replacements, and other routine maintenance tasks are crucial for overall reliability and performance. A well-maintained vehicle will not only run better but also last longer, saving you money in the long run.
By understanding the function of coil packs, recognizing the symptoms of failure, and following a systematic troubleshooting approach, you can effectively diagnose and repair coil pack issues in your 2005 Nissan Altima. Remember to prioritize preventative maintenance and choose quality replacement parts to ensure long-lasting performance.
