Diagram Of Garage Door Parts
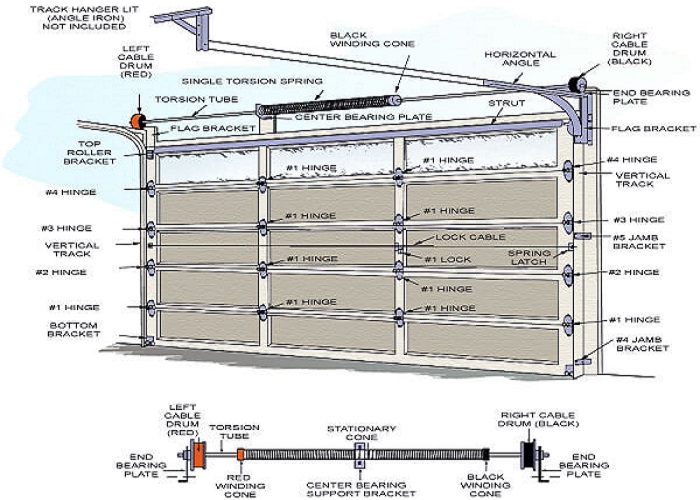
Understanding the anatomy of your garage door is crucial for both preventative maintenance and troubleshooting when issues arise. While a garage door might seem like a simple, single unit, it's actually a complex system comprised of numerous interconnected parts working in harmony. This guide will provide a clear diagram of garage door parts, along with explanations of each component's function, helping you better understand and care for your garage door.
The Essential Diagram of Garage Door Parts
Instead of a traditional diagram, we'll break down the garage door system into logical sections, detailing each component and its role. Think of it as an interactive diagram of garage door parts that you can refer back to.
Door Panels
The most visible part of your garage door, the door panels, are typically constructed from steel, wood, aluminum, or composite materials. These panels are hinged together, allowing the door to bend as it moves along the tracks.
* Insulation: Many panels have insulation to regulate temperature within the garage. * Style: Panels come in various styles, from traditional raised panels to modern flush designs. * Material: The material affects durability, maintenance, and aesthetics.Key Function: Provides the primary barrier for your garage, offering security and protection from the elements.
Tracks
Garage door tracks are metal rails that guide the door's movement. There are typically two tracks, one on each side of the door opening, running vertically and then curving horizontally along the garage ceiling.
* Vertical Tracks: Run alongside the door opening. * Horizontal Tracks: Extend along the ceiling, allowing the door to rest in the open position. * Track Brackets: Secure the tracks to the garage walls.Key Function: Provides a pathway for the rollers to travel, ensuring smooth and controlled up-and-down movement of the door.
Rollers
Rollers are small wheels that fit inside the tracks and connect to the door panels. As the door opens and closes, the rollers glide along the tracks, facilitating smooth movement.
* Material: Rollers are typically made of nylon or steel. Nylon rollers tend to be quieter. * Maintenance: Regular lubrication is essential to prevent wear and tear.Key Function: Allows the door to move easily and quietly within the tracks.
Spring System
The spring system is arguably the most crucial (and dangerous) part of the garage door. It provides the counterbalancing force necessary to lift and lower the heavy door. There are two main types of garage door springs:
- Torsion Springs: Mounted above the door opening, torsion springs twist to generate force. These are generally more durable and longer-lasting.
- Extension Springs: Located on either side of the door, along the horizontal tracks, extension springs stretch to provide lift.
* Safety Cables: Required for extension springs, safety cables prevent the spring from becoming a dangerous projectile if it breaks. * Tension: Springs are carefully calibrated to match the weight of the door.Key Function: Provides the necessary force to lift and lower the door safely and efficiently. WARNING: Garage door springs are under extreme tension. Never attempt to repair or adjust them yourself. Always consult a qualified technician.
Garage Door Opener
The garage door opener is the motorized unit that automates the opening and closing of the door. It's typically mounted on the ceiling and connected to the door via an opener arm.
* Motor: Powers the lifting and lowering mechanism. * Drive System: Connects the motor to the door. Common types include chain drive, belt drive, and screw drive. * Safety Sensors: Prevent the door from closing if an obstruction is detected. * Remote Control: Allows for convenient operation.Key Function: Provides automated control over the garage door's movement.
Cables
Garage door cables are steel ropes that connect the spring system to the bottom brackets of the door. They work in conjunction with the springs to lift and lower the door.
* Cable Drum: Located at the ends of the torsion spring shaft, the cable drum winds and unwinds the cables as the door moves. * Bottom Brackets: Secure the cables to the bottom of the door.Key Function: Transmits the force from the springs to the door, assisting in lifting and lowering.
Hinges
Hinges connect the individual door panels, allowing them to flex as the door moves along the tracks. They are numbered from the bottom up, with the bottom hinge bearing the most weight.
* Gauge: Hinges come in various gauges (thicknesses), with heavier-duty hinges used for heavier doors. * Numbering: Hinge numbers indicate their position on the door.Key Function: Connects the door panels and allows them to articulate as the door opens and closes.
Bottom Brackets
The bottom brackets are located at the bottom corners of the door and connect the cables to the door panels. These brackets are under significant tension due to the cables.
* Durability: Because they bear a lot of weight, these brackets must be strong and durable.Key Function: Securely connect the lifting cables to the bottom of the garage door.
Top Fixtures
The top fixture is attached to the top panel of the garage door, providing a secure mounting point for the top roller and connecting the panel to the rest of the system.
Key Function: Connects the top panel to the roller and provides structural support.
Center Stile
The center stile is a vertical support piece that runs along the center of each garage door section, providing added strength and stability to the panel. Not all doors have these.
Key Function: Provides added strength and rigidity to the garage door panels.
Weather Stripping
Weather stripping is a flexible material installed along the bottom of the door and around the door frame to seal gaps and prevent drafts, water, and pests from entering the garage.
* Bottom Seal: Seals the gap between the door and the floor. * Side and Top Seals: Seal the gaps around the door frame.Key Function: Seals gaps and protects the garage from the elements.
Locking Mechanism
The locking mechanism provides security by securing the door to the tracks. Many garage doors have a manual locking system, while others integrate with the garage door opener.
* Manual Locks: Typically consist of a T-handle that engages with the tracks. * Automatic Locks: Integrated into the garage door opener for added security.Key Function: Secures the garage door and prevents unauthorized entry.
Maintenance Tips Based on the Diagram of Garage Door Parts
Understanding the diagram of garage door parts allows you to perform preventative maintenance and catch potential problems early. Here are some essential maintenance tips:
* Lubricate Moving Parts: Regularly lubricate rollers, hinges, and springs with a silicone-based lubricant. * Inspect Cables and Springs: Visually inspect cables and springs for signs of wear and tear. Never attempt to repair or replace these components yourself. * Tighten Hardware: Periodically tighten loose bolts and screws. * Test Safety Features: Test the safety sensors to ensure they are functioning correctly. * Clean Tracks: Clean the tracks to remove debris and ensure smooth roller movement. * Inspect Weather Stripping: Replace worn or damaged weather stripping.When to Call a Professional
While some garage door maintenance tasks can be performed by homeowners, others require the expertise of a qualified technician. Call a professional if you encounter any of the following:
* Broken springs * Damaged cables * Malfunctioning garage door opener * Door that is off track * Any repairs involving high-tension componentsBy understanding the diagram of garage door parts and performing regular maintenance, you can keep your garage door operating smoothly and safely for years to come. Remember to prioritize safety and consult a professional when needed.
