Engine Turns Off When Braking
Experiencing your engine turning off unexpectedly, especially when braking, can be unsettling and potentially dangerous. This isn't a normal occurrence and requires investigation to prevent future incidents. This article explores the common reasons why your engine turns off when braking, offering practical advice and troubleshooting steps to help you understand and address the problem.
Common Causes of Engine Stalling When Braking
Several factors can contribute to your engine stalling when you apply the brakes. These range from simple maintenance issues to more complex mechanical problems. Let's delve into some of the most frequent culprits:
1. Faulty Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve
The Idle Air Control (IAC) valve regulates the amount of air entering the engine when the throttle is closed (i.e., when idling or braking). A malfunctioning IAC valve can fail to maintain a proper idle speed, causing the engine to stall. This is especially noticeable when the engine is under load, such as when braking.
Symptoms of a faulty IAC valve:
- Engine stalling, particularly when braking or at idle.
- Rough idling.
- High idle speed.
- Hesitation or stumbling during acceleration.
Troubleshooting and solutions: You can try cleaning the IAC valve with a specialized cleaner. If cleaning doesn't resolve the issue, replacement may be necessary. Consult a mechanic for proper diagnosis and replacement.
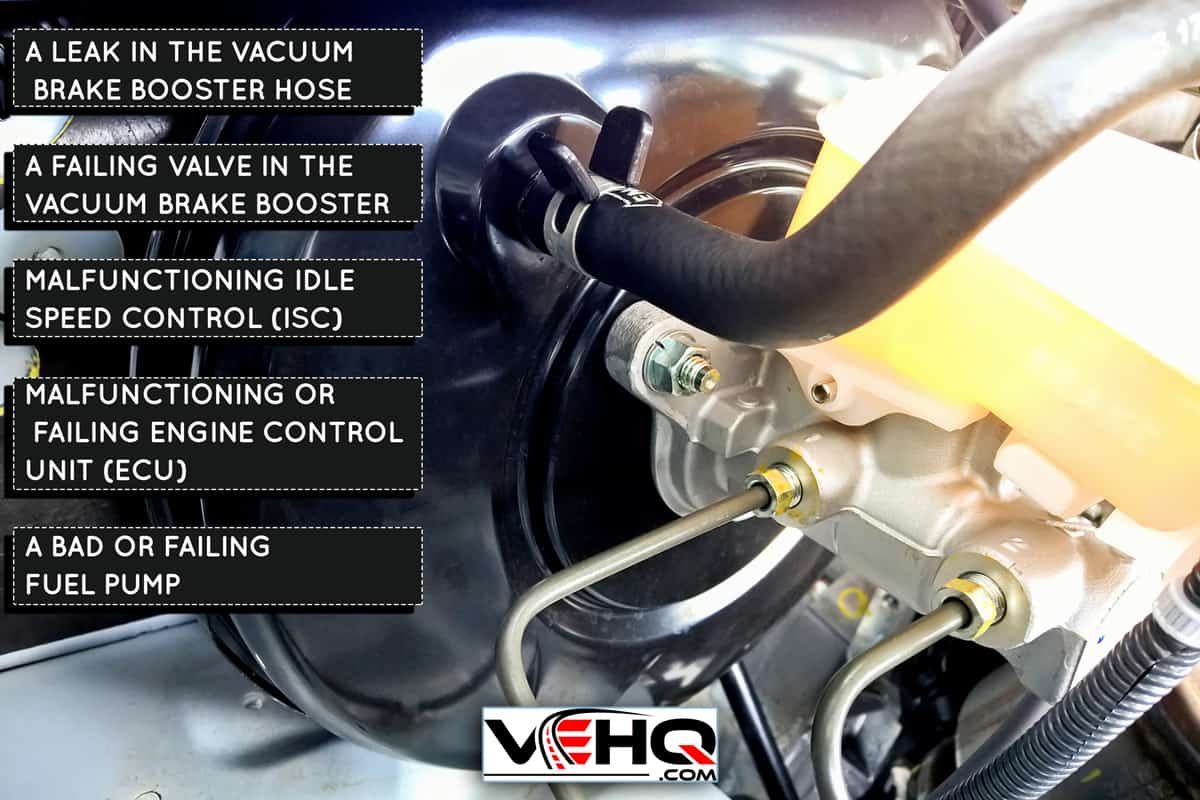
2. Vacuum Leaks
Vacuum leaks can disrupt the engine's air-fuel mixture, leading to various performance problems, including stalling. When you brake, the engine experiences changes in vacuum pressure. A leak can exacerbate these changes, causing the engine to stumble and die.
Common locations for vacuum leaks:
- Vacuum hoses (cracked or disconnected).
- Intake manifold gasket.
- Brake booster hose.
- PCV valve and hose.
Symptoms of vacuum leaks:
- Engine stalling, especially when braking or idling.
- Rough idle.
- Hissing sound from the engine bay.
- Poor fuel economy.
- Check engine light illumination.
Troubleshooting and solutions: Visually inspect all vacuum hoses for cracks or disconnections. You can also use a spray bottle with soapy water to check for leaks around the intake manifold and other potential leak areas. If you suspect a vacuum leak, have it diagnosed and repaired by a qualified mechanic.
3. Problems with the Brake Booster
The brake booster uses engine vacuum to assist in braking, making it easier to stop. A failing brake booster or a leak in its vacuum hose can cause the engine to stall when the brakes are applied. If the booster itself is leaking internally, this can create a significant vacuum leak directly into the engine.
Symptoms of brake booster problems:
- Engine stalling when braking.
- Hard brake pedal (requiring more effort to stop).
- Hissing sound when applying the brakes.
Troubleshooting and solutions: Inspect the brake booster vacuum hose for cracks or damage. If the hose is in good condition and you suspect the booster itself is faulty, have it inspected and potentially replaced by a mechanic.
4. Fuel System Issues
Problems with the fuel system, such as a clogged fuel filter, a weak fuel pump, or faulty fuel injectors, can deprive the engine of the necessary fuel supply, leading to stalling. These issues become more apparent when the engine is under load or experiencing changes in demand, such as during braking.
Symptoms of fuel system issues:
- Engine stalling, especially when braking or accelerating.
- Rough idling.
- Poor fuel economy.
- Hesitation or stumbling during acceleration.
Troubleshooting and solutions: Check the fuel filter and replace it if necessary. A fuel pressure test can help determine if the fuel pump is functioning correctly. Fuel injector issues may require professional diagnosis and cleaning or replacement.
5. Dirty or Faulty Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor
The Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor measures the amount of air entering the engine. This information is crucial for the engine control unit (ECU) to calculate the correct air-fuel mixture. A dirty or faulty MAF sensor can provide inaccurate readings, leading to an improper air-fuel mixture and potentially causing the engine to stall when braking.
Symptoms of a faulty MAF sensor:
- Engine stalling, particularly when braking or idling.
- Rough idling.
- Poor fuel economy.
- Hesitation or stumbling during acceleration.
- Check engine light illumination.
Troubleshooting and solutions: You can try cleaning the MAF sensor with a specialized MAF sensor cleaner. Be careful not to damage the delicate wires inside the sensor. If cleaning doesn't resolve the issue, replacement may be necessary.
6. Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) Problems
The Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) monitors the position of the throttle plate. A faulty TPS can send incorrect signals to the ECU, leading to improper fuel delivery and potentially causing the engine to stall when braking or decelerating.
Symptoms of a faulty TPS:
- Engine stalling, especially when braking or decelerating.
- Erratic idling.
- Hesitation or stumbling during acceleration.
- Check engine light illumination.
Troubleshooting and solutions: A multimeter can be used to test the TPS for proper voltage output. If the TPS is faulty, it will need to be replaced.
7. Electrical Issues
Less commonly, electrical problems can also cause engine stalling. A loose or corroded electrical connection, a faulty sensor, or a problem with the ECU can disrupt the engine's operation and lead to stalling, especially when braking.
Troubleshooting and solutions: Inspect all electrical connections for corrosion or looseness. A diagnostic scan can help identify any fault codes related to sensors or the ECU. Electrical problems often require professional diagnosis and repair.
8. Torque Converter Issues (Automatic Transmissions)
In vehicles with automatic transmissions, a malfunctioning torque converter can sometimes cause the engine to stall when braking. The torque converter is responsible for transferring power from the engine to the transmission. If it fails to disengage properly when braking, it can place excessive load on the engine, leading to stalling.
Symptoms of torque converter problems:
- Engine stalling when braking, especially when coming to a complete stop.
- Shuddering or vibration at low speeds.
- Difficulty shifting gears.
Troubleshooting and solutions: Torque converter problems typically require professional diagnosis and repair or replacement of the torque converter.
Preventive Maintenance
Regular maintenance can help prevent many of the issues that cause engine stalling when braking. Here are some key maintenance tasks:
- Regularly replace the fuel filter.
- Clean or replace the air filter as needed.
- Inspect and replace vacuum hoses as needed.
- Clean the throttle body periodically.
- Ensure proper engine tuning.
- Follow the manufacturer's recommended maintenance schedule.
What to Do If Your Engine Stalls While Braking
If your engine turns off when braking, safety should be your top priority:
- Stay Calm: Panic can make the situation worse. Try to remain calm and focused.
- Steer Safely: Use your power steering (if available) to guide the vehicle to a safe location off the road.
- Engage Hazard Lights: Alert other drivers to your situation.
- Restart the Engine: Attempt to restart the engine. If it starts, carefully drive to a safe location or a mechanic.
- Call for Assistance: If you cannot restart the engine or if the stalling continues, call for roadside assistance or a tow truck.
Conclusion
An engine turning off when braking is a serious issue that requires prompt attention. By understanding the common causes and following the troubleshooting steps outlined in this article, you can gain valuable insights into the problem and potentially resolve it. However, for complex or persistent issues, it's always best to consult with a qualified mechanic for a thorough diagnosis and repair. Regular maintenance is key to preventing these types of problems and ensuring the safe and reliable operation of your vehicle.
