How Do You Put Freon In Your Car
Is your car's air conditioning blowing warm air? You might be low on refrigerant, often referred to by the trade name Freon (though modern cars use different refrigerants). While topping off your AC system can seem like a DIY project, it's crucial to understand the process, the risks involved, and when it's best to consult a professional. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of how to put Freon in your car, covering everything from identifying the problem to safely recharging your AC.
Understanding Automotive Air Conditioning Systems
Before diving into the process, let's break down the basics of your car's AC system. It's a closed-loop system that circulates refrigerant to cool the air entering your cabin. Key components include:
- Compressor: Compresses the refrigerant gas, increasing its temperature and pressure.
- Condenser: Cools the high-pressure, high-temperature refrigerant gas, turning it into a liquid.
- Receiver/Drier (or Accumulator): Filters the refrigerant and removes moisture.
- Expansion Valve (or Orifice Tube): Reduces the pressure of the liquid refrigerant, causing it to cool rapidly.
- Evaporator: Absorbs heat from the air passing over it, cooling the air before it enters the cabin.
Refrigerant leaks are a common cause of AC problems. These leaks can occur at any point in the system, often at connection points or through worn-out seals. Low refrigerant levels result in reduced cooling efficiency, and eventually, the AC may stop working altogether.
Is It Really a Refrigerant Issue? Diagnosing AC Problems
Before assuming you need to add refrigerant, it's essential to rule out other potential problems. Here are some common issues that can mimic low refrigerant symptoms:
- Blown Fuse: A blown fuse can prevent the compressor from engaging. Check your car's fuse box for any blown fuses related to the AC system.
- Faulty Compressor: The compressor is the heart of the AC system. If it's not working, the refrigerant won't circulate, and the air won't cool. Listen for a clicking sound when you turn on the AC; if you don't hear it, the compressor might be the issue.
- Clogged Condenser: Debris can block airflow through the condenser, reducing its ability to cool the refrigerant.
- Broken Blend Door Actuator: The blend door controls the mix of hot and cold air. A malfunctioning actuator can prevent the door from moving, resulting in warm air.
- Electrical Problems: Wiring issues or faulty sensors can also disrupt the AC system's operation.
If you've checked these common issues and your AC is still blowing warm air, it's more likely that you have a refrigerant leak. A telltale sign of low refrigerant is the AC compressor cycling on and off rapidly. This happens because the low-pressure switch detects insufficient refrigerant and cuts power to the compressor to prevent damage.
Choosing the Right Refrigerant
Important: Using the wrong refrigerant can damage your AC system and is illegal in many jurisdictions. Older cars (typically those manufactured before 1995) often used R-12, commonly known as Freon. However, R-12 has been phased out due to its ozone-depleting properties. Modern cars use R-134a or the newer R-1234yf.
You *must* identify the correct refrigerant for your car before adding any. Look for a sticker under the hood, usually near the radiator or on the air conditioning components. This sticker will specify the type of refrigerant your car uses. If you're unsure, consult your owner's manual or a qualified mechanic.
R-1234yf is becoming increasingly common in newer vehicles. It's more expensive than R-134a and requires specialized equipment. If your car uses R-1234yf, it's highly recommended to have a professional recharge your AC system.
Gathering Your Tools and Supplies
If you're comfortable proceeding with recharging your AC system, you'll need the following tools and supplies:
- Refrigerant: The correct type and amount for your car.
- Refrigerant Charging Kit: These kits typically include a charging hose, a gauge, and a can tap. Make sure the kit is compatible with the refrigerant your car uses.
- Gloves and Safety Glasses: Protect yourself from refrigerant exposure.
- Rag: For wiping up any spills.
- AC Manifold Gauge Set (Optional but Recommended): Provides more accurate pressure readings than a simple charging kit gauge.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Put Freon in Your Car
Warning: Working with refrigerants can be dangerous. Always wear gloves and safety glasses to protect yourself from chemical burns and eye damage. Work in a well-ventilated area and avoid inhaling refrigerant fumes. If you're not comfortable with any of these steps, consult a qualified mechanic.
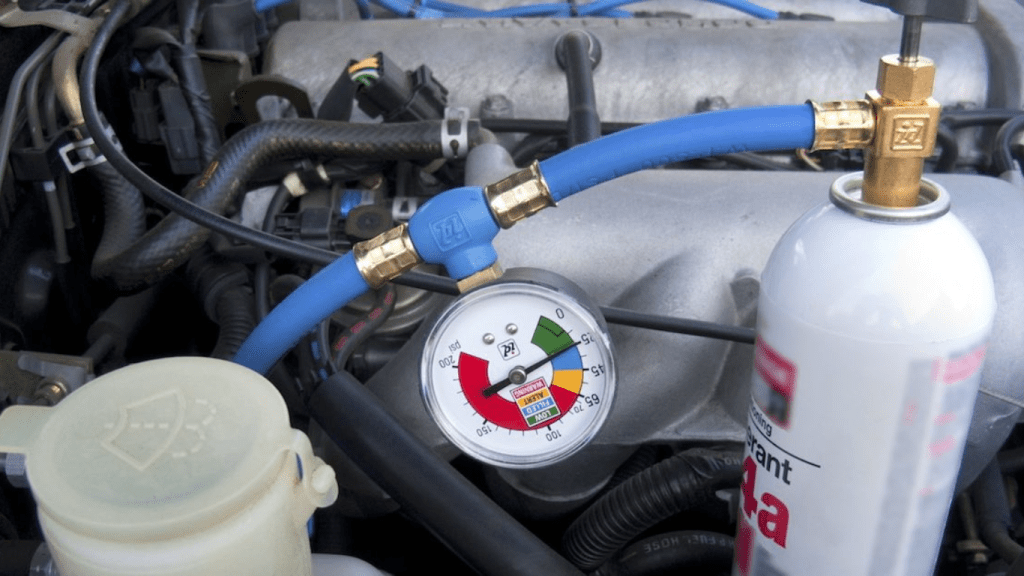
- Locate the Low-Pressure Port: The low-pressure port is typically located on the larger of the two AC lines, usually near the accumulator or compressor. It will have a cap labeled "L" or "Low." Consult your car's repair manual if you're having trouble finding it.
- Connect the Charging Hose: Remove the cap from the low-pressure port and attach the charging hose from your kit. The connector is usually a quick-connect type, so it should snap into place.
- Check the Pressure Reading: With the charging hose connected, check the pressure reading on the gauge. This will give you an idea of how low your refrigerant level is. Consult the gauge's instructions for the proper pressure range for your car. Do this with the AC off, and the engine off.
- Start the Engine and Turn on the AC: Start your car's engine and turn on the AC to the coldest setting with the fan on high.
- Add Refrigerant: With the engine running and the AC on, slowly add refrigerant to the system. Follow the instructions on your refrigerant can and charging kit. Shake the can gently and hold it upright. Open the valve on the can tap slowly, allowing refrigerant to flow into the system.
- Monitor the Pressure: As you add refrigerant, constantly monitor the pressure gauge. Avoid overcharging the system, as this can damage the compressor. Add refrigerant until the gauge reads within the recommended range.
- Check the Air Temperature: After adding refrigerant, check the temperature of the air coming from the vents. It should be significantly colder than before.
- Disconnect the Charging Hose: Once you've reached the desired pressure and air temperature, close the valve on the can tap and disconnect the charging hose from the low-pressure port. Replace the cap on the port.
Safety Precautions and Troubleshooting
- Overcharging: Overcharging the system is a common mistake. It can damage the compressor and other components. Use the pressure gauge carefully and avoid adding too much refrigerant.
- Leaks: If you notice refrigerant leaking from the system, stop immediately and consult a mechanic. Continuing to add refrigerant to a system with a leak is wasteful and environmentally damaging.
- Refrigerant Burns: Refrigerant can cause severe frostbite if it comes into contact with your skin. Wear gloves and safety glasses at all times when working with refrigerants.
- Empty Can Disposal: Dispose of empty refrigerant cans properly according to local regulations.
When to Consult a Professional
While recharging your AC system can be a DIY project, there are times when it's best to consult a professional:
- You're Not Comfortable: If you're not comfortable working with refrigerants or you're unsure about any of the steps, it's best to leave the job to a qualified mechanic.
- You Suspect a Major Leak: If your AC system loses refrigerant quickly after being recharged, it indicates a significant leak. A mechanic can use specialized equipment to locate and repair the leak.
- Your Car Uses R-1234yf: As mentioned earlier, R-1234yf requires specialized equipment and training.
- You've Tried Recharging and the AC Still Doesn't Work: If recharging doesn't fix the problem, there may be other issues with the AC system, such as a faulty compressor or a clogged condenser.
Finding a Reliable Mechanic
If you decide to consult a mechanic, it's important to find a reputable and experienced one. Here are some tips:
- Ask for Recommendations: Ask friends, family, or colleagues for recommendations.
- Read Online Reviews: Check online reviews on websites like Google, Yelp, and Angie's List.
- Check for Certifications: Look for mechanics who are certified by organizations like ASE (Automotive Service Excellence).
- Get an Estimate: Get an estimate before authorizing any repairs.
- Ask Questions: Don't be afraid to ask the mechanic questions about the problem and the proposed solution.
Conclusion
Knowing how to put Freon in your car can save you money and keep you cool during the summer months. However, it's crucial to understand the risks involved and to follow safety precautions carefully. If you're unsure about any of the steps or you suspect a major problem, it's always best to consult a qualified mechanic. By following this guide, you can make an informed decision about whether to recharge your AC system yourself or to seek professional assistance. Remember to always prioritize safety and use the correct refrigerant for your vehicle. Regular maintenance and prompt attention to AC issues will help keep your car's air conditioning system running smoothly for years to come.
