How To Adjust Auto Headlights
Proper headlight alignment is crucial for both driver safety and the safety of other road users. Misaligned headlights can significantly reduce visibility, creating dangerous situations, especially at night or in adverse weather conditions. This article provides an in-depth look at how to adjust auto headlights, delving into the technical specifications, engineering choices behind headlight design, and real-world performance considerations. We'll also compare different headlight technologies, discuss reliability and maintenance, and touch upon future trends in automotive lighting.
Understanding Headlight Systems
Before delving into the adjustment process, it's important to understand the different types of headlight systems commonly found in vehicles. The most common types are:
- Halogen Headlights: These are the most widely used and are relatively inexpensive. They use a tungsten filament enclosed in a halogen gas-filled bulb.
- Xenon (HID) Headlights: Xenon High-Intensity Discharge lamps produce a brighter and whiter light compared to halogen. They don't have a filament; instead, they create light by passing an electric arc through xenon gas.
- LED Headlights: Light Emitting Diodes offer high efficiency, long lifespan, and design flexibility. They are becoming increasingly common in new vehicles.
- Laser Headlights: These are the most advanced and expensive option, offering exceptional brightness and range. They are typically used in high-end vehicles.
Each of these systems has its own unique characteristics in terms of light output, color temperature, energy efficiency, and lifespan. The adjustment procedure may vary slightly depending on the type of headlight. The legal requirements for headlight alignment also differ by region, but the general principles remain the same: the headlights must be aimed so that they illuminate the road ahead without causing excessive glare for oncoming drivers.
Technical Specifications and Adjustment Procedure
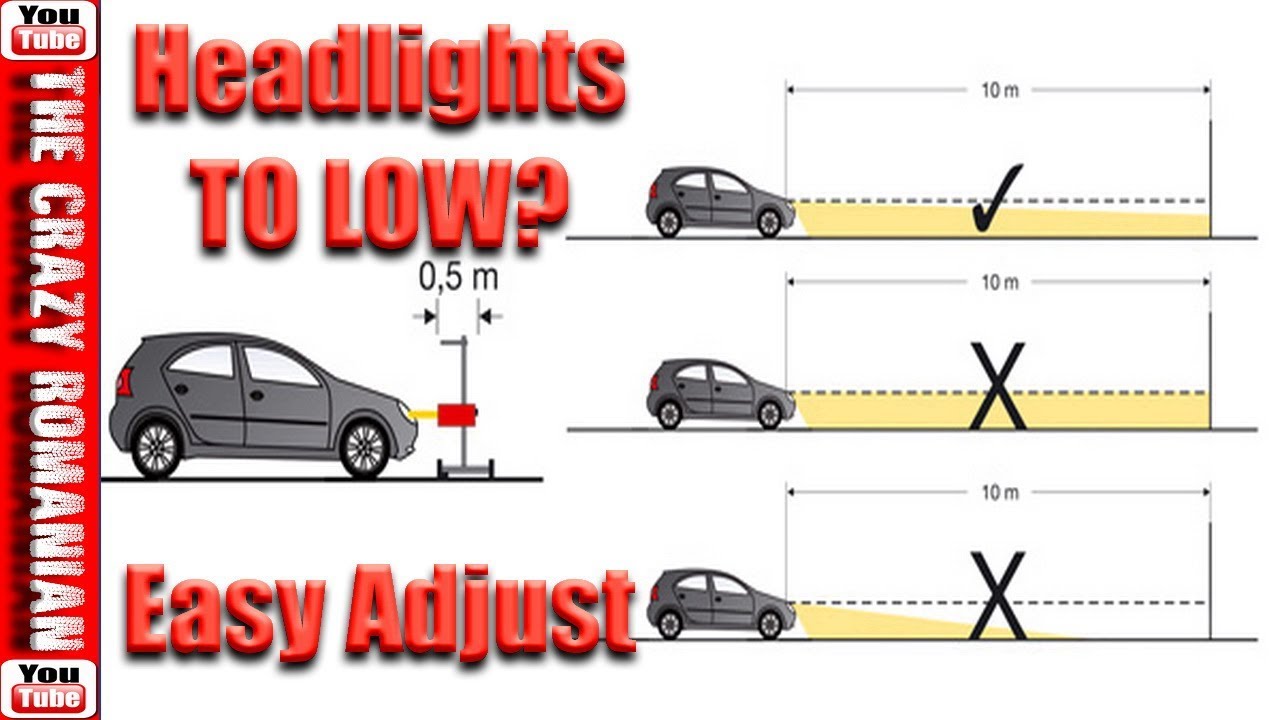
The process of adjusting headlights involves ensuring that the beam is aimed correctly both vertically (up and down) and horizontally (left and right). This is typically done using adjustment screws located on the headlight assembly. The following steps outline a general procedure:
- Preparation: Park the vehicle on a level surface, facing a blank wall (a garage door works well) at a distance of approximately 25 feet (7.6 meters). Ensure the vehicle is properly loaded, simulating typical driving conditions. This means having the driver in the vehicle and any frequently carried items in the trunk. Tire pressure should also be correct.
- Measurement: Measure the distance from the ground to the center of the headlight lens. Mark this height on the wall with tape. Also, mark the center line of the vehicle on the wall and the location of each headlight.
- Beam Pattern: Refer to the vehicle's owner's manual or a repair manual for the specific aiming instructions for your vehicle's headlights. Generally, the high-intensity portion of the beam should be aimed slightly below and to the right of the corresponding marks on the wall. This prevents glare for oncoming drivers while still providing adequate illumination.
- Adjustment: Locate the adjustment screws on the headlight assembly. These are typically located near the top and side of the headlight. Use a screwdriver or wrench to turn the screws, adjusting the beam pattern as needed. Most headlights have separate adjusters for vertical and horizontal alignment. Be patient, as small adjustments can have a significant impact on the beam pattern.
- Verification: After making adjustments, double-check the beam pattern against the marks on the wall. It's also a good idea to take the vehicle for a test drive at night to ensure that the headlights are properly aimed and provide adequate visibility without causing glare.
Tools Required
- Measuring tape
- Level
- Screwdriver or wrench (depending on the adjustment screws)
- Masking tape or marker
- Vehicle's owner's manual or repair manual
Engineering Choices and Real-World Performance
The design of headlight systems involves numerous engineering choices that affect their performance. For example, the shape of the reflector or projector lens plays a crucial role in focusing the light and creating the desired beam pattern. The type of bulb used also affects the light output, color temperature, and lifespan. Engineers must balance these factors to achieve optimal visibility, safety, and cost-effectiveness.
In real-world performance, factors such as weather conditions, road surface, and the presence of other vehicles can significantly impact headlight effectiveness. For example, rain and snow can scatter light, reducing visibility. Dirty headlight lenses can also significantly reduce light output. Regular cleaning and maintenance are essential to ensure optimal performance. SAE and ECE standards define specific performance requirements for headlights, including minimum light output, beam pattern, and glare levels.
Comparison with Alternatives: Halogen vs. HID vs. LED
Each headlight technology has its own set of advantages and disadvantages:
Halogen Headlights:
Pros: Inexpensive, readily available, easy to replace.
Cons: Lower light output, shorter lifespan, less energy-efficient.
Xenon (HID) Headlights:
Pros: Brighter light output, longer lifespan than halogen.
Cons: More expensive than halogen, require a ballast, can cause glare if not properly aimed.
LED Headlights:
Pros: High efficiency, long lifespan, design flexibility, instant-on capability.
Cons: More expensive than halogen, can be complex to repair, heat management is crucial.
The choice of headlight technology depends on various factors, including budget, performance requirements, and design considerations. LED headlights are becoming increasingly popular due to their superior efficiency and lifespan, but halogen headlights remain a cost-effective option for many vehicles. HID headlights offer a good balance of performance and cost.
Reliability and Maintenance
Headlight systems are generally reliable, but they can be affected by factors such as vibration, heat, and moisture. Bulb failure is the most common issue, and replacing bulbs is a relatively simple task. However, other components, such as ballasts (in HID systems) and control modules (in LED systems), can also fail. Regular maintenance, including cleaning the lenses and checking the alignment, can help to prolong the lifespan of headlight systems and ensure optimal performance.
Here are some maintenance tips:
- Clean headlight lenses regularly: Use a mild soap and water solution or a dedicated headlight cleaner.
- Check headlight alignment periodically: Especially after hitting a large bump or pothole.
- Replace bulbs as needed: Don't wait until a bulb completely burns out, as a dim bulb can also reduce visibility.
- Inspect wiring and connectors: Look for signs of corrosion or damage.
Future Trends in Automotive Lighting
The automotive lighting industry is constantly evolving, with new technologies and innovations emerging regularly. Some of the key trends include:
- Adaptive Headlights: These systems automatically adjust the beam pattern based on driving conditions, such as speed, steering angle, and the presence of other vehicles. This improves visibility and reduces glare for other drivers.
- Matrix LED Headlights: These advanced LED systems use multiple individual LEDs that can be controlled independently. This allows for precise beam shaping and dynamic lighting effects.
- Laser Headlights: Laser headlights offer exceptional range and brightness, but they are currently only used in a limited number of high-end vehicles. As the technology matures and costs decrease, they are likely to become more widespread.
- Integration with Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS): Future headlight systems will be increasingly integrated with ADAS features, such as automatic emergency braking and lane keeping assist. This will allow for even more sophisticated lighting control and improved safety.
- Digital Light: This technology uses millions of micro-mirrors to project light patterns onto the road, providing information to the driver and other road users.
These advancements are pushing the boundaries of what's possible with automotive lighting, promising to improve safety, visibility, and driver comfort.
Conclusion
Proper headlight alignment is essential for safe driving. By understanding the different types of headlight systems, the adjustment procedure, and the factors that affect performance, automotive professionals can ensure that vehicles are properly equipped for nighttime driving. As headlight technology continues to evolve, it's important to stay abreast of the latest advancements and best practices. The automotive industry is undergoing a rapid transformation, with electrification, autonomous driving, and connected car technologies all converging. Lighting systems will play an increasingly important role in this future, providing not only illumination but also communication and sensory input for advanced driver-assistance systems. By embracing these changes and investing in training and resources, automotive professionals can position themselves for success in this exciting new era.
