How To Disarm Seatbelt Alarm
The persistent chime of a seatbelt alarm can be one of the most irritating sounds a driver can experience. While seatbelt alarms are crucial safety features designed to encourage seatbelt use, there are situations where they malfunction or become overly sensitive. This article provides practical advice for car owners and mechanics on troubleshooting and addressing seatbelt alarm issues, focusing on maintenance, real-world problems, and responsible solutions.
Understanding Seatbelt Alarm Systems
Modern vehicles utilize complex systems to detect seatbelt usage. These systems typically involve sensors in the seatbelt buckle, wiring harnesses, and the car's computer (ECU) which monitors the sensor inputs. When the system detects that the driver or passenger is unbelted while the vehicle is in motion, it triggers the audible and visual warnings. Malfunctions in any component of this system can lead to false alarms or a complete failure to warn when a seatbelt is not fastened.
Common Symptoms of Seatbelt Alarm Problems
Identifying the specific symptoms is the first step toward resolving the issue. Here are some typical scenarios:
- Constant Chime: The alarm sounds continuously, even when the seatbelt is fastened.
- Intermittent Chime: The alarm sounds sporadically, often without a clear reason.
- Alarm Fails to Sound: The alarm doesn't activate even when the vehicle is in motion and occupants are unbelted.
- Passenger Seat Alarm Issues: The passenger seat alarm chimes even when the seat is unoccupied or when an object is placed on the seat.
- Error Messages: The dashboard displays error messages related to the seatbelt system.
Troubleshooting Seatbelt Alarm Issues
When tackling a seatbelt alarm problem, a systematic approach is crucial. Start with the simplest solutions and progressively investigate more complex issues.
Step 1: Visual Inspection
Begin with a thorough visual inspection of the seatbelt buckle and surrounding area. Look for:
- Obstructions: Check for debris, dirt, or small objects lodged in the buckle mechanism. These can interfere with the proper functioning of the sensor.
- Damage: Inspect the buckle and seatbelt webbing for any signs of physical damage, such as cracks, tears, or frayed edges.
- Wiring: Examine the wiring harness connected to the seatbelt buckle for loose connections, frayed wires, or corrosion.
Example: In a 2010 Honda Civic, a common issue is food crumbs getting stuck inside the seatbelt buckle. Simply cleaning out the buckle with compressed air and a small brush can often resolve the problem.
Step 2: Seatbelt Buckle Functionality Test
Test the mechanical operation of the seatbelt buckle. Fasten and unfasten the seatbelt several times to ensure it clicks securely and releases smoothly. A sticky or difficult-to-operate buckle may indicate a mechanical problem that needs lubrication or replacement.
Solution: Use a silicone-based lubricant (avoid oil-based lubricants as they can attract dirt) to lubricate the buckle mechanism. Spray a small amount of lubricant into the buckle opening and work the mechanism several times.
Step 3: Sensor and Wiring Checks
The seatbelt buckle contains a sensor that detects when the seatbelt is fastened. Use a multimeter to test the sensor's continuity when the seatbelt is buckled and unbuckled. Consult the vehicle's wiring diagram for the specific pin locations and expected resistance values.
Procedure:
- Disconnect the seatbelt buckle wiring harness.
- Set the multimeter to the continuity testing mode.
- Connect the multimeter probes to the sensor terminals.
- Fasten and unfasten the seatbelt and observe the multimeter reading. The reading should change (open or closed circuit) when the seatbelt is buckled and unbuckled.
If the sensor fails to respond or provides inconsistent readings, it may need replacement. Damaged wiring can also cause similar issues. Inspect the wiring harness for shorts, opens, or corrosion. Repair or replace any damaged wires.
Example: On some Ford F-150 models, chafing of the seatbelt wiring harness under the seat is a known issue. Repairing the damaged wiring can often solve intermittent seatbelt alarm problems.
Step 4: Seat Occupancy Sensor (Passenger Seat)
The passenger seat often includes a seat occupancy sensor that detects whether the seat is occupied. This sensor can be overly sensitive and trigger the alarm even when a light object is placed on the seat.
Troubleshooting:
- Calibration: Some vehicles allow you to calibrate the seat occupancy sensor using a scan tool. Consult the vehicle's service manual for instructions.
- Sensor Replacement: If the sensor is faulty, it may need replacement. This typically involves removing the seat cover and replacing the sensor pad.
Important Note: Replacing a seat occupancy sensor can affect the airbag system. Ensure you disconnect the battery before working on the sensor and consult a qualified technician if you are not comfortable with this procedure.
Step 5: Scan Tool Diagnosis
A scan tool can provide valuable diagnostic information by reading error codes stored in the vehicle's computer. Connect a scan tool to the vehicle's OBD-II port and scan for any codes related to the seatbelt system or airbag system. These codes can provide clues about the underlying cause of the problem.
Example: A code like "B100A - Driver Seatbelt Buckle Switch Circuit Malfunction" indicates a problem with the driver's seatbelt buckle sensor.
Note: Some scan tools may allow you to clear the error codes after the problem has been resolved. However, the codes may reappear if the underlying issue persists.
Step 6: Module Reset and Recalibration
In some cases, the seatbelt alarm system may require a reset or recalibration after repairs have been made. This can be done using a specialized scan tool that supports module programming and configuration. Consult the vehicle's service manual or a qualified technician for instructions.
Responsible Disablement (Use with Extreme Caution and Consider Legal Implications)
While strongly discouraged due to safety concerns, some individuals may consider disabling the seatbelt alarm. This is not recommended and may be illegal in some jurisdictions. Disabling the seatbelt alarm can compromise safety in the event of an accident. If you choose to proceed, do so with extreme caution and only as a temporary measure while addressing the underlying issue.
Potential Methods (Use at Your Own Risk):
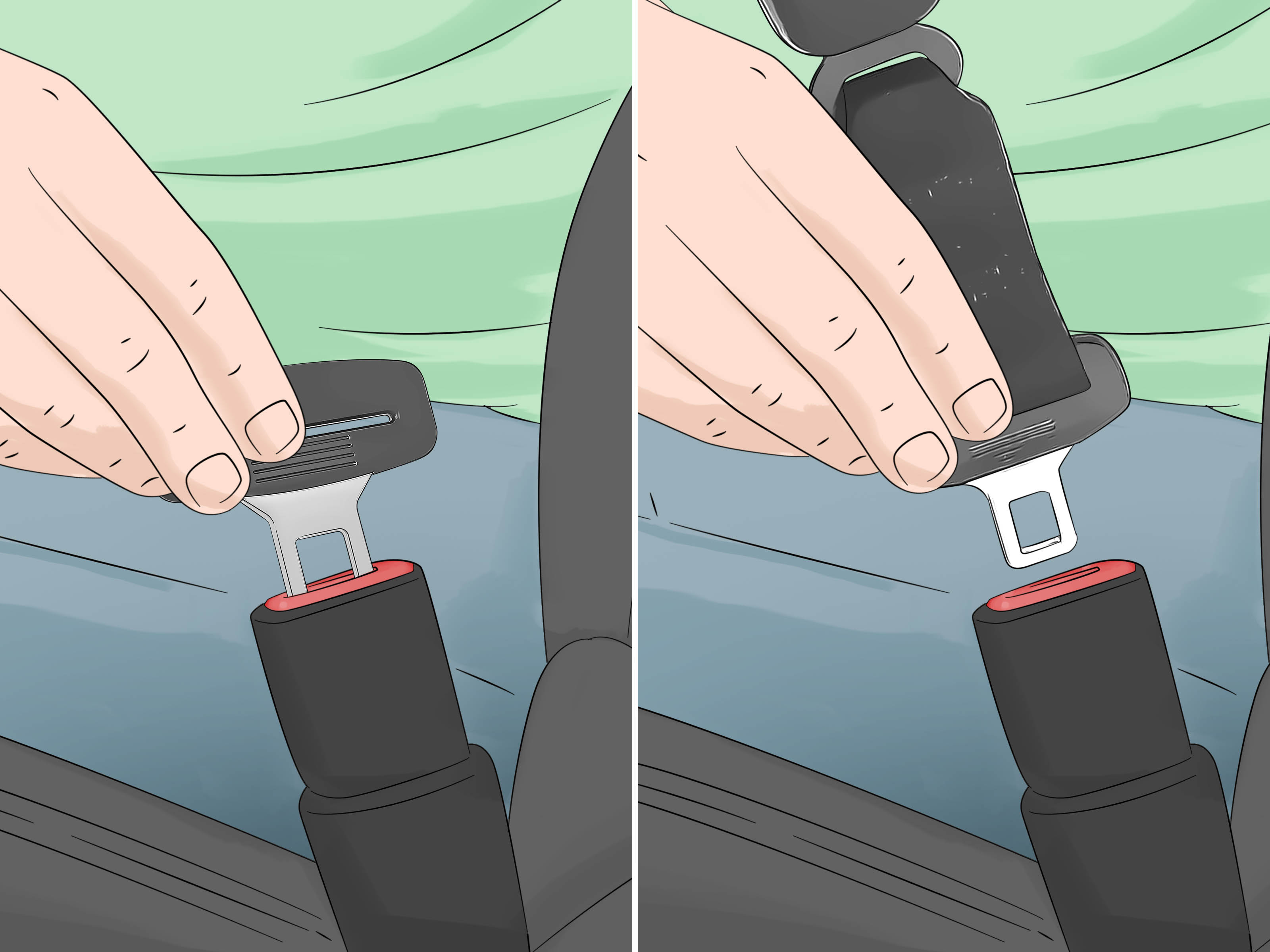
- Seatbelt Extender: Inserting a seatbelt extender into the buckle will trick the system into thinking the seatbelt is fastened. However, this does not provide any actual protection.
- Software Disable: Some aftermarket scan tools allow you to disable the seatbelt alarm through software programming. However, this may void the vehicle's warranty and can affect the performance of the airbag system.
- Wiring Modification (Extremely Risky): Cutting or modifying the wiring harness to disable the alarm is highly discouraged and can be extremely dangerous. It can damage the vehicle's electrical system and compromise safety.
Important Disclaimer: The information provided above is for informational purposes only and should not be interpreted as an endorsement of disabling the seatbelt alarm. Always prioritize safety and consult a qualified technician before making any modifications to your vehicle's safety systems.
Real-World Examples and Model-Specific Issues
- Toyota Camry (2007-2011): These models are prone to issues with the seat occupancy sensor in the passenger seat, often triggering the alarm when a light object is placed on the seat. Recalibration or sensor replacement may be necessary.
- Nissan Altima (2013-2018): Corrosion in the seatbelt buckle wiring harness is a common problem. Cleaning the connections or replacing the harness can resolve the issue.
- Chevrolet Silverado (2014-2019): Issues with the seatbelt pretensioners can trigger the seatbelt alarm and airbag warning lights. A scan tool diagnosis and pretensioner replacement may be required.
Preventive Maintenance and Long-Term Care
Regular maintenance can help prevent seatbelt alarm problems and keep your car in top condition:
- Keep it Clean: Regularly clean the seatbelt buckles and surrounding areas to remove debris and dirt.
- Inspect Regularly: Inspect the seatbelts, buckles, and wiring harnesses for damage or wear.
- Lubricate: Periodically lubricate the seatbelt buckles with a silicone-based lubricant.
- Address Issues Promptly: Don't ignore warning lights or unusual noises. Address any potential problems as soon as they arise to prevent further damage.
- Professional Inspection: Have your vehicle inspected by a qualified mechanic at regular intervals to identify and address any potential issues before they become major problems.
By understanding the workings of the seatbelt alarm system, proactively troubleshooting potential problems, and adhering to a regular maintenance schedule, car owners and mechanics can effectively address seatbelt alarm issues and ensure the safety and reliability of their vehicles.
Remember, a properly functioning seatbelt system is a critical safety feature. Never compromise safety for convenience.
