How To Tell If Ac Compressor Is Working
The air conditioning (A/C) system in your vehicle is a complex interplay of components, all working in harmony to deliver that refreshing blast of cool air on a sweltering day. At the heart of this system lies the A/C compressor, a vital pump responsible for circulating refrigerant throughout the system. When it malfunctions, the consequences range from mildly uncomfortable to downright unbearable, depending on the climate you live in. Accurately diagnosing a faulty compressor is crucial, saving you time, money, and potential further damage to your A/C system.
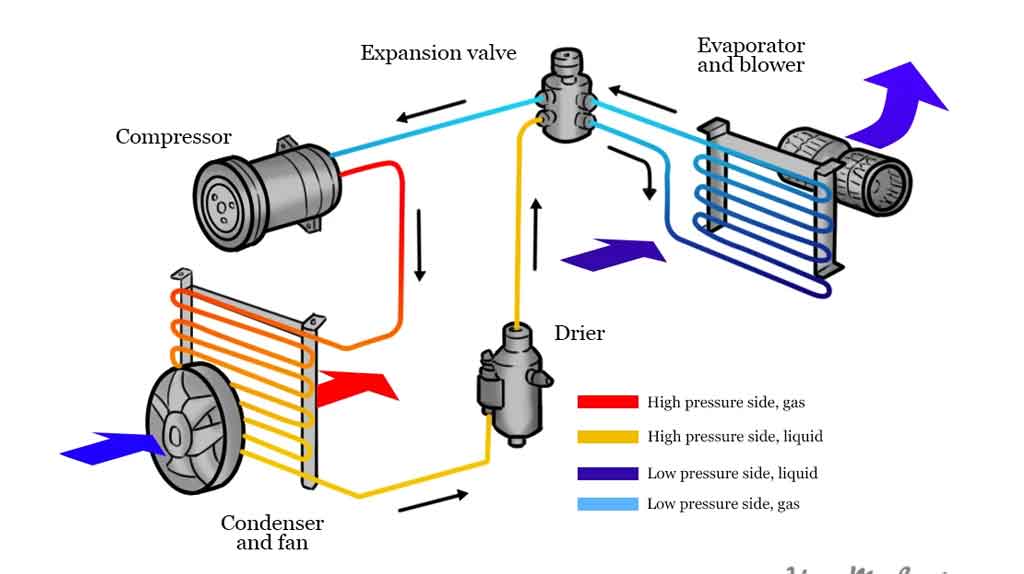
Understanding the A/C System: A Quick Refresher
Before diving into diagnostic procedures, let's briefly recap the A/C system's core components:
- Compressor: Compresses the refrigerant gas, raising its pressure and temperature.
- Condenser: Dissipates heat from the high-pressure refrigerant gas, causing it to condense into a high-pressure liquid.
- Expansion Valve (or Orifice Tube): Meters the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator, causing a pressure drop and rapid cooling.
- Evaporator: Absorbs heat from the cabin air, causing the refrigerant to evaporate and cool the air.
- Receiver Drier (or Accumulator): Filters debris and absorbs moisture from the refrigerant.
The refrigerant, typically R-134a or the newer R-1234yf (depending on your vehicle's year and model), is the lifeblood of the system, cycling continuously through these components.
Symptoms of a Failing A/C Compressor
Recognizing the symptoms is the first step in diagnosing a potential compressor issue. Here are some common indicators:
- Lack of Cold Air: This is the most obvious symptom. If the compressor isn't compressing refrigerant effectively, the evaporator won't get cold enough to cool the air blowing into the cabin.
- Weak Airflow: While airflow issues can stem from a clogged cabin air filter or a faulty blower motor, a failing compressor can also contribute to reduced airflow, especially when the A/C is engaged.
- Unusual Noises: Grinding, squealing, or rattling noises coming from the compressor area are often signs of internal damage. These noises may be intermittent or constant, depending on the severity of the issue.
- Clutch Problems: The compressor clutch engages and disengages the compressor pulley from the engine, allowing the compressor to cycle on and off as needed. A faulty clutch can prevent the compressor from engaging, resulting in no cold air. You might hear a clicking sound but no engagement.
- Leaking Refrigerant: Leaks are often detectable by the presence of oily residue around the compressor or other A/C components. Refrigerant leaks reduce the system's charge, leading to poor cooling performance. Specialized leak detection dyes and UV lights are often used to pinpoint the source of leaks.
- Compressor Not Engaging: This could be due to a faulty clutch, low refrigerant pressure (a safety mechanism to prevent compressor damage), or a problem with the electrical circuit controlling the compressor.
- Increased Fuel Consumption: A struggling compressor places a heavier load on the engine, potentially impacting fuel economy. While subtle, this can be a contributing factor in the overall diagnosis.
Diagnostic Procedures: Checking if Your A/C Compressor is Working
Now, let's get into the specifics of diagnosing the A/C compressor. Remember to exercise caution when working with automotive systems, especially those involving refrigerants and electrical components. If you're not comfortable performing these tests, it's always best to consult a qualified mechanic.
1. Visual Inspection
Start with a thorough visual inspection of the compressor. Look for:
- Visible Damage: Cracks, dents, or other signs of physical damage to the compressor housing.
- Leaks: Oily residue around the compressor fittings and hoses.
- Clutch Condition: Check the clutch for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Is the clutch plate properly aligned with the pulley?
- Belt Condition: Inspect the drive belt that powers the compressor. Is it worn, cracked, or glazed? A slipping belt can prevent the compressor from operating correctly.
2. Compressor Clutch Engagement Test
This test verifies whether the compressor clutch is engaging when the A/C is turned on.
- Start the Engine: Turn on the engine and let it idle.
- Engage the A/C: Turn the A/C system to its maximum cooling setting and the blower fan on high.
- Observe the Compressor Clutch: Locate the A/C compressor pulley and clutch. The clutch is the plate at the front of the pulley. When the A/C is engaged, the clutch should engage, causing the center plate to spin along with the pulley.
- Listen for a Click: You should hear a distinct click when the clutch engages. This indicates that the clutch is receiving power and attempting to engage.
- No Engagement: If the clutch doesn't engage, proceed to the next steps to further investigate the cause.
3. Electrical Circuit Testing
If the clutch isn't engaging, the issue could be with the electrical circuit that powers it.
- Check the A/C Relay and Fuse: Locate the A/C relay and fuse in your vehicle's fuse box (refer to your owner's manual for their location). Use a multimeter to test the fuse for continuity. If the fuse is blown, replace it with a new one of the same amperage. If the fuse blows again immediately, there's likely a short circuit in the system.
- Test for Voltage at the Compressor Clutch: Use a multimeter to check for voltage at the compressor clutch connector when the A/C is engaged. You should see approximately 12 volts. If there's no voltage, the problem could be a faulty relay, wiring issue, or a problem with the A/C control unit.
4. Refrigerant Pressure Check
Low refrigerant pressure can prevent the compressor from engaging as a safety measure to prevent damage. You'll need a set of A/C manifold gauges to perform this test.
- Connect the Gauges: Connect the manifold gauges to the high and low-pressure service ports on the A/C system.
- Read the Pressure: Start the engine and engage the A/C. Observe the gauge readings.
- Analyze the Readings: Compare the readings to the specifications for your vehicle's A/C system (refer to a service manual or online resources). Low pressure on both the high and low sides indicates a refrigerant leak. Extremely high pressure on the high side can indicate a blockage in the system or a faulty expansion valve.
Important Note: Working with refrigerant requires specialized equipment and knowledge. It's illegal and environmentally irresponsible to vent refrigerant into the atmosphere. If you suspect a refrigerant leak or need to add refrigerant, it's best to have the system serviced by a qualified A/C technician.
5. Listening for Compressor Noise with a Mechanic's Stethoscope
A mechanic's stethoscope can be incredibly useful for isolating noises coming from the compressor. Place the stethoscope probe on the compressor housing while the engine is running and the A/C is engaged. Listen for any unusual noises, such as grinding, rattling, or squealing. Compare the noise to a known good compressor. This can help you determine if the compressor's internal components are damaged.
When to Consult a Professional
While some diagnostic procedures can be performed by DIY enthusiasts, complex A/C system issues often require the expertise of a qualified mechanic. Consider seeking professional help if:
- You're not comfortable working with electrical components or refrigerant.
- You suspect a refrigerant leak.
- You've replaced the compressor, but the system still isn't working correctly.
- You lack the necessary tools or equipment.
Cost of A/C Compressor Replacement
Replacing an A/C compressor can be a significant expense. The cost will vary depending on the vehicle's make and model, the type of compressor (new, remanufactured, or used), and the labor charges of the mechanic. Generally, you can expect to pay anywhere from $500 to $1200 for a complete A/C compressor replacement, including parts and labor. It's always a good idea to get quotes from multiple mechanics to ensure you're getting a fair price.
Preventive Maintenance for Your A/C System
Regular maintenance can help prolong the life of your A/C compressor and prevent costly repairs. Here are some tips:
- Run the A/C Regularly: Even during the winter months, run the A/C for a few minutes each week to keep the compressor lubricated.
- Inspect the Drive Belt: Check the drive belt for wear and tear and replace it as needed.
- Replace the Cabin Air Filter: A clogged cabin air filter restricts airflow and can put extra strain on the A/C system. Replace it according to the manufacturer's recommendations.
- Have the System Serviced Regularly: Consider having your A/C system serviced by a qualified technician every few years. This includes checking the refrigerant level, inspecting the components for leaks, and cleaning the condenser fins.
By understanding the A/C system and performing regular maintenance, you can keep your A/C blowing cold for years to come. Remember that accurate diagnosis is key to preventing unnecessary repairs and ensuring your comfort on the road.
