Infiniti G37 Transmission Fluid Capacity
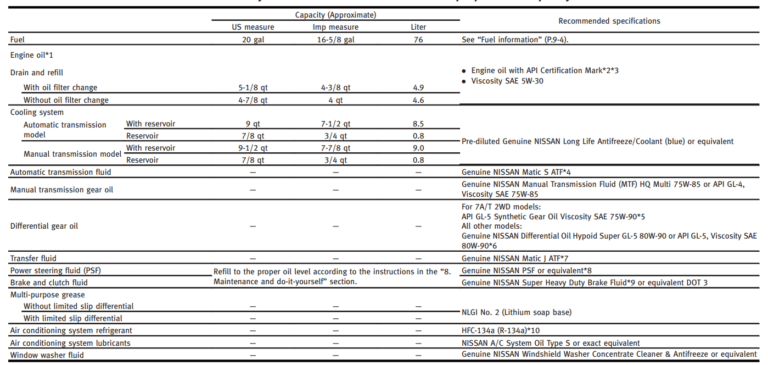
The Infiniti G37, a vehicle celebrated for its performance and luxurious appointments, has secured its place in automotive history. While discussions often center on its engine and design, a critical aspect frequently overlooked is its transmission. Specifically, the transmission fluid capacity and its implications for longevity and performance.
Historically, knowing the correct transmission fluid capacity was essential for routine maintenance. Overfilling or underfilling could lead to serious mechanical problems. However, the automotive landscape is undergoing a seismic shift. Let's explore how emerging technologies, the rise of electric vehicles (EVs), and smart automotive solutions are changing the very nature of transmissions and, consequently, the need for traditional transmission fluid knowledge.
The Electric Revolution: A Transmission Fluid Obituary?
The most significant disruption to the traditional transmission is undoubtedly the rise of electric vehicles. EVs, in their purest form, often eliminate the need for a complex multi-gear transmission altogether. Single-speed transmissions, or even direct-drive systems, are common. This simplification dramatically reduces the need for transmission fluid. In some EVs, a fluid is still used for cooling and lubrication of gears and bearings within the reduction gear set, but the volume and characteristics are vastly different from the fluids used in a G37's 7-speed automatic.
This isn't to say that all EVs will forever lack traditional transmissions. Some manufacturers are experimenting with multi-speed gearboxes to optimize both acceleration and high-speed efficiency. Porsche's Taycan, for example, utilizes a two-speed transmission. However, even in these cases, the demands on the transmission fluid are generally less severe due to the electric motor's inherent torque characteristics.
The challenge here isn't just technological; it's infrastructural and societal. The transition to a fully electric fleet requires a massive investment in charging infrastructure, battery technology advancements to increase range and reduce charging times, and a fundamental shift in consumer behavior. Range anxiety remains a real concern for many potential EV buyers. The environmental impact of battery production and disposal also requires careful consideration and sustainable solutions.
Hybrid Systems: Bridging the Gap
Hybrid vehicles represent an intermediate step, often incorporating both an internal combustion engine (ICE) and an electric motor. The transmission in a hybrid system can vary significantly depending on the architecture. Some hybrids use traditional transmissions, while others employ continuously variable transmissions (CVTs) or e-CVTs (electronically controlled CVTs). e-CVTs, often found in Toyota and Lexus hybrids, are particularly interesting as they use a planetary gearset to split power between the engine and electric motor. These systems typically require specialized fluids with specific frictional properties.
While hybrids still require transmission fluid, the demands on the fluid can be different from those in a purely ICE vehicle. The electric motor assists the engine, reducing the load on the transmission during certain driving conditions. Furthermore, regenerative braking helps to recapture energy, further lessening the burden. However, maintaining the correct fluid level and using the specified fluid type remains crucial for hybrid transmission longevity.
The primary challenge for hybrid technology lies in optimizing the interplay between the ICE and electric motor for maximum efficiency and performance. This requires sophisticated control algorithms and advanced powertrain management systems. Furthermore, the complexity of hybrid systems can lead to higher manufacturing costs and potential maintenance complexities.
The Smart Transmission: Learning and Adapting
Beyond electrification, smart automotive solutions are revolutionizing transmission technology. Imagine a transmission that learns your driving habits and adjusts its shift points accordingly. This is becoming increasingly common with adaptive transmissions. Modern vehicles often feature sophisticated software that monitors various parameters, such as throttle position, vehicle speed, and road conditions, to optimize shift patterns for performance, fuel economy, or a combination of both.
Looking ahead, we can anticipate even more intelligent transmissions that incorporate real-time data from connected car services. For example, the transmission could anticipate upcoming hills or traffic congestion based on GPS data and adjust its gearing accordingly. This level of proactive adaptation could significantly improve fuel efficiency and driving experience.
Furthermore, advancements in sensor technology are enabling more precise monitoring of transmission health. Sensors can detect changes in fluid viscosity, temperature, and pressure, providing early warnings of potential problems. This data can be used to schedule preventative maintenance, reducing the risk of costly repairs. The integration of AI and machine learning algorithms could further enhance diagnostic capabilities, allowing the transmission to predict failures before they occur.
Challenges in this area include ensuring data privacy and security, as well as developing robust and reliable sensor technologies. The complexity of these systems also requires skilled technicians who can interpret the data and perform necessary repairs.
Synthetic Fluids and the Future of Lubrication
The evolution of transmission fluids themselves is also playing a crucial role. Synthetic fluids offer superior performance compared to conventional fluids, providing better protection against wear, oxidation, and thermal breakdown. They also maintain their viscosity over a wider temperature range, ensuring optimal performance in both hot and cold climates.
Future transmission fluids may incorporate nanotechnology to further enhance their lubricating properties. Nanoparticles could be added to the fluid to reduce friction and wear, extending the life of the transmission and improving fuel efficiency. Self-healing fluids, capable of repairing minor damage to the transmission components, are also a possibility in the long term.
The development of these advanced fluids requires significant research and development efforts. Furthermore, ensuring compatibility with existing transmission designs and addressing potential environmental concerns are important considerations.
The future of mobility is not just about electric vehicles. It's about creating intelligent, connected, and sustainable transportation ecosystems.
The automotive industry is poised for radical transformation. The G37's transmission fluid capacity, while seemingly a small detail, represents a connection to a past era of automotive engineering. As we move towards electric, hybrid, and smart mobility solutions, the role of traditional transmissions will diminish. But the underlying principles of lubrication, heat management, and mechanical efficiency will remain vital. The engineers and scientists who once focused on optimizing transmission fluid for a G37 will now be innovating in areas like battery thermal management, electric motor design, and AI-powered control systems.
Mobility is evolving from a product to a service. Ride-sharing, autonomous vehicles, and subscription models are changing the way people access transportation. This shift will further impact the demand for traditional vehicle ownership and maintenance, including transmission fluid changes.
The challenge lies in adapting to these changes and embracing new technologies while ensuring that mobility remains accessible, affordable, and sustainable for all.
Imagine a future where vehicles are seamlessly integrated into smart cities, communicating with each other and with the infrastructure to optimize traffic flow and reduce emissions. Where autonomous vehicles transport goods and people efficiently and safely. Where transportation is no longer a burden but a seamless and enjoyable experience.
This is the vision that drives innovation in the automotive industry, a vision where the seemingly mundane task of checking transmission fluid capacity is replaced by a focus on creating a brighter, more sustainable, and more connected future of mobility.
