Nissan Rogue Vehicle Information Display
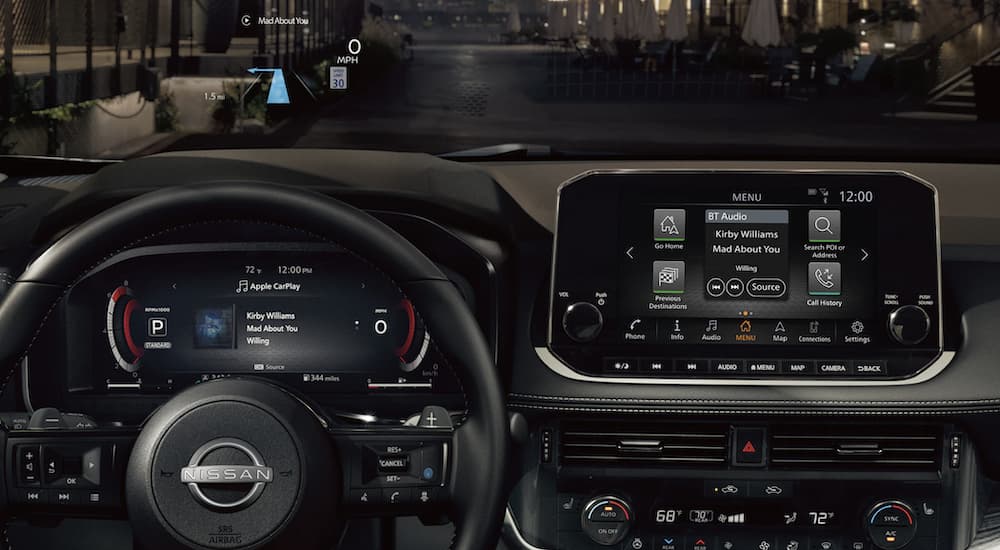
The Nissan Rogue, like many modern vehicles, boasts a sophisticated Vehicle Information Display (VID) that provides the driver with a wealth of data about the vehicle's operation and status. Understanding how to navigate and interpret this information can be invaluable for both routine maintenance and troubleshooting potential problems. This article dives deep into the Rogue's VID, explaining its functions, common displays, and how to use it effectively for diagnostics and personalization.
Understanding the Rogue's Vehicle Information Display
The VID is essentially a digital interface, typically located within the instrument cluster, that presents information gathered from various sensors and modules throughout the vehicle. The exact content and functionality can vary slightly depending on the Rogue's model year and trim level. However, the core principles and many of the common displays remain consistent across models.
The VID is controlled by buttons usually located on the steering wheel. These buttons allow you to cycle through different display screens and adjust settings. Familiarize yourself with their specific functions in your owner's manual.
Key Display Categories
The VID typically organizes information into several categories. Here are some of the most common:
- Trip Information: This is perhaps the most frequently used category. It provides data related to your current and previous trips. Expect to see things like:
- Trip A and Trip B: These are independent trip odometers that track distance traveled since they were last reset.
- Average Fuel Economy: This displays the average fuel consumption for the current trip.
- Instantaneous Fuel Economy: Shows your fuel consumption in real-time.
- Distance to Empty (DTE): An estimate of how far you can drive before running out of fuel, based on your current fuel level and recent fuel economy. This is often referred to as range.
- Elapsed Time: The duration of the current trip.
- Average Speed: The average speed during the current trip.
- Vehicle Information: This category presents information about the vehicle's overall health and status. Examples include:
- Coolant Temperature: Indicates the engine coolant temperature. An excessively high temperature can signal a cooling system problem.
- Oil Temperature (if equipped): Some models may display oil temperature.
- Battery Voltage: Shows the current voltage of the vehicle's battery. Low voltage can indicate a charging system issue or a failing battery.
- Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS): Displays the individual tire pressures for each tire. Alerts are triggered if any tire pressure falls below the recommended level.
- Odometer: The total distance the vehicle has traveled since it was new.
- Safety and Driver Assistance Systems: Information related to the vehicle's safety features and driver aids. This may include:
- Blind Spot Warning (BSW) status: Indicates whether the BSW system is active or if there's a malfunction.
- Rear Cross Traffic Alert (RCTA) status: Shows the status of the RCTA system.
- Lane Departure Warning (LDW) status: Displays the status of the LDW system.
- Intelligent Cruise Control (ICC) settings and status: Allows you to set and monitor the ICC system's speed and following distance.
- ProPILOT Assist status (if equipped): Shows the status and settings of the ProPILOT Assist system.
- Settings: This category allows you to customize various vehicle settings, such as:
- Language: Change the display language.
- Units: Switch between metric and imperial units (e.g., Celsius/Fahrenheit, kilometers/miles).
- Brightness: Adjust the brightness of the VID.
- Warning Chime Volume: Adjust the volume of various warning chimes.
- Clock Settings: Set the time and date.
- Maintenance Reminders: Set reminders for routine maintenance tasks, such as oil changes and tire rotations.
- Warning Messages: Critical alerts and warnings that indicate a potential problem with the vehicle. These messages are often accompanied by an audible chime and a warning light on the instrument panel. Pay close attention to these messages and address the underlying issue promptly.
Interpreting Warning Messages
Warning messages are the VID's way of communicating critical issues. Here's a breakdown of some common warning messages and their possible causes:
- "Low Tire Pressure": Indicates that one or more tires are below the recommended pressure. Check the tire pressure and inflate accordingly.
- "Engine Oil Low": Indicates that the engine oil level is critically low. Stop the vehicle as soon as it's safe to do so and check the oil level. Add oil if necessary.
- "Charging System Fault": Indicates a problem with the vehicle's charging system. This could be due to a failing alternator, a bad battery, or a problem with the wiring.
- "Brake System Warning": A serious warning indicating a potential problem with the braking system. This could be due to low brake fluid, worn brake pads, or a malfunctioning ABS system. Have the brakes inspected immediately.
- "Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)" or "Check Engine Light": This is a generic warning that indicates a problem with the engine or emissions system. The light can illuminate for a wide range of issues, from a loose gas cap to a more serious engine problem. Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve the diagnostic trouble code (DTC) and identify the specific problem.
- "Airbag Warning Light": Indicates a problem with the airbag system. Have the system inspected by a qualified technician.
- "ABS Warning Light": Indicates a problem with the Anti-lock Braking System (ABS). While you will still have regular braking function, the ABS feature will not be available.
Using the VID for Diagnostics
While the VID isn't a substitute for a dedicated diagnostic tool, it can provide valuable insights into the vehicle's condition. Here are some ways to use the VID for basic diagnostics:
- Monitoring Fluid Levels: Keep an eye on the coolant temperature and oil temperature (if displayed). Significant deviations from the normal operating range can indicate a problem.
- Tracking Fuel Economy: A sudden drop in fuel economy can be a sign of a problem with the engine, emissions system, or drivetrain.
- Checking Tire Pressures: Regularly check the tire pressures to ensure they are within the recommended range. This can improve fuel economy, handling, and tire life.
- Identifying Warning Messages: Pay close attention to any warning messages that appear on the VID. These messages can provide valuable clues about potential problems.
- Observing System Status: Regularly monitoring the status of the driver assistance systems, like blind spot monitoring and lane departure warning, can help ensure they are functioning correctly.
Advanced Troubleshooting and OBD-II Scanners
For more in-depth diagnostics, you'll need to use an OBD-II scanner. The OBD-II (On-Board Diagnostics II) system is a standardized system that monitors various engine and emissions-related parameters. When a problem is detected, the OBD-II system stores a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) in the vehicle's computer.
An OBD-II scanner allows you to retrieve these DTCs and use them to diagnose the problem. There are many different types of OBD-II scanners available, ranging from inexpensive handheld units to more sophisticated professional-grade tools. A good scanner will not only read the DTCs, but also provide a description of the code and possible causes.
Once you have retrieved the DTC, you can use online resources or repair manuals to research the code and identify the possible causes. Be aware that a DTC only points you in the general direction of the problem. Further testing and diagnosis may be required to pinpoint the exact cause.
Important Note: Clearing DTCs without fixing the underlying problem will only result in the warning light reappearing. It's essential to diagnose and repair the issue before clearing the codes.
Customization and Personalization
The VID also allows you to customize various settings to suit your preferences. Refer to your owner's manual for detailed instructions on how to access and adjust these settings. Some common customization options include:
- Display Language: Change the language of the display.
- Units: Switch between metric and imperial units.
- Brightness: Adjust the brightness of the VID.
- Warning Chime Volume: Adjust the volume of various warning chimes.
- Maintenance Reminders: Set reminders for routine maintenance tasks.
Conclusion
The Nissan Rogue's Vehicle Information Display is a powerful tool that provides drivers with a wealth of information about their vehicle. By understanding how to navigate and interpret the information presented on the VID, you can stay informed about your vehicle's condition, troubleshoot potential problems, and customize settings to suit your preferences. Remember to consult your owner's manual for detailed instructions on using the VID in your specific model and trim level. By combining the information provided by the VID with a good understanding of automotive systems and the use of diagnostic tools like OBD-II scanners, you can become a more informed and capable car owner.
