Nissan Sentra Power Window Fuse
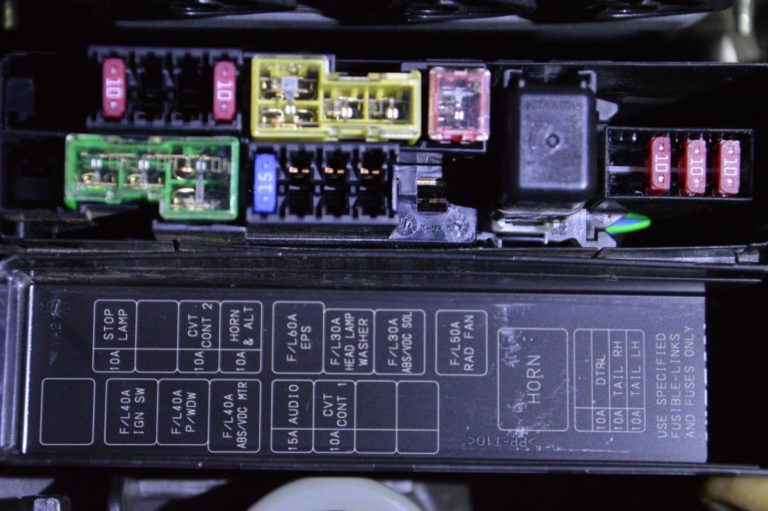
The seemingly simple act of raising or lowering a car window is underpinned by a surprisingly complex electrical system. At the heart of this system lies the power window fuse, a small but critical component that protects the entire circuit from overcurrents and potential damage. This article delves into the intricacies of the Nissan Sentra's power window fuse, exploring its function, location, diagnostic procedures, and replacement strategies. We'll also touch upon the broader context of power window systems and their evolution.
Understanding the Power Window System
Before dissecting the role of the fuse, it's crucial to understand the architecture of a typical power window system. In the Nissan Sentra, as with most modern vehicles, each window has its own electric motor. This motor is responsible for driving a regulator mechanism, which converts the motor's rotational motion into the linear motion required to raise or lower the glass pane. The entire assembly is controlled by a switch, usually located on the door panel for each window and often with a master control panel on the driver's side.
When you press the power window switch, you're essentially completing an electrical circuit. This circuit allows current to flow from the car's battery, through the fuse, to the window motor. Depending on whether you're raising or lowering the window, the polarity of the voltage applied to the motor changes, causing it to rotate in the appropriate direction. Limit switches, either mechanical or electronic, prevent the motor from overrunning at the top and bottom of its travel.
Modern Sentras also incorporate safety features such as anti-pinch systems. These systems use sensors to detect obstructions in the window's path and automatically reverse the window's direction to prevent injury. These features are often integrated into the motor controller or body control module (BCM) and add another layer of complexity to the system.
The Power Window Fuse: A Guardian Against Electrical Overload
The power window fuse acts as a sacrificial element, designed to break the circuit if the current exceeds a safe threshold. This protects the more expensive and vital components, such as the window motor, wiring harness, and control modules, from damage. Imagine a sudden surge in current caused by a short circuit in the wiring or a malfunctioning motor; without a fuse, this surge could overheat the wiring, potentially leading to a fire or causing irreparable damage to the motor. The fuse, being a relatively inexpensive component, is designed to fail first, interrupting the flow of electricity and preventing catastrophic consequences.
Fuses are rated in amperes (amps), which represents the maximum current they can handle before blowing. The correct amperage rating for the Nissan Sentra's power window fuse is specified in the owner's manual and often labeled on the fuse box itself. Using a fuse with a higher amperage rating than specified is extremely dangerous as it defeats the purpose of the fuse and could allow excessive current to flow, potentially causing a fire.
Locating the Power Window Fuse in a Nissan Sentra
The location of the power window fuse can vary slightly depending on the specific year and trim level of the Nissan Sentra. However, it is typically found in one of two fuse boxes:
- The interior fuse box: This fuse box is usually located under the dashboard on the driver's side. It may be behind a small access panel or require the removal of a trim piece. Refer to your owner's manual for the exact location and removal procedure.
- The engine compartment fuse box: This fuse box is located under the hood, typically near the battery. While less common, some Sentra models may have the power window fuse located here.
Once you've located the fuse box, consult the fuse box diagram, which is usually printed on the inside of the fuse box cover or in your owner's manual. The diagram will show the location of each fuse and its corresponding function. Look for the fuse labeled "Power Window," "PWR WDW," or a similar designation. The diagram will also specify the fuse's amperage rating.
Diagnosing a Blown Power Window Fuse
If your power windows are not working, the first step is to check the power window fuse. Here's a systematic approach to diagnosing a blown fuse:
- Visual Inspection: Carefully remove the suspected fuse from the fuse box. Examine it closely. A blown fuse will typically have a broken filament or a blackened or melted appearance. A good fuse will have an intact filament.
- Continuity Testing: Even if the fuse appears intact, it's best to confirm its functionality using a multimeter. Set the multimeter to the continuity setting (often indicated by a diode symbol or a buzzer sound). Place one probe on each end of the fuse. If the multimeter shows continuity (a beep or a low resistance reading), the fuse is good. If the multimeter shows no continuity (an open circuit), the fuse is blown.
- Fuse Tester: A dedicated fuse tester is a simple and inexpensive tool that can quickly determine if a fuse is blown. These testers typically have a light that illuminates when the fuse is good.
Important Note: If you find a blown fuse, it's crucial to determine the underlying cause before simply replacing it. Repeatedly blowing fuses indicates a more serious problem, such as a short circuit in the wiring or a malfunctioning motor. Ignoring the underlying issue and continually replacing the fuse could lead to further damage or even a fire.
Investigating the Root Cause of a Blown Fuse
If the fuse blows immediately after being replaced, or if it blows frequently, you need to investigate the cause of the overcurrent. Here are some potential causes:
- Short Circuit in Wiring: A short circuit occurs when a wire carrying electrical current comes into contact with ground (the car's chassis). This creates a path of very low resistance, causing a large amount of current to flow. Inspect the wiring harness that runs to the window motor for any signs of damage, such as frayed insulation, exposed wires, or pinched wires. Pay particular attention to areas where the wiring passes through the door jamb, as this is a common location for wear and tear.
- Faulty Window Motor: A failing window motor can draw excessive current, especially if it's struggling to overcome resistance. This can be caused by worn-out gears, a binding regulator mechanism, or internal short circuits within the motor itself. Try to operate each window individually. If one window consistently blows the fuse, that window's motor is the prime suspect.
- Binding Window Regulator: If the window regulator mechanism is stiff or binding, the motor will have to work harder to move the window, drawing more current. Lubricate the regulator mechanism with a suitable grease and check for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Water Intrusion: Water can cause corrosion and short circuits in electrical components. Check for signs of water damage around the window motor, wiring harness, and fuse box.
- Aftermarket Accessories: The installation of aftermarket accessories, such as window tint or security systems, can sometimes interfere with the power window system and cause fuses to blow. Disconnect any aftermarket accessories to see if the problem resolves itself.
Replacing the Power Window Fuse
Once you've diagnosed a blown fuse and addressed the underlying cause, replacing the fuse is a straightforward process:
- Turn off the Ignition: Always turn off the ignition before working on the electrical system. This prevents accidental shorts or sparks.
- Locate the Blown Fuse: As described earlier, locate the fuse box and identify the blown power window fuse using the fuse box diagram.
- Remove the Blown Fuse: Use a fuse puller (usually included in the fuse box) to carefully remove the blown fuse. Avoid using pliers or other tools that could damage the fuse box or adjacent fuses.
- Install a New Fuse: Insert a new fuse with the correct amperage rating into the empty slot. Double-check the owner's manual or fuse box diagram to ensure you're using the correct amperage.
- Test the System: Turn on the ignition and test the power windows to ensure they are working properly.
Preventative Maintenance
While fuses are designed to protect the electrical system, some preventative maintenance can help extend the life of your power window system and minimize the risk of blown fuses:
- Lubricate Window Tracks: Periodically lubricate the window tracks with a silicone-based lubricant. This will help reduce friction and make it easier for the motor to move the window.
- Keep Windows Clean: Clean windows reduce friction and strain on the motor.
- Avoid Overloading the System: Avoid holding the power window switch down after the window has reached its full open or closed position. This can put unnecessary strain on the motor and potentially lead to overheating.
Conclusion
The power window fuse is a small but vital component in the Nissan Sentra's electrical system. Understanding its function, location, and diagnostic procedures can save you time and money in the event of a power window malfunction. By following the steps outlined in this guide and practicing preventative maintenance, you can ensure the reliable operation of your power windows for years to come. Remember, safety is paramount when working with electrical systems. If you are uncomfortable performing any of these procedures, it's always best to consult a qualified automotive technician.
Always refer to your vehicle's owner's manual for specific information regarding fuse locations and amperage ratings. Incorrect fuse usage can lead to serious damage.
