Nissan Titan Fuse Box Diagram
The Nissan Titan, a formidable contender in the full-size pickup truck segment, boasts a complex electrical system that powers everything from its advanced driver-assistance technologies to the basic functions that keep you on the road. At the heart of this intricate network lies the fuse box, a critical component responsible for protecting sensitive electrical circuits from overcurrents. Understanding the Nissan Titan fuse box diagram is crucial for troubleshooting electrical issues and performing basic maintenance. This guide will delve into the intricacies of the Titan's fuse box layout, function, and common problems, providing a comprehensive overview for curious minds and amateur engineers alike.
Fuse Box Locations and Access
The Nissan Titan, depending on the model year and trim, typically features multiple fuse box locations. Identifying these locations is the first step in diagnosing any electrical problem. Here's a breakdown:
- Interior Fuse Box: Usually located inside the cabin, often behind a small panel on the driver's side dashboard or under the dashboard near the steering column. Accessing this fuse box generally involves removing a plastic cover, often secured by clips or screws. This box typically houses fuses responsible for interior lights, power windows, the audio system, and other cabin-related electronics.
- Engine Compartment Fuse Box: Found under the hood, typically near the battery or the engine control unit (ECU). This fuse box is usually more robust and weather-sealed, protecting fuses that control vital engine components, headlights, and other essential systems. Look for a rectangular black box with a latching mechanism.
Always consult your owner's manual for the exact location of the fuse boxes in your specific Titan model year. The manual will also provide a detailed fuse box diagram tailored to your vehicle.
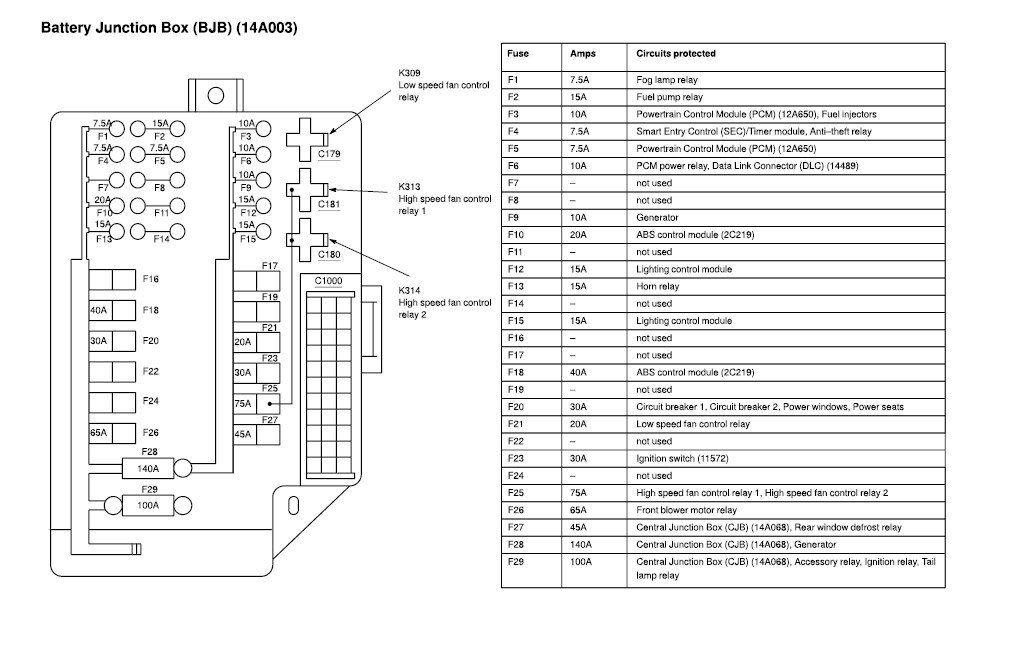
Understanding the Fuse Box Diagram
Once you've located the fuse box, the next step is interpreting the fuse box diagram. This diagram, usually printed on the inside of the fuse box cover or found in the owner's manual, is a schematic representation of the fuses and relays within the box. Each fuse is assigned a specific number or identifier, and the diagram indicates the corresponding circuit that the fuse protects.
Here's what you need to know to decipher the diagram:
- Fuse Number/Identifier: Each fuse slot is labeled with a unique number or alphanumeric code. This is the key to matching a fuse to its function.
- Circuit Description: Next to the fuse number, the diagram will provide a brief description of the circuit that the fuse protects. For example, you might see "Headlights," "Fuel Pump," "Power Windows," or "ABS."
- Fuse Ampere Rating: The diagram also specifies the amperage rating of each fuse. This is indicated by a number followed by "A" (e.g., 10A, 20A, 30A). The amperage rating indicates the maximum current that the fuse can handle before it blows, protecting the circuit from overcurrent damage. Using a fuse with the incorrect amperage rating can be dangerous and can damage your vehicle's electrical system.
- Fuse Symbol: Sometimes, the diagram will use symbols to represent different fuse types or circuit types. Consult your owner's manual for a key to these symbols.
Example: Imagine a fuse labeled "15" with the description "Tail Lights (Left)" and a rating of "10A." This means that fuse number 15 protects the left tail light circuit and has a maximum current capacity of 10 amps. If the left tail light stops working, this would be the first fuse to check.
Fuse Types and Their Function
Fuses come in various shapes and sizes, each designed for specific applications. Understanding the different types of fuses used in the Nissan Titan is helpful for proper replacement.
- Blade Fuses (ATO/ATC): These are the most common type of fuse found in modern vehicles. They have a plastic body with two metal prongs that plug into the fuse box. Blade fuses are color-coded to indicate their amperage rating.
- Mini Blade Fuses: A smaller version of the blade fuse, often used in newer vehicles to save space. They share the same operating principle as standard blade fuses.
- Maxi Fuses: Larger blade fuses designed for high-current applications, such as the main power supply to the vehicle's electrical system or the anti-lock braking system (ABS).
- Cartridge Fuses: Cylindrical fuses with metal caps on each end. They are typically used for high-current applications and are often found in the engine compartment.
Fuses work by containing a thin metal filament that melts and breaks the circuit when an overcurrent condition occurs. This prevents excessive current from flowing through the circuit and potentially damaging components. A blown fuse is easily identifiable by a broken or melted filament.
Troubleshooting Electrical Problems with Fuses
Checking the fuses is often the first step in troubleshooting electrical problems in your Nissan Titan. Here's a systematic approach:
- Identify the Symptom: Determine which electrical component is not working. This will help you narrow down the possible fuse candidates.
- Consult the Fuse Box Diagram: Locate the fuse diagram for your vehicle and identify the fuse(s) that control the affected component.
- Inspect the Fuse: Carefully remove the fuse using a fuse puller (a small plastic tool designed to grip and remove fuses). Examine the filament inside the fuse. If the filament is broken or melted, the fuse is blown and needs to be replaced.
- Test the Fuse (Optional): For a more precise diagnosis, you can use a multimeter to test the fuse for continuity. Set the multimeter to the continuity setting (usually indicated by a sound symbol) and touch the probes to each end of the fuse. If the multimeter beeps or displays a low resistance reading, the fuse is good. If there is no continuity, the fuse is blown.
- Replace the Fuse: Replace the blown fuse with a new fuse of the exact same amperage rating. Do not use a fuse with a higher amperage rating, as this could damage the circuit.
- Test the Component: After replacing the fuse, test the affected component to see if it is now working. If the component still doesn't work, there may be a more serious problem in the circuit, such as a short circuit or a faulty component.
Common Causes of Blown Fuses
A blown fuse is a symptom, not the root cause of the problem. Understanding the common causes of blown fuses can help you prevent future issues.
- Short Circuit: A short circuit occurs when a wire or component comes into contact with ground, creating a low-resistance path for current to flow. This can cause a sudden surge of current that blows the fuse.
- Overload: An overload occurs when a circuit is drawing more current than it is designed to handle. This can happen if you connect too many devices to a single circuit or if a component is malfunctioning and drawing excessive current.
- Faulty Component: A malfunctioning component, such as a motor or a solenoid, can draw excessive current and blow the fuse.
- Loose Wiring: Loose or corroded wiring connections can create resistance in the circuit, which can lead to overheating and blown fuses.
- Water Damage: Water intrusion can cause corrosion and short circuits, leading to blown fuses.
If a fuse repeatedly blows, it's crucial to diagnose the underlying cause of the problem rather than simply replacing the fuse each time. Continued fuse blowing indicates a persistent electrical fault that needs to be addressed.
Safety Precautions
Working with electrical systems can be dangerous. Always follow these safety precautions when working with the Nissan Titan fuse box:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical components, disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent accidental shorts.
- Use the Correct Tools: Use a fuse puller to remove fuses. Avoid using pliers or other metal tools, as they can damage the fuse box or create a short circuit.
- Replace with the Correct Fuse: Always replace a blown fuse with a new fuse of the same amperage rating. Using a fuse with a higher amperage rating can damage the circuit and potentially cause a fire.
- Consult a Professional: If you are uncomfortable working with electrical systems, or if you are unable to diagnose the problem, consult a qualified mechanic.
Conclusion
The Nissan Titan fuse box is a vital component that protects the vehicle's electrical system. By understanding the fuse box layout, fuse types, and troubleshooting techniques, you can diagnose and resolve many common electrical problems. Remember to always prioritize safety and consult a professional if you are unsure about any aspect of the electrical system. With a little knowledge and patience, you can keep your Nissan Titan running smoothly and reliably.
