Nissan Versa Fuse Box Diagram
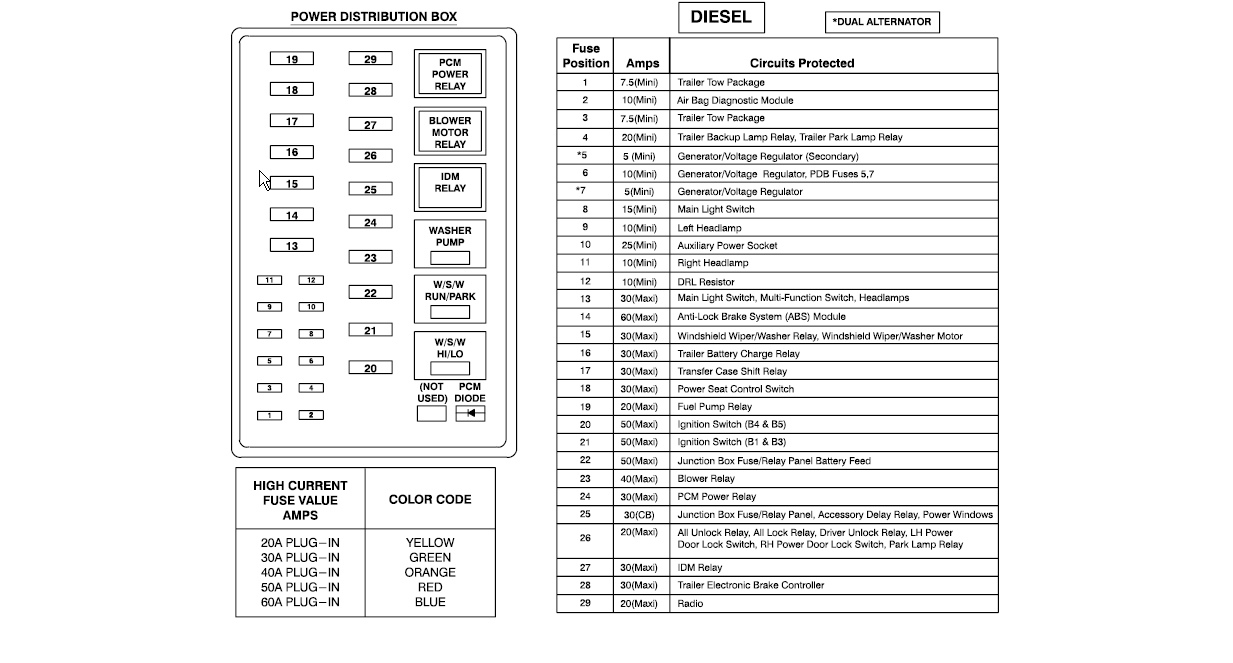
The humble fuse box, often overlooked until the moment something electrical malfunctions in your car, is a critical component. Even in a seemingly basic vehicle like the Nissan Versa, understanding its fuse box diagram is essential for troubleshooting and basic maintenance. But let's not dwell solely on the present. Let's use this seemingly mundane starting point to launch into a broader discussion about the future of automotive technology and how even the fuse box – and its digital descendants – will be revolutionized.
The Evolving Automotive Landscape: Beyond Internal Combustion
We are living through a period of unprecedented transformation in the automotive industry. The internal combustion engine, the dominant force for over a century, is facing increasing pressure from electric vehicles (EVs), hybrid systems, and alternative fuels. This shift isn't just about swapping engines; it's about rethinking the entire architecture of the vehicle, from the drivetrain to the software that controls it all. The Nissan Versa, even in its current form, represents an entry point to this world for many, and understanding its systems lays a foundation for comprehending the complexities of more advanced vehicles.
Electric vehicles are undoubtedly the headline grabbers. Battery technology is improving rapidly, driving down costs and increasing range. We're seeing advancements in solid-state batteries, which promise greater energy density, faster charging times, and improved safety. However, challenges remain. The availability of raw materials like lithium and cobalt, the development of robust charging infrastructure, and consumer acceptance of EVs in diverse climates are all hurdles that need to be overcome. The long-term environmental impact of battery production and disposal also requires careful consideration.
Hybrid systems offer a more gradual transition. They combine the benefits of internal combustion and electric power, providing improved fuel economy and reduced emissions. Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) offer even greater flexibility, allowing drivers to cover shorter distances on electric power alone. Nissan has been a significant player in the hybrid space with models like the Leaf and various e-Power systems abroad, showcasing their commitment to electrification, a commitment that could filter down to even entry-level models like the Versa in the future.
The Role of Software and Smart Automotive Solutions
Beyond the powertrain, software is becoming increasingly crucial. Modern vehicles are essentially computers on wheels, with sophisticated systems controlling everything from engine management to advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). ADAS features like automatic emergency braking, lane departure warning, and adaptive cruise control are becoming increasingly common, enhancing safety and convenience. The Versa, even in its current generation, offers some of these features, hinting at the increasing integration of technology across the entire automotive spectrum.
Smart automotive solutions extend beyond individual vehicles. Connected car technologies are enabling vehicles to communicate with each other and with the surrounding infrastructure, paving the way for safer and more efficient transportation. Imagine a world where traffic congestion is minimized, accidents are avoided, and parking is effortless. This is the promise of connected and autonomous driving.
Autonomous driving, while still in its early stages, has the potential to revolutionize mobility. Self-driving cars could improve accessibility for people who are unable to drive themselves, reduce traffic accidents, and free up time for passengers to work or relax during their commute. However, the ethical and legal implications of autonomous driving are complex and require careful consideration. Issues such as liability in the event of an accident, data privacy, and the potential displacement of professional drivers need to be addressed.
The Fuse Box: A Microcosm of Change
Returning to our starting point, the fuse box itself will undergo significant changes. In traditional vehicles, the fuse box is a relatively simple device containing fuses that protect electrical circuits from overloads. However, as vehicles become more complex and rely on sophisticated electronic systems, the fuse box is evolving into a more integrated and intelligent power distribution unit (PDU).
Future PDUs will likely incorporate solid-state circuit breakers, which offer several advantages over traditional fuses. Solid-state circuit breakers are more reliable, faster acting, and can be reset electronically. They can also be integrated with the vehicle's central control unit, allowing for remote monitoring and control of electrical circuits. This means that potential problems can be identified and addressed before they lead to a failure.
Furthermore, with the increasing adoption of electric vehicles, the PDU will play a critical role in managing the flow of power between the battery, the motor, and other electrical components. It will also need to handle the higher voltages and currents associated with electric powertrains. The fuse box diagram, therefore, becomes a much more complex schematic representing a highly sophisticated power management system.
The evolution of the fuse box reflects the broader trend towards increased digitalization and integration in the automotive industry.
The diagnostic process will also transform. Instead of physically checking fuses, technicians will be able to use diagnostic tools to remotely monitor the status of each circuit and identify any faults. This will lead to faster and more accurate troubleshooting, reducing downtime and improving customer satisfaction. Even for the average owner, app-based diagnostics could provide early warnings and simpler solutions for minor electrical issues, moving beyond the need to even locate, let alone interpret, a physical fuse box diagram.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the future of automotive technology is bright, there are also significant challenges that need to be addressed. The cost of new technologies, particularly electric vehicles and autonomous driving systems, remains a barrier to widespread adoption. The development of robust and reliable charging infrastructure is also crucial for the success of EVs. Cybersecurity is another growing concern, as connected vehicles are vulnerable to hacking and data breaches. Investing in cybersecurity measures and protecting vehicle data is essential to ensure the safety and privacy of drivers and passengers.
However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation. The automotive industry is attracting new players, including technology companies, startups, and venture capitalists. This influx of investment and talent is driving innovation and accelerating the development of new technologies. Collaboration between automakers, technology companies, and governments is essential to overcome the challenges and realize the full potential of the future of mobility.
The shift to electric vehicles and smart automotive solutions also creates new opportunities for job creation. New skills are needed in areas such as battery technology, software development, data analytics, and cybersecurity. Investing in education and training programs is crucial to prepare the workforce for the jobs of the future.
Ultimately, the future of mobility is about creating a transportation system that is safer, more efficient, more sustainable, and more accessible to all. This requires a holistic approach that considers not only the technology itself, but also the social, economic, and environmental implications. The Nissan Versa, while perhaps not the most technologically advanced vehicle on the road today, represents a starting point for many individuals as they navigate this evolving landscape. Understanding its basic systems is a stepping stone to grasping the complexities of future automotive technologies.
A Visionary Note
Imagine a future where transportation is seamless and personalized. Autonomous vehicles whisk us away to our destinations, optimizing routes in real-time to minimize congestion and emissions. Smart cities anticipate our needs, providing personalized recommendations for transportation options based on our preferences and schedules. The air is clean, the roads are safe, and transportation is no longer a source of stress but a source of freedom. This is not just a dream; it's a vision that we can achieve through innovation, collaboration, and a commitment to creating a better future for all. And yes, even the humble fuse box – or its intelligent, digitally-managed descendant – will play a vital, albeit hidden, role in making that vision a reality. The future of mobility is not just about getting from point A to point B; it's about creating a world where transportation is truly sustainable, equitable, and empowering.
