Two Stroke Oil In Diesel Fuel
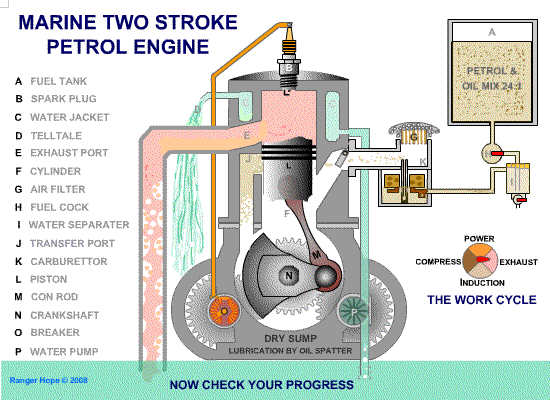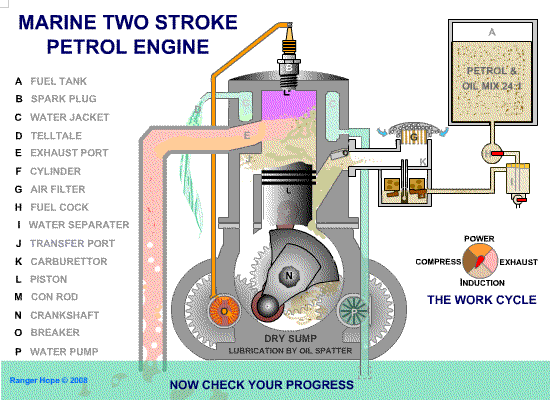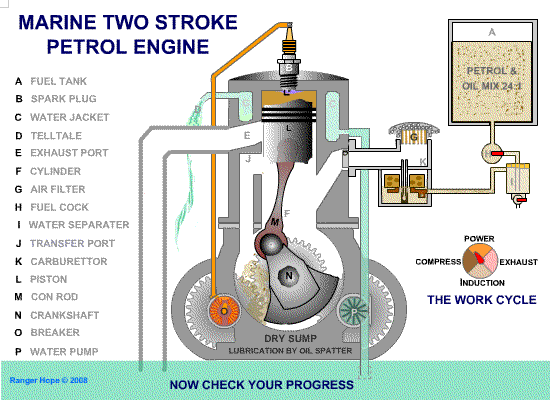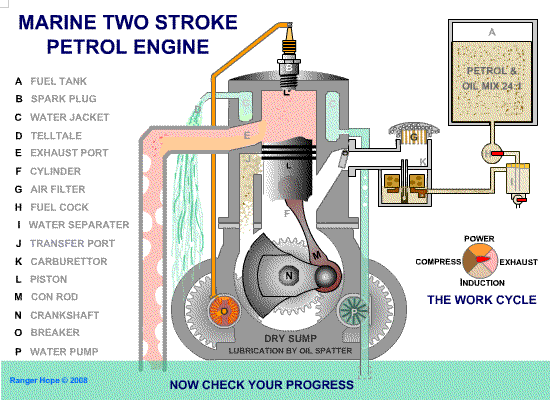
The practice of adding two-stroke oil to diesel fuel has been debated for years, with proponents claiming improved lubrication and fuel economy, while critics warn of potential damage. This article explores the realities of this practice, offering insights for both car owners and mechanics. We’ll cover the claimed benefits, potential problems, troubleshooting techniques, and best practices for maintaining your diesel engine. While this is not universally endorsed, understanding the arguments and potential consequences is crucial.
The Rationale Behind Adding Two-Stroke Oil
The core argument for adding two-stroke oil to diesel centers around the decreasing sulfur content in modern diesel fuels. Sulfur acts as a lubricant, and its reduction, while environmentally beneficial, can potentially lead to increased wear and tear on fuel pumps and injectors. Two-stroke oil is designed to provide lubrication in two-stroke engines, and some believe it can supplement the lost lubrication in modern diesel fuel. This is particularly relevant in older diesel engines designed for fuels with higher sulfur content. However, modern diesel fuels already contain additives to address lubrication concerns. Furthermore, using the incorrect two-stroke oil or mixing ratio can be detrimental.
Claimed Benefits:
- Improved Lubrication: Reduced wear on fuel pumps and injectors.
- Quieter Engine Operation: Less "diesel knock" due to better combustion.
- Cleaner Injectors: Prevention of injector nozzle coking.
- Slightly Improved Fuel Economy: More efficient combustion.
However, these benefits are often anecdotal and lack robust scientific backing. Moreover, the actual improvement, if any, is often marginal and can be overshadowed by potential drawbacks.
Potential Problems and Risks
Adding two-stroke oil to diesel fuel is not without risks. It's crucial to understand the potential downsides before attempting this practice.
Potential Drawbacks:
- Clogging of Fuel Filters: Some two-stroke oils can leave deposits that clog fuel filters, leading to reduced fuel flow and engine performance issues.
- Damage to Catalytic Converters and Diesel Particulate Filters (DPF): The ash content in some two-stroke oils can damage or shorten the lifespan of emissions control systems. This is a major concern in modern diesel vehicles.
- Injector Coking: While some claim it cleans injectors, improper mixing or certain types of two-stroke oil can actually contribute to injector coking.
- Warranty Voidance: Using additives not approved by the manufacturer can void your vehicle's warranty.
- Incomplete Combustion: Some two-stroke oils may not burn completely in a diesel engine, leading to increased emissions and soot.
Modern diesel engines, particularly those with common rail injection systems, are highly sensitive to fuel quality. Introducing an unapproved additive can have severe consequences.
Troubleshooting: Symptoms, Causes, and Fixes
If you suspect that adding two-stroke oil to your diesel fuel is causing problems, here's a troubleshooting guide:
Symptom: Reduced Fuel Economy
- Possible Cause: Incorrect mixing ratio, clogged fuel filter, or incomplete combustion of the two-stroke oil.
- Fix:
- Check the mixing ratio. If you are adding two-stroke oil, use a very low concentration (e.g., 1:200 or 1:250).
- Replace the fuel filter.
- Discontinue the use of two-stroke oil and monitor fuel economy.
Symptom: Rough Idle or Stalling
- Possible Cause: Clogged fuel filter, injector problems, or air in the fuel system.
- Fix:
- Check and replace the fuel filter.
- Have the injectors professionally inspected and cleaned or replaced if necessary.
- Check for air leaks in the fuel lines.
- If two-stroke oil has been recently added, drain the fuel tank and refill with clean diesel.
Symptom: Black Smoke from Exhaust
- Possible Cause: Incomplete combustion, over-fueling, or DPF issues.
- Fix:
- Reduce or eliminate the addition of two-stroke oil.
- Check the air filter and replace if necessary.
- Have the injectors inspected for proper operation.
- Check the DPF for clogging and consider professional cleaning or replacement.
Symptom: Engine Knocking or Misfiring
- Possible Cause: Injector problems, incorrect fuel timing, or low fuel pressure.
- Fix:
- Have the injectors professionally diagnosed and repaired.
- Check the fuel pump and fuel pressure regulator.
- Consult a qualified mechanic for engine diagnostics.
Example: Common Rail Diesel (e.g., VW TDI, BMW 320d, Mercedes CDI)
Common rail diesel engines are particularly sensitive. Adding two-stroke oil to a VW TDI, BMW 320d, or Mercedes CDI carries a higher risk of damaging the high-pressure fuel pump and injectors. The precise tolerances and intricate design of these systems require fuel that meets very specific specifications. Using an unapproved additive can disrupt the delicate balance and lead to costly repairs. For example, in a VW TDI, even a slight change in fuel viscosity can affect the injector spray pattern, leading to incomplete combustion and increased emissions.
Example: Older Diesel Engines (e.g., Mercedes W123 Diesel, Older Toyota Hilux)
Older diesel engines, such as those found in the Mercedes W123 Diesel or older Toyota Hilux models, might be more tolerant of fuel additives, but the risks still exist. While the fuel systems are less sophisticated, clogging of fuel filters and potential damage to injector nozzles are still concerns. It's important to consider the age and condition of the engine before attempting to add any additive. Even in these older engines, sticking to manufacturer-recommended maintenance schedules and using high-quality diesel fuel is generally the best approach.
Real-World Considerations
Many factors influence whether adding two-stroke oil is beneficial or harmful. These include the type of two-stroke oil used, the mixing ratio, the engine type, and the overall condition of the vehicle. It's important to note that the quality of the two-stroke oil is crucial. Avoid using cheap, low-quality oils, as they may contain additives that are harmful to your diesel engine. TC-W3 rated two-stroke oils are often cited as being "safe" than other types, although its still up for debate. Remember to consult a qualified mechanic before adding anything to your fuel tank, especially if you have a newer vehicle.
In many cases, investing in high-quality diesel fuel with appropriate additives is a safer and more effective way to maintain your diesel engine. Many fuel manufacturers already include detergents, lubricants, and cetane boosters in their premium diesel fuels.
Alternative Solutions
Instead of adding two-stroke oil, consider the following alternatives:
- Use High-Quality Diesel Fuel: Opt for premium diesel fuels that contain detergents and lubricants.
- Fuel Additives Designed for Diesel Engines: Consider using fuel additives specifically formulated for diesel engines, such as injector cleaners and fuel stabilizers. Follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully.
- Regular Maintenance: Stick to the recommended maintenance schedule, including fuel filter replacements and injector servicing.
- Professional Injector Cleaning: Periodically have your injectors professionally cleaned to remove deposits and ensure optimal performance.
Keeping Your Car in Top Condition
The best way to keep your diesel car in top condition is to follow these guidelines:
- Regular Maintenance: Adhere to the manufacturer's recommended maintenance schedule. This includes oil changes, filter replacements, and other routine services.
- Use Quality Fluids and Parts: Use only high-quality engine oil, fuel filters, and other components that meet the manufacturer's specifications.
- Proper Driving Habits: Avoid aggressive driving and excessive idling, which can put unnecessary strain on the engine.
- Address Problems Promptly: Don't ignore warning signs or unusual noises. Address any issues as soon as they arise to prevent them from escalating into more serious problems.
- Seek Professional Advice: Consult a qualified mechanic for any major repairs or concerns. They can provide expert advice and ensure that your vehicle is properly maintained.
- Maintain the Fuel System: Replace your fuel filter at the recommended intervals. This prevents contaminants from reaching your engine.
- Regularly Check Fluid Levels: Ensure that your engine oil, coolant, and other fluids are at the proper levels.
Ultimately, the decision of whether or not to add two-stroke oil to your diesel fuel is a personal one. However, it's crucial to weigh the potential benefits against the risks and to consider the specific needs of your vehicle. In most cases, sticking to manufacturer-recommended maintenance schedules and using high-quality diesel fuel is the safest and most effective approach. Remember to consult with a qualified mechanic if you have any concerns about your diesel engine.
