What Antifreeze Should I Use
Choosing the right antifreeze, also known as engine coolant, isn't just about grabbing the cheapest jug off the shelf. It's a decision that impacts your engine's longevity, cooling efficiency, and even the lifespan of various components within your cooling system. This guide delves into the technical aspects of antifreeze, helping you understand the different types available and how to make the best choice for your vehicle.
Understanding the Basics: What is Antifreeze?
At its core, antifreeze is a liquid designed to perform two primary functions:
- Preventing Freezing: During cold weather, water-based coolant can freeze, expanding in volume and potentially cracking engine blocks and other vital components. Antifreeze lowers the freezing point of the coolant mixture, protecting against this damage.
- Preventing Overheating: Conversely, antifreeze raises the boiling point of the coolant, preventing it from vaporizing and causing overheating in hot weather. This is crucial for efficient engine operation.
However, antifreeze isn't just about freeze and boil protection. It also contains additives that perform critical secondary functions:
- Corrosion Inhibition: Engines are made of various metals, including aluminum, cast iron, copper, and brass. These metals are susceptible to corrosion in the presence of water. Antifreeze additives create a protective layer on these surfaces, preventing rust and other forms of corrosion.
- Lubrication: Antifreeze provides some degree of lubrication for the water pump, extending its lifespan.
- pH Buffering: Coolant acidity can damage cooling system components. Additives maintain a stable pH level, preventing the coolant from becoming too acidic or alkaline.
- Scale Inhibition: Minerals in the water can form scale deposits within the cooling system, reducing heat transfer efficiency. Additives prevent scale buildup.
Types of Antifreeze: A Deep Dive
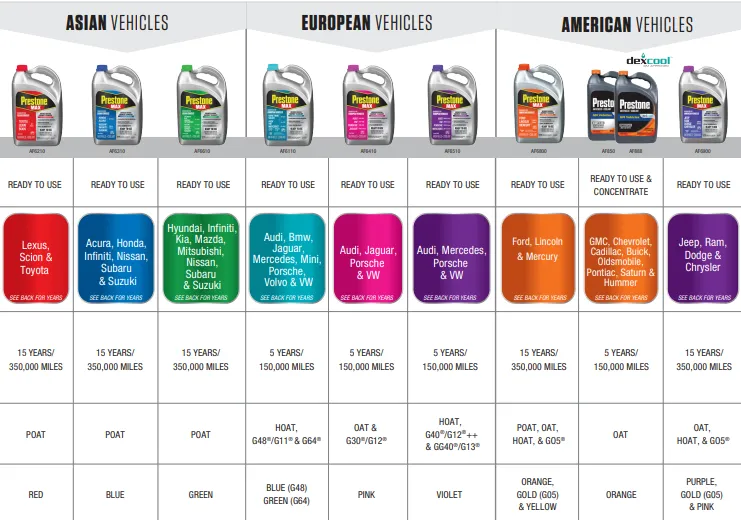
The key difference between antifreeze types lies in the corrosion inhibitor technology they employ. Understanding these technologies is crucial for choosing the right coolant for your vehicle.
Inorganic Additive Technology (IAT)
IAT antifreeze, typically dyed green, is the oldest type. It uses inorganic corrosion inhibitors such as silicates and phosphates. While effective, IAT coolant has a relatively short lifespan, typically around 2 years or 30,000 miles. The silicates can also drop out of solution over time, forming abrasive deposits that can damage the water pump seal. Therefore, frequent changes are crucial.
Key Characteristics of IAT Antifreeze:
- Color: Typically green
- Lifespan: 2 years or 30,000 miles
- Inhibitors: Silicates and Phosphates
- Pros: Inexpensive, readily available
- Cons: Short lifespan, potential for silicate dropout
Organic Acid Technology (OAT)
OAT antifreeze uses organic acids, such as sebacate and 2-ethylhexanoic acid (2-EHA), as corrosion inhibitors. OAT coolants typically have a much longer lifespan than IAT coolants, often lasting 5 years or 150,000 miles. However, some OAT formulations are incompatible with certain metals, particularly those found in older cooling systems. 2-EHA, in particular, can be aggressive towards some silicone gaskets. Therefore, it's essential to check your vehicle manufacturer's recommendations before using OAT coolant.
Key Characteristics of OAT Antifreeze:
- Color: Often orange, red, or purple (but color is not always a reliable indicator)
- Lifespan: 5 years or 150,000 miles
- Inhibitors: Organic acids (e.g., sebacate, 2-EHA)
- Pros: Long lifespan, excellent corrosion protection
- Cons: Potential incompatibility with some older cooling systems, 2-EHA concerns
Hybrid Organic Acid Technology (HOAT)
HOAT antifreeze combines the benefits of both IAT and OAT technologies. It uses organic acids for long-term corrosion protection, along with a small amount of silicates or phosphates for enhanced protection of aluminum components. HOAT coolants offer a good balance of lifespan and compatibility, making them a popular choice for many modern vehicles. Examples include G-05 and some "universal" coolants. However, even within the HOAT category, there are variations in the specific inhibitors used, so it's still important to consult your vehicle manufacturer's recommendations.
Key Characteristics of HOAT Antifreeze:
- Color: Often yellow or gold (but color is not always a reliable indicator)
- Lifespan: 5 years or 150,000 miles
- Inhibitors: Organic acids with silicates or phosphates
- Pros: Good balance of lifespan and compatibility, enhanced aluminum protection
- Cons: Variations within the HOAT category require careful selection
Phosphate-Free HOAT (POAT)
Some manufacturers, particularly Japanese automakers, prefer phosphate-free formulations. These coolants are designed to avoid the potential for phosphate-related scale formation in certain water conditions. They still utilize organic acids and silicates for corrosion protection, offering a similar lifespan and performance to standard HOAT coolants.
Propylene Glycol Based Antifreeze
The more common ethylene glycol based antifreeze has a sweet taste, making it attractive to animals, who can be fatally poisoned if they ingest it. Propylene glycol is a less toxic alternative, but it is also a less effective antifreeze, requiring a higher concentration to achieve the same level of freeze protection. While more environmentally friendly, it is generally more expensive and offers slightly reduced performance.
Choosing the Right Antifreeze: A Practical Guide
With so many options available, how do you choose the right antifreeze for your vehicle?
- Consult Your Owner's Manual: This is the most important step. Your vehicle manufacturer's recommendations are the definitive source of information on the correct antifreeze type for your vehicle.
- Consider Your Vehicle's Age and Cooling System Materials: Older vehicles with cooling systems containing a significant amount of copper or brass may not be compatible with some OAT coolants. In such cases, IAT or HOAT coolants may be a better choice.
- Avoid Mixing Different Types of Antifreeze: Mixing different types of antifreeze can lead to chemical reactions that reduce the effectiveness of the corrosion inhibitors and potentially cause damage to the cooling system. If you're unsure what type of antifreeze is currently in your vehicle, it's best to completely flush the cooling system and refill it with the correct type.
- Use Distilled Water for Mixing: Tap water contains minerals that can contribute to scale buildup and corrosion. Always use distilled water when mixing antifreeze with water to create the correct coolant concentration. A 50/50 mix is typically recommended, but consult your owner's manual for specific recommendations based on your climate.
- Color is Not Always a Reliable Indicator: While antifreeze types are often associated with specific colors, these colors are primarily for marketing purposes and can vary between brands. Do not rely solely on color to identify antifreeze type. Always check the product label and specifications.
- Consider a Coolant Flush: Before switching to a different type of antifreeze or if your coolant is old or contaminated, consider performing a coolant flush. This will remove any old coolant, debris, and contaminants from the cooling system, ensuring optimal performance and preventing potential compatibility issues.
Concentrate vs. Pre-mixed Coolant
Antifreeze is available in both concentrated and pre-mixed forms. Concentrated antifreeze must be mixed with distilled water before use, typically in a 50/50 ratio. Pre-mixed coolant is already diluted and ready to use. While pre-mixed coolant is more convenient, it is generally more expensive per volume of antifreeze. Concentrated antifreeze allows you to adjust the coolant concentration based on your climate, providing greater flexibility. For example, in extremely cold climates, a 60/40 mix (60% antifreeze, 40% water) may be recommended for increased freeze protection.
Conclusion
Choosing the right antifreeze is a critical aspect of vehicle maintenance. By understanding the different types of antifreeze available and considering your vehicle's specific needs, you can ensure optimal cooling system performance and protect your engine from costly damage. Always consult your owner's manual, and when in doubt, seek the advice of a qualified mechanic. Proper coolant maintenance is an investment in your vehicle's longevity and reliability.
