What Does Retarding Timing Do
Hey there! Having engine trouble? Feeling a lack of power or maybe hearing some strange noises? If you've been searching online, you've probably come across the term "retarded timing." Let's break down what that means, what it does, and how it can impact your car's performance. I'm here to help you understand if this might be the root of your problem, and what your options are to get back on the road smoothly.
Understanding Ignition Timing: The Basics
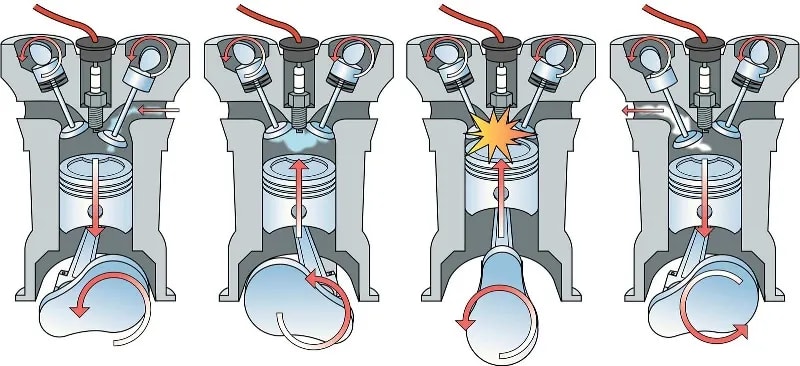
First, let's clarify what ignition timing is. In a gasoline engine, the air-fuel mixture needs to be ignited at precisely the right moment to push the piston down and generate power. This ignition is caused by a spark plug firing. Ignition timing refers to when that spark plug fires in relation to the position of the piston in the cylinder.
Ideally, the spark should occur slightly *before* the piston reaches the very top of its stroke (Top Dead Center or TDC). This is called *advanced timing*. Advancing the timing gives the air-fuel mixture enough time to burn completely and exert maximum pressure on the piston as it travels down. Think of it like lighting a fuse - you want to light it a little early so the explosion happens right when you need it.
However, if the spark happens *after* the piston passes TDC, we have *retarded timing*. This means the fuel is burning later in the cycle, and the combustion is happening less efficiently.
What Does Retarding Timing Do, Then? The Symptoms & Effects
So, what happens when your engine's timing is retarded? Quite a few things, and none of them are good for overall performance or the health of your engine. Here's a breakdown:
1. Loss of Power
This is often the first thing drivers notice. With retarded timing, the fuel isn't burning fully when the piston is at its most advantageous position. This means you're not getting the full force of the explosion, resulting in a noticeable decrease in horsepower and torque. You might struggle to accelerate, especially uphill, or feel like your car is "sluggish."
2. Poor Fuel Economy
Inefficient combustion directly translates to worse gas mileage. Your engine has to work harder to produce the same amount of power, which means it burns more fuel. You might find yourself filling up your tank more often than usual.
3. Overheating
Retarded timing can cause the exhaust gases to be much hotter than normal. The fuel is still burning as the exhaust valve opens, dumping that unburnt fuel and heat into the exhaust system. This can lead to overheating problems, especially under heavy load (like towing or driving in hot weather). You might even see your temperature gauge creeping higher than normal or hear the engine "pinging" or "knocking" due to excessive heat.
4. Increased Emissions
Because the fuel isn't burning completely, retarded timing increases the amount of unburnt hydrocarbons (HC) and carbon monoxide (CO) released into the atmosphere. This is bad for the environment and can cause you to fail an emissions test.
5. Backfiring
In severe cases of retarded timing, unburnt fuel can accumulate in the exhaust system. This fuel can then ignite, causing a loud "backfire" that can be damaging to your exhaust components.
6. Rough Idling
Retarded timing can lead to an unstable idle, making the engine shake or sputter when you're stopped at a light or parked.
What Causes Retarded Timing?
Several factors can contribute to retarded ignition timing. Here are some common culprits:
1. Faulty Timing Components
In older vehicles with distributor-based ignition systems, the distributor itself can wear out or become misaligned. This can throw off the timing. Also, problems with the timing chain or belt can affect the camshaft and crankshaft relationship, impacting timing. These components stretch and wear out over time.
2. Defective Sensors
Modern engines rely on a network of sensors to determine the optimal ignition timing. A faulty crankshaft position sensor (CKP) or camshaft position sensor (CMP) can send incorrect information to the engine control unit (ECU), leading to retarded timing.
3. Vacuum Leaks
Vacuum leaks can disrupt the air-fuel mixture, causing the engine to run lean. The ECU might then retard the timing to compensate for the lean condition, preventing knocking.
4. Carbon Buildup
Excessive carbon deposits in the combustion chamber can increase compression, making the engine more prone to knocking. The ECU might then retard the timing to prevent this.
5. Incorrect Fuel Octane
Using fuel with a lower octane rating than recommended by the manufacturer can cause the engine to knock. Again, the ECU might retard the timing to protect the engine.
6. ECU Malfunction
In rare cases, the ECU itself can malfunction and incorrectly command retarded timing.
Diagnosing Retarded Timing: What to Look For
If you suspect your engine has retarded timing, here are some steps you can take to diagnose the problem:
- Listen for engine knocking or pinging: This is a sign that the engine is detonating improperly, which can be a result of or a precursor to timing being off.
- Check for error codes: Use an OBD-II scanner to check for any trouble codes stored in the ECU. Codes related to the CKP, CMP, or ignition system can point to timing issues. You can pick up a basic OBD-II scanner for around $20-$50 at most auto parts stores, or get a fancier one with more features for $100-$300.
- Inspect timing components: If your vehicle has a distributor, check its condition and alignment. If it's a timing belt-driven engine, inspect the condition of the belt and its tension.
- Check vacuum lines: Look for any cracked, loose, or disconnected vacuum lines.
- Consider professional help: If you're not comfortable working on your car, it's always best to take it to a qualified mechanic for diagnosis.
Fixing Retarded Timing: Solutions and Costs
The solution to retarded timing depends on the underlying cause. Here are some common fixes and their approximate costs:
1. Adjusting Distributor Timing (Older Vehicles)
Description: Using a timing light, the distributor is rotated until the timing is set to the manufacturer's specifications.
Tools Needed: Timing light, wrench.
Approximate Cost: $50-$150 (labor only, if done by a mechanic).
2. Replacing Faulty Sensors (CKP, CMP)
Description: The defective sensor is replaced with a new one.
Tools Needed: Wrench, socket set, OBD-II scanner (to clear codes).
Approximate Cost: $100-$300 (parts and labor).
3. Repairing Vacuum Leaks
Description: Damaged or leaking vacuum lines are replaced.
Tools Needed: Screwdrivers, pliers.
Approximate Cost: $50-$200 (parts and labor, depending on the severity of the leak).
4. Replacing Timing Belt or Chain
Description: The worn timing belt or chain is replaced with a new one. This is a complex repair that often involves replacing other components like water pump and tensioners.
Tools Needed: Extensive mechanical knowledge and specialized tools are required.
Approximate Cost: $500-$1500 (parts and labor). This is a job best left to the professionals.
5. ECU Reprogramming or Replacement
Description: If the ECU is malfunctioning, it may need to be reprogrammed or replaced. This is a specialized repair that requires diagnostic equipment and expertise.
Tools Needed: Requires specialized diagnostic equipment.
Approximate Cost: $300-$1200 (parts and labor).
Preventative Measures
While some causes of retarded timing are unavoidable (like wear and tear), there are things you can do to help prevent problems:
- Use the correct fuel octane: Always use the fuel octane rating recommended by the manufacturer.
- Perform regular maintenance: Follow the manufacturer's recommended maintenance schedule, including oil changes, spark plug replacement, and inspection of timing components.
- Address problems promptly: If you notice any symptoms of engine trouble, address them as soon as possible to prevent further damage.
Retarded timing can cause a variety of performance issues and potentially damage your engine. By understanding the causes and symptoms, you can take steps to diagnose and fix the problem before it becomes more severe. If you're unsure about tackling the repair yourself, don't hesitate to seek professional help. A qualified mechanic can quickly identify the cause of the retarded timing and recommend the best course of action to get your car running smoothly again. Good luck, and safe driving!
