Where Is A Tps Sensor Located
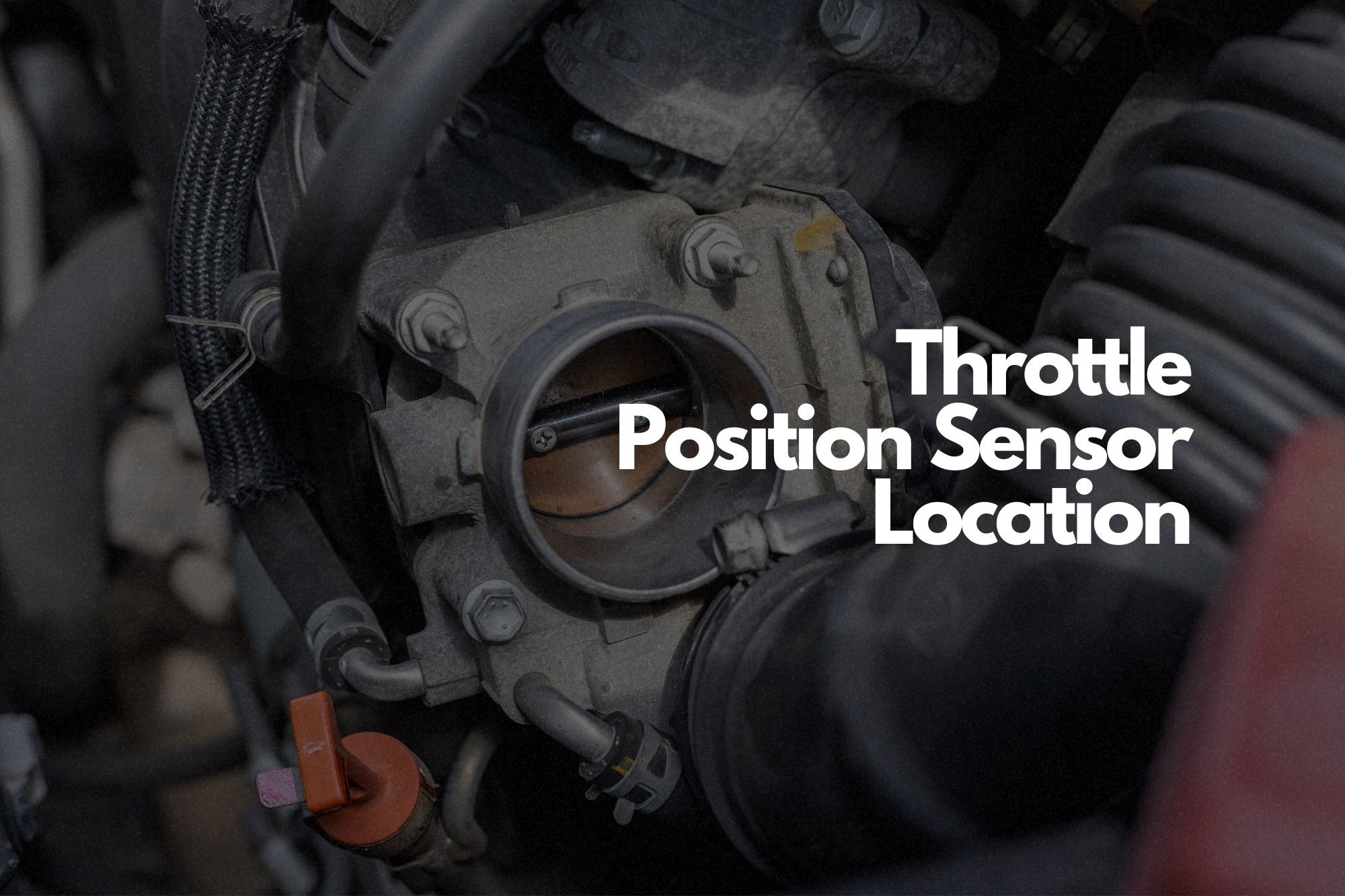
Experiencing hesitation, rough idling, or poor fuel economy with your vehicle? These can be frustrating symptoms, and one potential culprit is a faulty Throttle Position Sensor, or TPS. But before you start tearing into your engine, the first crucial step is knowing where to find this little but important component.
Understanding the TPS and Its Role
The Throttle Position Sensor is a vital part of your vehicle's engine management system. Its primary function is to monitor the position of the throttle plate – the valve that controls the amount of air entering the engine. The TPS then sends this information to the Engine Control Unit (ECU), also known as the engine computer. The ECU uses this data, along with input from other sensors, to determine the correct amount of fuel to inject into the cylinders for optimal combustion and performance.
Think of it this way: the TPS is like the ECU's eyes on your accelerator pedal. It tells the computer how much you're pressing down, allowing it to adjust fuel delivery accordingly. When the TPS fails or malfunctions, the ECU receives inaccurate data, leading to the symptoms we mentioned earlier: hesitation, stalling, poor acceleration, and decreased fuel efficiency.
Locating the TPS: A Vehicle-Specific Task
Now, let's get to the heart of the matter: finding the TPS. Unfortunately, there's no one-size-fits-all answer to this question. The location of the TPS varies significantly depending on the make, model, and year of your vehicle. However, there's a common theme: it's almost always attached to the throttle body.
The throttle body is a component that regulates airflow into the engine's intake manifold. It usually houses the throttle plate and the mechanism that controls its movement. So, your hunt for the TPS should start there.
Here's a general guide to help you narrow down the search:
- Under the Hood: Open your vehicle's hood and locate the air intake system. Follow the air intake duct from the air filter housing towards the engine. You'll eventually reach the throttle body. It's typically a metal or plastic housing with a butterfly valve inside.
- Visually Inspect the Throttle Body: Carefully examine the throttle body. The TPS is usually a small, rectangular or cylindrical sensor mounted directly to the throttle body. It will have an electrical connector attached to it.
- Consider Vehicle Configuration:
- Older Vehicles (Cable-Operated Throttle): On older vehicles with a mechanical throttle cable, the TPS is typically located on the side of the throttle body, near where the throttle cable connects.
- Newer Vehicles (Electronic Throttle Control - ETC): Newer vehicles with electronic throttle control, often called "drive-by-wire," may have the TPS integrated into the throttle body assembly. In some cases, you might not be able to replace the TPS separately; you might need to replace the entire throttle body.
- Consult Your Vehicle's Repair Manual or Online Resources: The best and most accurate way to locate the TPS is to consult your vehicle's repair manual or an online repair database specific to your vehicle. These resources will provide detailed diagrams and instructions for your particular make and model. Websites like AlldataDIY, Mitchell 1 DIY, or even searching YouTube for your specific vehicle can be incredibly helpful.
Important Safety Tip: Before working on any electrical components in your vehicle, disconnect the negative terminal of your battery to prevent electrical shock and potential damage to your vehicle's electrical system.
What to Look For: Identifying the TPS
Once you've located the throttle body, look for the TPS. It's usually a small sensor, typically black or grey in color, and attached to the throttle body with screws or bolts. It will have a wiring harness connected to it.
Here are some identifying features:
- Shape: Rectangular, square, or cylindrical.
- Size: Relatively small, usually a few inches in length.
- Mounting: Attached to the throttle body with screws or bolts.
- Connector: An electrical connector with multiple wires leading to it.
- Possible Markings: May have part numbers or manufacturer markings on it.
Tools You Might Need
If you plan to replace the TPS yourself (after confirming it's the issue and you can access it), here's a list of tools you might need:
- Socket Set or Wrenches: To remove the screws or bolts holding the TPS in place. The size will vary depending on your vehicle.
- Screwdrivers: Phillips head or flathead, depending on the type of screws used.
- Multimeter: To test the TPS for proper function (see testing section below).
- Scan Tool (OBD2 Scanner): To read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and clear them after replacing the TPS.
- Penetrating Oil (Optional): If the screws or bolts are corroded or difficult to remove.
- Throttle Body Cleaner (Optional): To clean the throttle body while you have access to it.
- New TPS Sensor: Be sure to get the correct part number for your vehicle.
Testing the TPS: Is It Really Faulty?
Before replacing the TPS, it's a good idea to test it to confirm that it's actually the source of the problem. You can do this using a multimeter. Here's a simplified overview of the testing process:
- Identify the TPS terminals: Consult your vehicle's repair manual or online resources to identify the correct terminals on the TPS for testing.
- Set your multimeter to measure voltage: Typically, you'll be measuring DC voltage.
- Connect the multimeter leads: Connect the positive lead to the signal wire terminal and the negative lead to the ground terminal on the TPS connector.
- Turn the ignition key to the "on" position (engine off): This will provide power to the TPS.
- Slowly open and close the throttle plate: As you open and close the throttle, the voltage reading on the multimeter should change smoothly and consistently. Look for any dead spots, spikes, or erratic readings.
- Interpret the results: A faulty TPS will often exhibit inconsistent or erratic voltage readings. If the voltage doesn't change smoothly, or if you see dead spots, the TPS is likely bad.
Important Note: Testing the TPS can be a bit complex, and it's essential to have the correct wiring diagrams and specifications for your vehicle. If you're not comfortable with electrical testing, it's best to consult a qualified mechanic.
Replacement Costs and Considerations
If you've confirmed that the TPS is faulty, you have two options: replace it yourself or take your vehicle to a mechanic.
- DIY Replacement: If you're comfortable working on your car and have the necessary tools, replacing the TPS yourself can save you money on labor costs. The cost of a new TPS sensor typically ranges from $30 to $150, depending on the make and model of your vehicle.
- Professional Replacement: If you're not comfortable with DIY repairs, or if you're unsure about the diagnosis, it's best to take your vehicle to a qualified mechanic. Labor costs for TPS replacement can vary depending on the shop and the complexity of the job, but you can typically expect to pay between $50 and $200 in labor, in addition to the cost of the sensor. So, total cost might range from $80 to $350.
Additional Considerations:
- Throttle Body Cleaning: When replacing the TPS, it's often a good idea to clean the throttle body as well. A dirty throttle body can contribute to similar symptoms as a faulty TPS.
- Throttle Body Replacement: As mentioned earlier, on some newer vehicles, the TPS is integrated into the throttle body assembly. In these cases, you might need to replace the entire throttle body, which can be more expensive than replacing just the TPS. The cost of a new throttle body can range from $200 to $600 or more, depending on the vehicle.
- Calibration: After replacing the TPS, some vehicles may require a throttle position sensor calibration procedure. This procedure helps the ECU learn the new TPS's operating range. A scan tool is often required for this calibration.
In Conclusion
Locating the TPS is the first step in diagnosing and resolving engine performance issues related to throttle position. While the exact location varies, understanding its function and connection to the throttle body will guide your search. Remember to consult your vehicle's repair manual, use online resources, and take safety precautions when working on your vehicle. If you're unsure about any aspect of the diagnosis or repair process, don't hesitate to seek professional help. A correctly functioning TPS is crucial for optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency, so addressing any issues promptly is essential.
