What Are The Three Purposes Of A Piston?
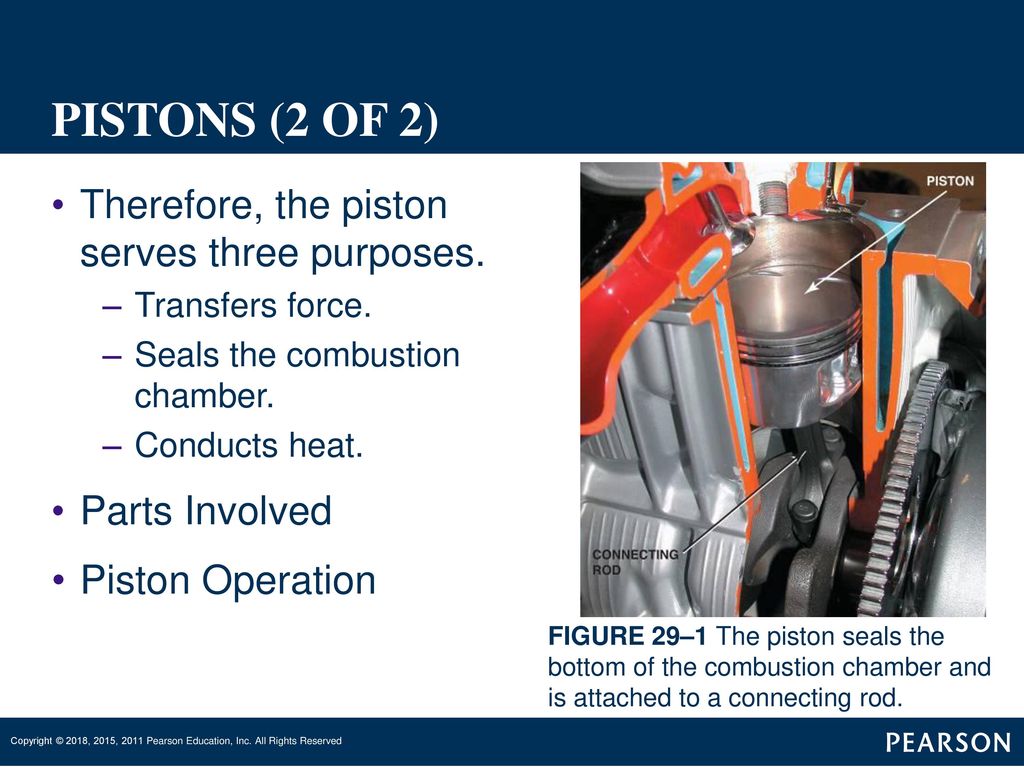
Engines are complex machines, and the piston is a crucial component working tirelessly within each cylinder. Understanding its purpose is key to diagnosing many engine-related problems. When a piston isn't performing correctly, it can lead to a cascade of issues. This article will explore the three primary functions of a piston, helping you identify potential problems and understand the necessary solutions.
Recognizing Piston Problems: What Are the Symptoms?
Before diving into the "why," let's look at the "how" – how do you *know* you might have a piston issue? Recognizing the symptoms early can prevent catastrophic engine damage.
Common Symptoms of Piston Issues:
- Excessive Oil Consumption: This is a major red flag. If you're adding oil more frequently than usual, especially without any visible leaks, the pistons or piston rings might be the culprit. You could be seeing blueish smoke from the exhaust.
- Loss of Power: Noticeable sluggishness, difficulty accelerating, or a general lack of engine power could indicate a compression problem caused by faulty pistons.
- Engine Knocking or Pinging: This metallic sound, often most noticeable under acceleration, can be caused by a piston slapping against the cylinder wall due to excessive wear (piston slap) or pre-ignition/detonation due to improper combustion caused by piston issues affecting compression or heat transfer.
- Misfires: A misfire occurs when one or more cylinders fail to fire correctly. This can be due to poor compression caused by damaged piston rings or a cracked piston. You might feel a jerking motion while driving.
- Rough Idling: An uneven or shaky idle, often accompanied by the engine struggling to maintain a consistent RPM, can be another symptom of compression issues within the cylinders.
- Smoke from the Exhaust: Different colors of smoke indicate different problems. Blue smoke indicates burning oil, often due to worn piston rings. White smoke can indicate a coolant leak into the cylinders, which could be exacerbated by piston damage. Black smoke indicates a rich fuel mixture, which, while not directly caused by the piston, can be worsened by poor cylinder sealing.
- Increased Blow-by: Blow-by refers to combustion gases leaking past the piston rings into the crankcase. This can pressurize the crankcase, leading to oil leaks and reduced engine efficiency.
The Three Crucial Roles of a Piston
The piston's job is threefold, all essential for optimal engine performance:
1. Receiving Combustion Pressure:
This is perhaps the most obvious function. The piston acts as a movable wall within the cylinder. When the air-fuel mixture ignites, the expanding gases create immense pressure. The piston receives this pressure and transmits it to the connecting rod, which, in turn, rotates the crankshaft, ultimately powering the vehicle. The crown of the piston (the top surface) is specifically designed to withstand this intense pressure and heat.
2. Sealing the Combustion Chamber:
This is where the piston rings come into play. These rings, located in grooves around the piston, create a tight seal between the piston and the cylinder wall. This seal prevents combustion gases from escaping into the crankcase (blow-by), ensuring maximum power transfer to the crankshaft. The rings also prevent oil from the crankcase from entering the combustion chamber, which would lead to excessive oil consumption and blue smoke.
3. Transferring Heat:
The combustion process generates tremendous heat. The piston plays a vital role in transferring this heat away from the combustion chamber to the cylinder walls, where it can be dissipated by the engine's cooling system. The piston's material (usually aluminum alloy) is chosen for its excellent thermal conductivity. Efficient heat transfer is crucial for preventing engine overheating and damage. Some pistons even have internal oil cooling channels to further improve heat dissipation. The skirt of the piston helps to distribute the force and heat, as well as help keep it aligned.
Ignoring Piston Problems: A Recipe for Disaster
Ignoring the symptoms mentioned above can lead to severe engine damage. Continued operation with damaged pistons can result in:
- Cylinder Wall Damage: A damaged piston or broken piston rings can score or scratch the cylinder walls, requiring expensive machining or even engine replacement.
- Bearing Failure: Excessive vibration and pressure fluctuations caused by piston issues can damage the connecting rod bearings and crankshaft bearings.
- Complete Engine Failure: In severe cases, a broken piston can shatter within the cylinder, causing catastrophic engine damage that renders the engine unrepairable.
- Catalytic Converter Damage: Burning excessive amounts of oil can damage the catalytic converter, leading to further repair costs and environmental concerns.
Recommended Fixes and Solutions
The appropriate fix depends on the extent of the damage. Here's a breakdown of potential solutions:
- Piston Ring Replacement: If the piston rings are worn or broken, replacing them can restore compression and reduce oil consumption. This usually involves removing the engine's cylinder head and oil pan.
- Piston Replacement: If the piston itself is cracked, damaged, or excessively worn, it must be replaced. This typically requires a complete engine rebuild, as the cylinders need to be honed or bored to accommodate new pistons.
- Cylinder Honing or Boring: If the cylinder walls are scored or damaged, they will need to be honed or bored to restore a smooth surface. Honing is a light resurfacing, while boring involves enlarging the cylinder diameter to accommodate oversized pistons.
- Engine Rebuild: In cases of severe damage, a complete engine rebuild may be necessary. This involves disassembling the entire engine, inspecting all components, and replacing any worn or damaged parts, including pistons, rings, bearings, and gaskets.
- Engine Replacement: In the most extreme cases, if the engine block itself is damaged beyond repair, replacing the entire engine may be the only option.
Cost Estimates and Shop Advice
Repair costs can vary significantly depending on the severity of the damage and the vehicle's make and model. Here's a general idea:
- Piston Ring Replacement: This can range from $1,500 to $4,000 or more, depending on the engine complexity and labor costs.
- Piston Replacement (single piston): Replacing a single piston will rarely be done, as you'd want to replace them all together. It can cost anywhere from $2,500-$6,000.
- Engine Rebuild: A complete engine rebuild can cost anywhere from $4,000 to $8,000 or more, depending on the extent of the work required and the parts used.
- Engine Replacement: Replacing the entire engine can cost anywhere from $5,000 to $10,000 or more, depending on whether you opt for a new, remanufactured, or used engine.
Shop Advice:
- Get a Professional Diagnosis: Don't rely solely on your own assessment. Take your vehicle to a qualified mechanic for a thorough diagnosis and compression test to pinpoint the source of the problem.
- Get Multiple Quotes: Obtain quotes from several different repair shops to compare prices and services.
- Ask About Warranty: Inquire about the warranty offered on the repair work and parts.
- Consider a Remanufactured Engine: If an engine replacement is necessary, a remanufactured engine can be a cost-effective alternative to a new engine.
Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) and Common Failures
Certain vehicle makes and models are prone to specific piston-related issues. Check for Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) issued by the manufacturer, which may provide information on known problems and recommended solutions. For example, some engines are known to have issues with excessive oil consumption due to poorly designed piston rings. Community forums dedicated to your car make and model may provide valuable insight on failure patterns. Some vehicles experience ring wear around 100,000 miles, while others are more robust. Talking with other owners and doing some research may assist your diagnosis.
Understanding the piston's role in your engine is the first step to ensuring your vehicle's longevity. By recognizing the symptoms of piston problems and addressing them promptly, you can prevent costly repairs and keep your engine running smoothly for years to come. Always consult a qualified mechanic for proper diagnosis and repair.
