When Does Power Come Back On 2025
Losing power, especially unexpectedly, is incredibly frustrating. Whether it's a planned outage or a surprise blackout, the question everyone asks is: When will the power come back on? Knowing the answer is vital for everything from preserving food to keeping your family safe and comfortable. In 2025, as infrastructure ages and weather patterns become more unpredictable, understanding power outage causes and solutions becomes even more critical. This article will help you diagnose potential reasons for your power being out, understand the expected restoration timeline, and what you can do to mitigate the impact.
Recognizing the Symptoms of a Power Outage
Before we dive into the restoration process, let's quickly identify the classic signs you're experiencing a power outage. Differentiating a localized issue from a broader outage is key.
- Complete darkness: This is the most obvious symptom. All lights within your home are off.
- Non-functional appliances: Refrigerators, ovens, washing machines, and other electrical appliances cease to operate.
- Lack of internet connectivity: Your Wi-Fi router is likely without power, preventing internet access.
- Television is off: Similar to other appliances, your television won't turn on.
- Neighbors affected (or not): Check if your neighbors have power. This helps determine if the outage is isolated to your home or a wider area.
- Streetlights out: Observe streetlights near your residence. Their status can indicate a widespread issue.
- Strange noises (or silence): A sudden silence from humming appliances or unusual sounds (like clicking) from electrical panels can signal a problem.
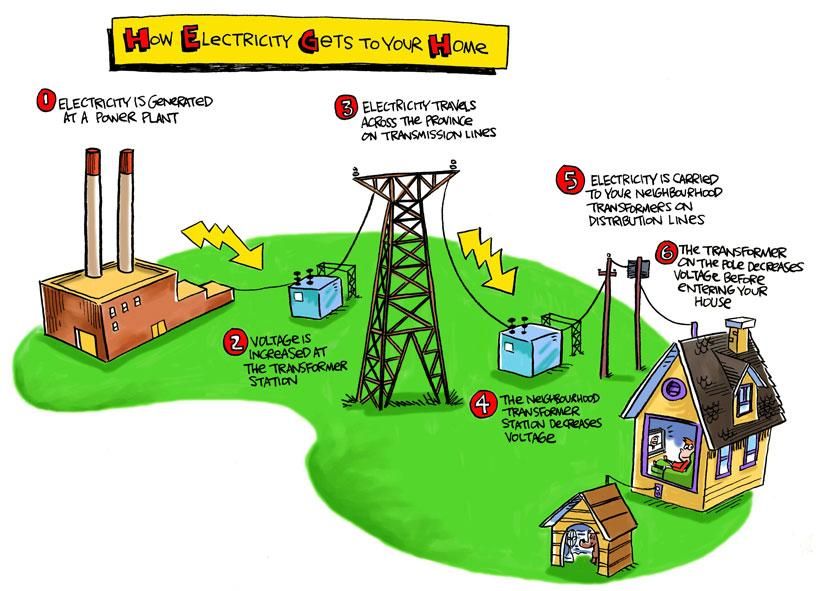
Understanding the Root Causes of Power Outages
Power outages can stem from a variety of sources. Identifying the underlying cause helps estimate the restoration time and understand if you need to contact your utility provider or an electrician.
1. Weather-Related Events
Severe weather is a primary culprit. High winds can topple trees onto power lines, ice storms can weigh down lines causing them to snap, and lightning strikes can directly damage equipment. In 2025, with potentially increased storm frequency and intensity, this becomes an even larger concern. Utility companies often have detailed weather preparedness plans, but restoration after a major storm can still take time.
2. Equipment Failure
Aging infrastructure is a reality. Transformers, power lines, and substations can fail due to wear and tear. Overloaded circuits can also cause transformers to blow. Regular maintenance is crucial, but unexpected failures can still occur. Utility companies often schedule planned outages for equipment upgrades, but these are typically announced in advance.
3. Human Error
Accidents happen. Construction crews digging near underground cables, car accidents involving utility poles, and even vandalism can lead to outages. These events are often unpredictable and require immediate attention from emergency services and utility repair crews.
4. Animal Interference
Believe it or not, animals can cause power outages. Squirrels, birds, and other wildlife can come into contact with electrical equipment, causing short circuits. This is a more common cause than many people realize.
5. Planned Outages
Utility companies sometimes schedule outages for maintenance, repairs, or upgrades to the electrical grid. These outages are usually announced in advance and are typically shorter in duration than unplanned outages.
What Happens If a Power Outage Is Ignored?
Ignoring a power outage isn't really an option, but understanding the potential consequences can motivate prompt action.
- Food spoilage: Refrigerated and frozen food can quickly spoil without power, leading to potential health risks.
- Damage to electronics: Power surges when the electricity returns can damage sensitive electronic devices. Consider using surge protectors.
- Security system failure: If your security system relies on electricity, it may become inoperable during an outage.
- Frozen pipes: In cold weather, pipes can freeze and burst without power to run heating systems.
- Inconvenience and discomfort: Lack of lighting, heating/cooling, and entertainment can make life difficult, especially for vulnerable individuals.
- Safety hazards: Using candles for light can create a fire hazard. Carbon monoxide poisoning is a risk if using generators improperly.
Recommended Fixes and Steps to Take
Here's a breakdown of what you should do when the power goes out:
1. Verify the Outage
Check your breakers and fuses first. A tripped breaker or blown fuse is a common cause of localized power loss. If the problem isn't within your home, check with your neighbors to see if they're also affected. This helps determine the scope of the outage.
2. Contact Your Utility Provider
Report the outage to your electricity company. They can provide updates on the cause and estimated restoration time. Most providers have online outage maps and reporting systems. Save their contact information for easy access.
3. Check Online Outage Maps
Many utility companies maintain online outage maps that show the extent of the outage and estimated restoration times. These maps are often updated in real-time and can provide valuable information.
4. Prepare for an Extended Outage
- Gather flashlights and batteries: Avoid using candles due to the fire risk.
- Charge mobile devices: Use portable chargers or car chargers to keep your phones and tablets powered.
- Preserve food: Keep refrigerator and freezer doors closed as much as possible.
- Stay informed: Monitor local news and weather reports for updates.
- Consider a generator: If you frequently experience outages, a generator can provide backup power. Ensure it's properly installed and operated to avoid carbon monoxide poisoning.
5. Protect Sensitive Electronics
Unplug sensitive electronic devices like computers and televisions to protect them from power surges when the electricity returns. Use surge protectors for devices you can't unplug.
6. If You Suspect a Problem With Your Home's Electrical System
If you've checked the breakers and fuses, and your neighbors have power, the problem might be with your home's electrical system. Call a qualified electrician to inspect and repair the issue. Do not attempt to fix electrical problems yourself unless you are a trained professional.
Cost Estimates and Shop Advice
The cost of resolving a power outage-related issue can vary significantly depending on the cause. Here's a general idea:
- Tripped breaker/blown fuse: No cost if you can reset the breaker or replace the fuse yourself.
- Electrician visit: A service call from an electrician can range from $75 to $200 or more, depending on the location and time of day. Repairs can add significantly to this cost.
- Generator purchase: Portable generators range from a few hundred dollars to several thousand, depending on their size and features.
- Surge protector: High-quality surge protectors cost between $20 and $100 or more.
Shop Advice:
- Get multiple quotes: When hiring an electrician, get quotes from several different companies to ensure you're getting a fair price.
- Check reviews: Read online reviews and ask for references before hiring an electrician.
- Verify licensing and insurance: Make sure the electrician is properly licensed and insured.
- Consider a whole-house surge protector: For comprehensive protection, consider installing a whole-house surge protector at your electrical panel. This can prevent damage from power surges affecting the entire home.
- Regularly inspect your electrical panel: Look for signs of corrosion, loose wires, or other damage. If you see anything suspicious, call an electrician.
Adding Credibility
While specific Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) don't directly address general power outages, utility companies often publish reports and guidelines on grid maintenance and reliability. Look for information from your local provider on their website. Community data and anecdotal evidence suggest that power outages are more frequent in areas with older infrastructure and during extreme weather events. Moreover, many home inspectors report that a significant percentage of homes, especially those over 30 years old, have outdated electrical panels that are more susceptible to problems and potentially contribute to localized power issues.
Understanding the potential causes of power outages, preparing for them, and knowing how to respond can significantly reduce their impact on your life. By staying informed and taking proactive steps, you can navigate power outages with greater confidence in 2025 and beyond.
