When To Use High Beams Vs Low Beams
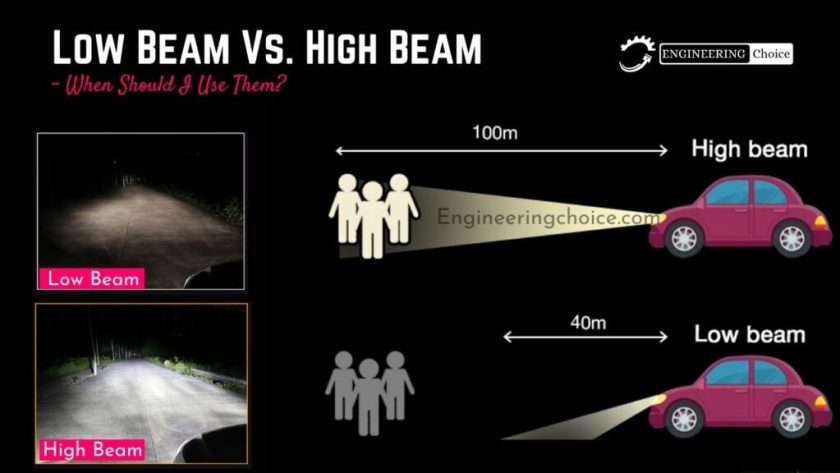
Knowing when to use your high beams (also known as main beams) versus low beams (dipped beams) is a crucial aspect of safe and responsible driving. The basic answer is: use your high beams when driving in dark, open roads with no oncoming traffic and when visibility is significantly reduced. Switch to low beams when approaching oncoming vehicles, driving behind another vehicle, or when driving in well-lit areas.
Why This Matters: Safety and Legality
Understanding the correct use of high and low beams goes beyond simply seeing better. It's about ensuring the safety of yourself and other drivers, and it's often a legal requirement. Using your lights inappropriately can lead to:
- Reduced Visibility for Others: High beams are incredibly bright. Shining them directly into the eyes of another driver can cause temporary blindness, significantly increasing the risk of an accident.
- Accidents: When drivers are blinded or have their vision impaired, the likelihood of collisions rises dramatically.
- Legal Penalties: Many jurisdictions have laws that specifically regulate the use of high beams. Violating these laws can result in fines or other penalties.
- Fatigue and Eye Strain: Continuously adjusting to the glare of improper headlight use from other drivers can cause driver fatigue.
Therefore, mastering the art of headlight etiquette is an essential skill for all drivers, not just new ones. Being aware of the needs of other road users and how to accommodate them is just as important as maintaining your own safety.
How to Choose the Right Beam: A Practical Guide
Choosing between high and low beams boils down to evaluating the surrounding environment and the presence of other vehicles. Here's a breakdown:
When to Use High Beams:
- Dark, Open Roads: This is the primary scenario for using high beams. When you're driving on a rural road, a highway, or any road with limited or no street lighting and no oncoming traffic, high beams provide maximum visibility. Make sure there are no cars ahead of you in your lane, or that you are not approaching any.
- Low Visibility Conditions (with no oncoming traffic): In situations like heavy rain, snow, or fog, high beams *might* seem helpful at first. However, they can reflect off the precipitation or fog, creating a "whiteout" effect and actually reducing your vision. However, in *very light* rain, snow, or fog and NO oncoming traffic, they can be used sparingly and with caution.
- Looking for Road Hazards: Use high beams when you are searching for deer or other animals that may run onto the road.
When to Switch to Low Beams:
- Approaching Oncoming Vehicles: As soon as you see the headlights of an oncoming vehicle, immediately switch to low beams. This prevents you from blinding the other driver. It is common courtesy, and also very smart.
- Driving Behind Another Vehicle: The reflection of your high beams in the rearview mirror of the car in front of you can be incredibly distracting and blinding. Always use low beams when following another vehicle, regardless of how far away they are.
- Driving in Well-Lit Areas: In cities, towns, or on highways with ample street lighting, low beams are sufficient. High beams are generally unnecessary and can be disruptive to other drivers and pedestrians.
- Fog or Heavy Rain (Generally): As mentioned above, high beams can worsen visibility in dense fog or heavy rain. Low beams are usually a better choice, especially when used in conjunction with fog lights (if your vehicle is equipped with them).
- Residential Areas: When driving through residential areas, even if they are not particularly well lit, use low beams to avoid disturbing residents.
Proactive vs. Reactive Switching:
It's important to be proactive in switching between high and low beams. Don't wait until the last second to dim your lights for an approaching vehicle. Anticipate the situation and switch well in advance to give the other driver ample time to adjust. Similarly, be aware of vehicles you are approaching from behind. If you are closing in, dim your lights well before you are directly behind them.
Understanding Automatic High Beam Systems:
Many modern vehicles are equipped with automatic high beam systems. These systems use sensors to detect oncoming vehicles and automatically switch between high and low beams. While convenient, these systems are not foolproof. It's crucial to understand how your vehicle's system works and be prepared to override it manually if necessary. For example, the system might not detect a cyclist with a dim taillight, or it might be slow to react in certain situations. Always remain vigilant and be ready to take control if the automatic system fails to perform as expected.
Real-World Owner Experiences
Many drivers find that the correct use of headlights isn't always intuitive. Some older drivers who learned before many roads were as well lit as they are now, may have to concentrate a little more on switching to low beams in situations where it would be proper. Meanwhile, newer drivers can have a tendency to forget that low beams even exist!
Here are a few anonymized accounts of what people experience in the real world:
- Sarah from Ohio: "I was driving on a rural highway late at night, and I saw a car approaching in the distance. I switched to low beams, but the other driver didn't. Their high beams were blinding! I had to slow down significantly to avoid an accident. It was a scary experience."
- Michael from California: "I live in a suburban area with streetlights, but some drivers still use their high beams. It's so unnecessary and annoying. It makes it harder to see pedestrians and cyclists."
- Emily from Texas: "I recently got a car with automatic high beams, and I love it. However, I've noticed that it sometimes takes a little too long to switch to low beams when a car is approaching. So I'm always ready to manually override it."
- David from Florida: "I think people often forget about bikes and motorcycles. My bike has lights, but they can be harder to see. If you’re driving in the dark, take extra care to look out for those vehicles before turning on your high beams."
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Is it illegal to drive with high beams on in the city?
A: Generally, yes. Most jurisdictions prohibit the use of high beams in well-lit urban areas. Check your local laws for specific regulations.
Q: What are fog lights, and when should I use them?
A: Fog lights are designed to provide improved visibility in fog, heavy rain, or snow. They are typically mounted low on the vehicle to illuminate the road surface below the fog layer. Use them in conjunction with low beams when visibility is significantly reduced due to these conditions.
Q: My high beams aren't working. What could be the problem?
A: Several factors could cause your high beams to malfunction, including a blown fuse, a faulty headlight bulb, or a problem with the headlight switch. Consult your vehicle's owner's manual or take it to a qualified mechanic for diagnosis and repair.
Q: Can I use my high beams if there is a median between me and oncoming traffic?
A: Even with a median, it's generally best to switch to low beams when approaching oncoming traffic. The median might not completely block the glare of your high beams, especially on curved roads or if the median is low.
Q: Are there any situations where using high beams is *required* by law?
A: While it's not generally *required* in the sense of a mandatory "must use" law, there might be situations where using headlights (high or low) is legally mandated due to reduced visibility, such as during nighttime or in inclement weather. Failure to use headlights in these conditions could result in a citation.
By following these guidelines and being mindful of other drivers, you can ensure safer and more pleasant driving experiences for everyone on the road.
