2-way Differential Lock Characteristics And Setup
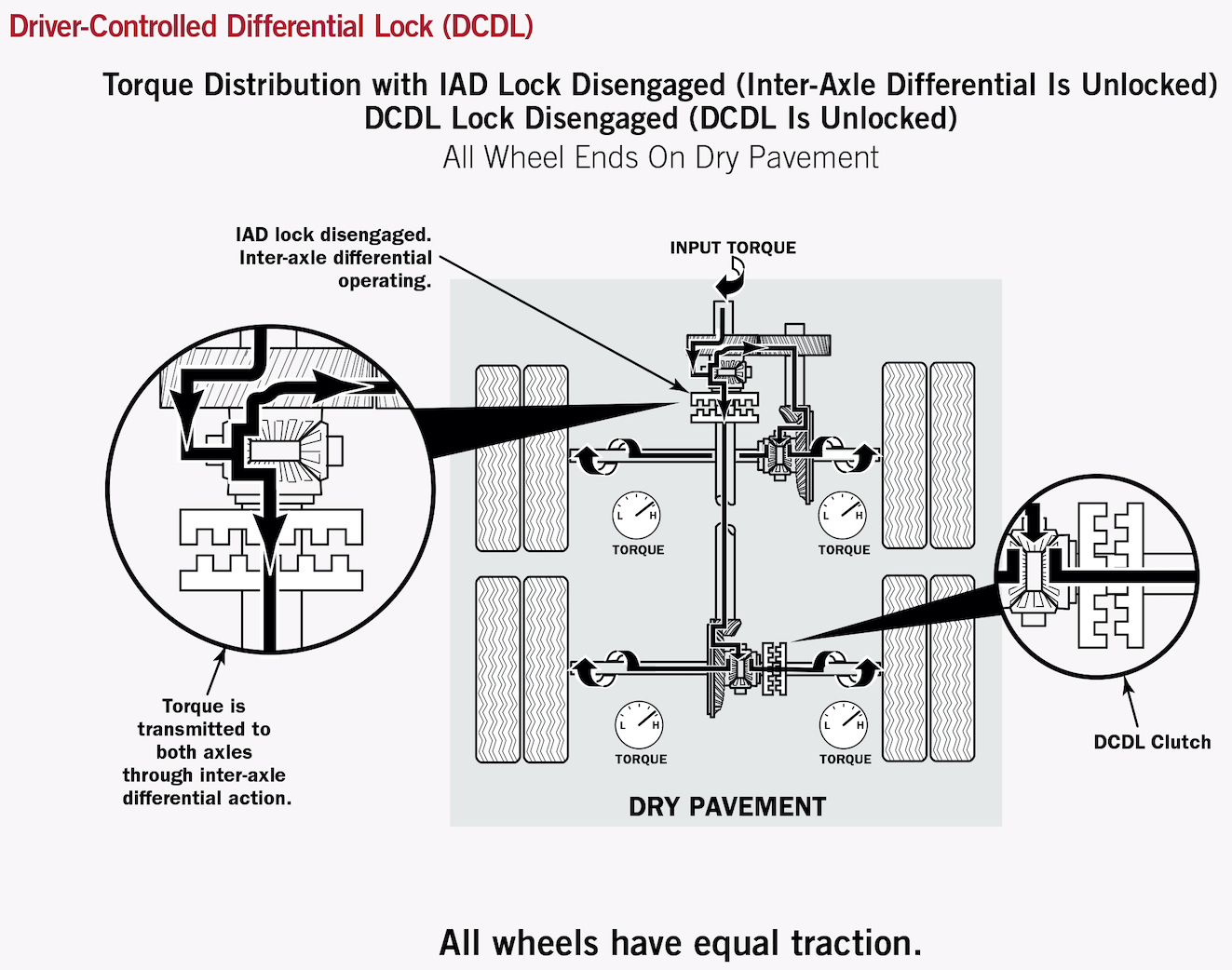
Understanding the intricacies of differential locks can significantly enhance your vehicle's off-road capabilities and overall performance. Among the various types, the 2-way differential lock stands out for its unique characteristics and specific setup requirements. This article delves into the 2-way differential lock, exploring its functionality, benefits, drawbacks, and providing a guide to its proper setup.
What is a 2-Way Differential Lock?
To grasp the concept of a 2-way differential lock, it's crucial to first understand the function of a standard differential. In a conventional vehicle, the differential allows each wheel on an axle to rotate at different speeds. This is essential when cornering, as the outer wheel travels a longer distance than the inner wheel. However, in off-road situations, this can become a liability. If one wheel loses traction (e.g., spinning on ice or mud), the differential will send all the power to that wheel, leaving the wheel with grip motionless.
A differential lock, in general, solves this problem by essentially forcing both wheels on an axle to rotate at the same speed, regardless of traction differences. This ensures that power is distributed equally, even if one wheel is slipping. A 2-way differential lock takes this concept a step further. It locks the differential under both acceleration and deceleration. This is in contrast to a 1-way locker, which typically only locks under acceleration.
In simpler terms, a 2-way locker provides maximum traction and control in a wider range of driving scenarios. It prevents wheel spin during acceleration and enhances braking performance by ensuring both wheels slow down evenly, minimizing the risk of uncontrolled skidding, especially on slippery surfaces.
Characteristics of a 2-Way Differential Lock
Several key characteristics define a 2-way differential lock:
- Full Locking: As mentioned earlier, a 2-way locker fully locks the axle shafts together under both acceleration and deceleration. This provides maximum traction and control.
- Aggressive Behavior: Due to its full locking nature, a 2-way locker can exhibit aggressive behavior, especially on paved roads. Expect some noise and potentially jerky handling during low-speed maneuvers.
- Predictable Handling: While aggressive, the behavior of a 2-way locker is generally predictable once you get used to it. This predictability is crucial for experienced off-road drivers who need precise control.
- Strength and Durability: 2-way lockers are typically built to withstand significant stress and torque, making them suitable for demanding off-road applications.
- Increased Wear: Due to the constant locking and unlocking action, especially if used frequently on paved roads, 2-way lockers can contribute to increased wear on axle shafts, bearings, and other drivetrain components.
Benefits of Using a 2-Way Differential Lock
The benefits of using a 2-way differential lock are numerous, particularly in off-road environments:
- Maximum Traction: The primary benefit is, of course, maximum traction. By ensuring both wheels rotate at the same speed, the 2-way locker prevents wheel spin and allows you to overcome obstacles that would be impossible with a standard differential.
- Enhanced Control: The locked differential provides enhanced control, especially in challenging terrain. This is particularly useful when navigating steep inclines, rocky trails, or slippery surfaces.
- Improved Braking Performance: Under deceleration, the 2-way locker ensures even braking force distribution, reducing the risk of wheel lockup and skidding. This is particularly advantageous on loose surfaces like gravel or snow.
- Increased Confidence: Knowing that you have maximum traction and control can significantly boost your confidence when tackling difficult trails.
Drawbacks of Using a 2-Way Differential Lock
Despite the benefits, there are also drawbacks to consider:
- On-Road Handling: The aggressive locking behavior can make on-road driving uncomfortable, especially at low speeds. Expect some noise, vibration, and potential wheel hop during turns.
- Increased Wear and Tear: The constant locking and unlocking can put extra stress on drivetrain components, leading to increased wear and tear.
- Potential for Damage: If not used properly, a 2-way locker can potentially damage axle shafts or other drivetrain components. It's crucial to understand its limitations and use it judiciously.
- Skill Requirement: Operating a vehicle with a 2-way locker effectively requires a certain level of skill and experience. Novice drivers may find it challenging to control.
- Cost: 2-way lockers are generally more expensive than other types of differential modifications.
Setting Up a 2-Way Differential Lock
The setup of a 2-way differential lock is a critical process that should be performed by a qualified mechanic. Improper installation can lead to serious damage to the differential and surrounding components. Here's a general overview of the steps involved:
- Preparation: Gather all necessary tools and parts, including the 2-way locker, new bearings (if recommended), shims, gear oil, and sealant. Ensure the vehicle is safely supported and the differential is accessible.
- Disassembly: Carefully disassemble the differential, removing the axles, carrier, and ring gear. Clean all components thoroughly and inspect them for wear or damage.
- Installation of the Locker: Install the 2-way locker into the differential carrier, following the manufacturer's instructions precisely. This may involve pressing on new bearings and setting the proper backlash.
- Ring Gear Installation: Install the ring gear onto the carrier, ensuring it is properly torqued to the manufacturer's specifications.
- Carrier Installation: Install the carrier back into the differential housing, using shims to achieve the correct pinion depth and backlash. This is a critical step that requires precision and careful measurement.
- Axle Installation: Reinstall the axles, ensuring they are properly seated and secured.
- Final Assembly: Replace the differential cover with a new gasket or sealant. Fill the differential with the appropriate gear oil to the correct level.
- Testing: After installation, carefully test the 2-way locker in a safe environment, starting with low-speed maneuvers. Listen for any unusual noises or vibrations.
Important Considerations During Setup:
- Backlash: Backlash refers to the amount of play between the ring gear and pinion gear. Proper backlash is crucial for smooth and quiet operation.
- Pinion Depth: Pinion depth refers to the distance between the pinion gear and the ring gear. Incorrect pinion depth can lead to premature wear and noise.
- Bearing Preload: Bearing preload is the amount of force applied to the bearings. Proper preload ensures that the bearings operate smoothly and efficiently.
- Torque Specifications: Always adhere to the manufacturer's torque specifications when tightening bolts and nuts. Overtightening can damage components, while undertightening can lead to loosening and failure.
Alternatives to 2-Way Differential Locks
While 2-way differential locks offer excellent traction, they may not be suitable for all drivers or vehicles. Several alternatives offer different levels of performance and suitability:
- Automatic Lockers (Lunchbox Lockers): These are more affordable and easier to install than 2-way lockers. They automatically lock the differential when wheel spin is detected, but can be less predictable than 2-way lockers.
- Limited Slip Differentials (LSDs): LSDs offer a compromise between a standard differential and a full locker. They allow some differential action but also provide some resistance to wheel spin. They are generally smoother and quieter than lockers on paved roads.
- Air Lockers: These use compressed air to engage and disengage the locking mechanism. They offer the convenience of on-demand locking and unlocking, but require an onboard air compressor.
- Electronic Lockers: These use electronic sensors and actuators to engage and disengage the locking mechanism. They offer similar benefits to air lockers but may be more reliable.
Conclusion
The 2-way differential lock is a powerful tool for enhancing off-road performance, providing maximum traction and control in challenging conditions. However, its aggressive behavior and potential for increased wear and tear make it essential to understand its characteristics and limitations. Proper setup is crucial for ensuring safe and reliable operation. If you're considering a 2-way locker, carefully weigh the benefits and drawbacks, and consult with a qualified mechanic to determine if it's the right choice for your vehicle and driving style. Remember, experience and skill are key to effectively utilizing this type of differential modification.
