1993 Nissan 240sx Fuse Box Diagram
The 1993 Nissan 240SX, a darling of the tuning and drifting communities, is a relatively simple machine compared to modern vehicles. However, understanding its electrical system is crucial for maintenance, modification, and troubleshooting. At the heart of this system lies the fuse box, a critical component that protects the car's electrical circuits from overcurrents and potential damage. This guide will delve into the intricacies of the 1993 Nissan 240SX fuse box diagram, offering a comprehensive overview for enthusiasts and aspiring automotive engineers alike.
Understanding Fuse Box Basics
Before diving into the specifics of the 240SX, let's establish a foundational understanding of fuse boxes in general. A fuse box is essentially a central distribution point for electrical power. It houses multiple fuses, each protecting a specific circuit or component. Fuses are sacrificial devices designed to break an electrical circuit if the current exceeds a safe level. This prevents damage to wiring, components, and potentially even prevents fires.
Fuses typically consist of a thin metal strip enclosed within a non-conductive housing. When the current flowing through the circuit becomes too high, the metal strip melts, breaking the circuit and stopping the flow of electricity. The amperage rating of a fuse indicates the maximum current it can handle before blowing.
Using the correct amperage fuse is absolutely critical. Replacing a blown fuse with one of a higher amperage can be extremely dangerous, as it bypasses the intended protection and could lead to overheating and potentially a fire. Conversely, using a fuse with a lower amperage will likely cause it to blow prematurely, interrupting the circuit unnecessarily.
Locating the Fuse Boxes in a 1993 240SX
The 1993 240SX has two primary fuse box locations:
The Interior Fuse Box
The main fuse box is located inside the cabin, typically under the driver's side dashboard, near the steering column. You might need to remove a small access panel or trim piece to expose it. This fuse box primarily controls circuits related to interior components, such as the lights, wipers, radio, and power windows.
The Engine Bay Fuse Box
A secondary fuse box is located in the engine bay, usually near the battery or on the inner fender. This fuse box handles circuits for critical engine components, such as the fuel pump, ignition system, cooling fan, and engine control unit (ECU).
Decoding the Fuse Box Diagram
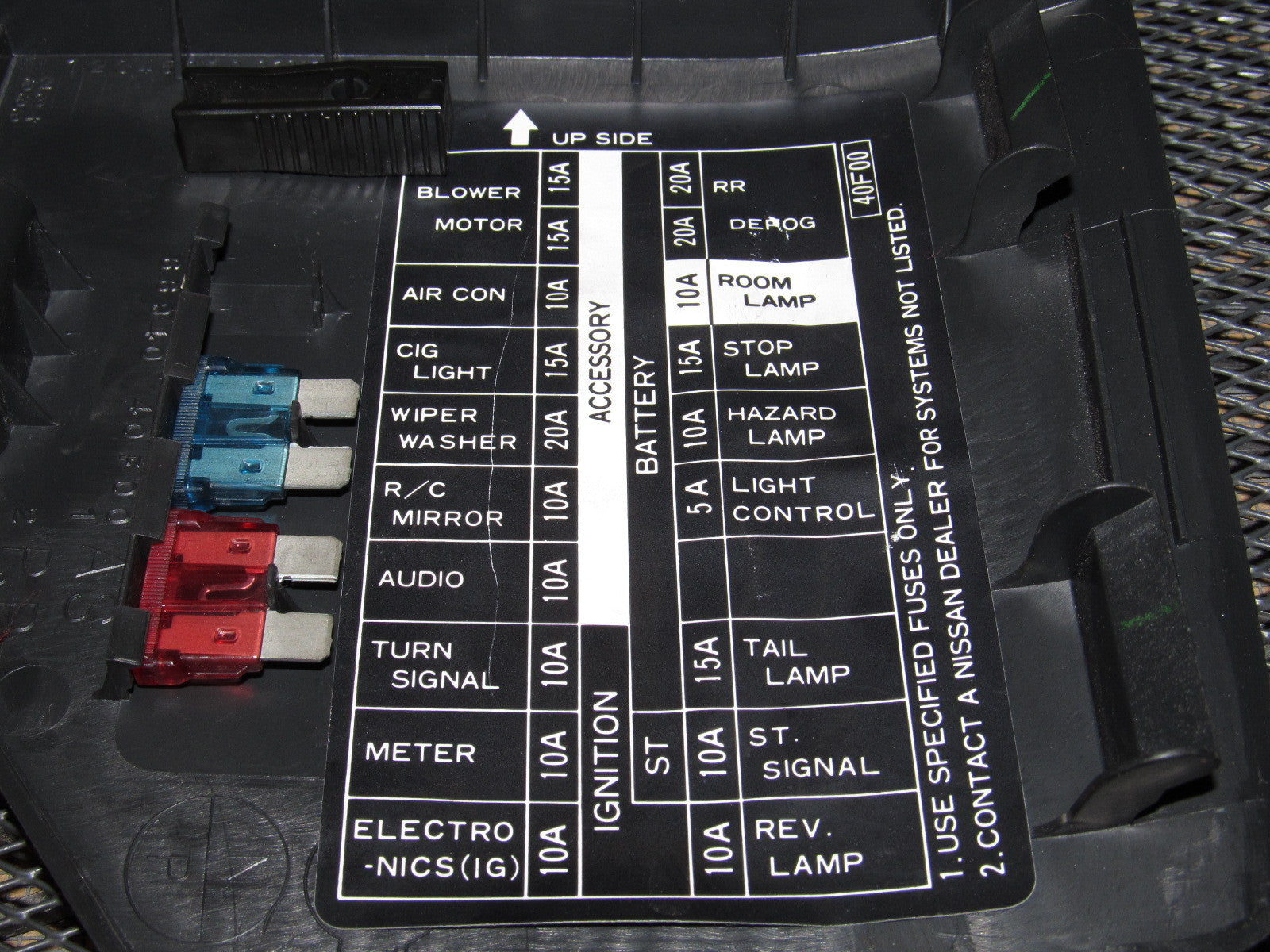
Each fuse box has a diagram, either printed directly on the cover or found on a separate label inside the cover. This diagram is essential for identifying the fuse associated with a specific circuit. The diagram typically uses symbols or abbreviations to represent different components.
Here's a breakdown of what you might typically find on a 1993 240SX fuse box diagram:
- Fuse Number: A numerical identifier for each fuse.
- Amperage Rating: The maximum current (in amps) that the fuse can handle before blowing. This is usually indicated by a number followed by the letter "A" (e.g., 10A, 15A, 20A).
- Circuit Description: A brief description of the component or circuit protected by the fuse (e.g., "Headlights," "Fuel Pump," "Turn Signals"). Abbreviations are common.
- Symbol (Sometimes): In some cases, a symbol is used to visually represent the component (e.g., a lightbulb for headlights).
Example Diagram Interpretation: Let's say the diagram shows "Fuse #7: 15A - Wipers." This means that fuse number 7, rated at 15 amps, protects the windshield wiper circuit. If your wipers stop working, this is the first fuse you should check.
Common Fuses and Their Functions
Here's a rundown of some of the common fuses you'll find in a 1993 240SX and their associated functions:
Interior Fuse Box (Example):
- Room Lamp: Powers the interior dome light.
- Headlight: Protects the headlight circuit (separate fuses for high and low beams might exist).
- Tail Lamp: Protects the tail lights and brake lights.
- Turn Signal: Protects the turn signal system.
- Wiper: Protects the windshield wiper motor.
- Radio: Powers the radio and audio system.
- Hazard: Protects the hazard lights.
- A/C: Powers the air conditioning system.
- Power Windows: Powers the power windows.
- Power Locks: Powers the power door locks.
Engine Bay Fuse Box (Example):
- Fuel Pump: Powers the fuel pump, which delivers fuel to the engine.
- Ignition: Protects the ignition system, which provides the spark to ignite the fuel-air mixture.
- ECU: Powers the engine control unit (ECU), the computer that manages engine functions.
- Cooling Fan: Powers the radiator cooling fan, which prevents the engine from overheating.
- Starter: Protects the starter motor circuit.
- ABS: If equipped, protects the anti-lock braking system.
- EGI: Engine Gas Injection system, this often ties into the fuel and ignition systems.
Important Note: Fuse layouts can vary slightly depending on the specific trim level and options of your 240SX. Always refer to the diagram that specifically matches your vehicle.
Troubleshooting Electrical Problems Using the Fuse Box
The fuse box is an invaluable tool for diagnosing electrical problems. If a particular component stops working, checking the corresponding fuse should be your first step.
Procedure:
- Consult the Fuse Diagram: Identify the fuse associated with the non-functional component.
- Locate the Fuse: Find the fuse in the appropriate fuse box (interior or engine bay).
- Visually Inspect the Fuse: Remove the fuse and hold it up to the light. Look for a break in the metal strip inside the fuse. A blown fuse will have a clearly visible gap.
- Test the Fuse (Optional): For more certainty, you can use a multimeter to test the fuse for continuity. Set the multimeter to the continuity setting (often indicated by a diode symbol or a sound when the probes are connected). Touch the probes to the metal contacts on either side of the fuse. If the multimeter shows continuity (or beeps), the fuse is good. If there is no continuity, the fuse is blown.
- Replace the Fuse: If the fuse is blown, replace it with a new fuse of the exact same amperage rating.
- Test the Component: After replacing the fuse, test the component to see if it is now working.
What if the Fuse Keeps Blowing?
If the new fuse blows immediately or shortly after being replaced, it indicates a short circuit or an overload in the circuit. This means there is a fault somewhere in the wiring or in the component itself. Do not simply keep replacing the fuse with a higher amperage one. This is a fire hazard. Instead, you'll need to investigate the circuit to find the cause of the short.
Possible causes of a short circuit include:
- Damaged wiring (e.g., frayed insulation, exposed wires).
- A faulty component (e.g., a shorted motor, a malfunctioning sensor).
- A loose connection.
Tracing short circuits can be a complex process, often requiring a multimeter, wiring diagrams, and a systematic approach. It's often best left to experienced mechanics or automotive electricians.
Modifications and Fuse Box Considerations
Many 240SX owners modify their cars, adding aftermarket components such as amplifiers, upgraded lighting, and performance parts. These modifications often require additional electrical circuits, which must be properly fused to protect the system.
When adding new circuits, it's crucial to:
- Calculate the current draw: Determine the maximum current that the new component will draw.
- Choose the correct fuse size: Select a fuse with an amperage rating slightly higher than the calculated current draw (typically 125% of the expected load).
- Use proper wiring and connectors: Ensure that the wiring and connectors are appropriately sized for the current and are properly installed.
- Add a dedicated fuse: Never tap into existing circuits to power new components. This can overload the existing circuit and cause problems. Instead, add a dedicated fuse and wiring run directly from the battery or a suitable power distribution point.
Properly fusing aftermarket components is essential for safety and reliability. It protects your car's electrical system from damage and reduces the risk of fire.
Conclusion
The fuse box is a vital component of the 1993 Nissan 240SX's electrical system. Understanding its layout, function, and troubleshooting techniques is crucial for maintaining and modifying your vehicle. By following the guidelines outlined in this article, you can effectively diagnose electrical problems, ensure proper protection for your car's circuits, and safely add aftermarket components. Always prioritize safety and consult a qualified professional when dealing with complex electrical issues.
