2000 Nissan Frontier Catalytic Converter
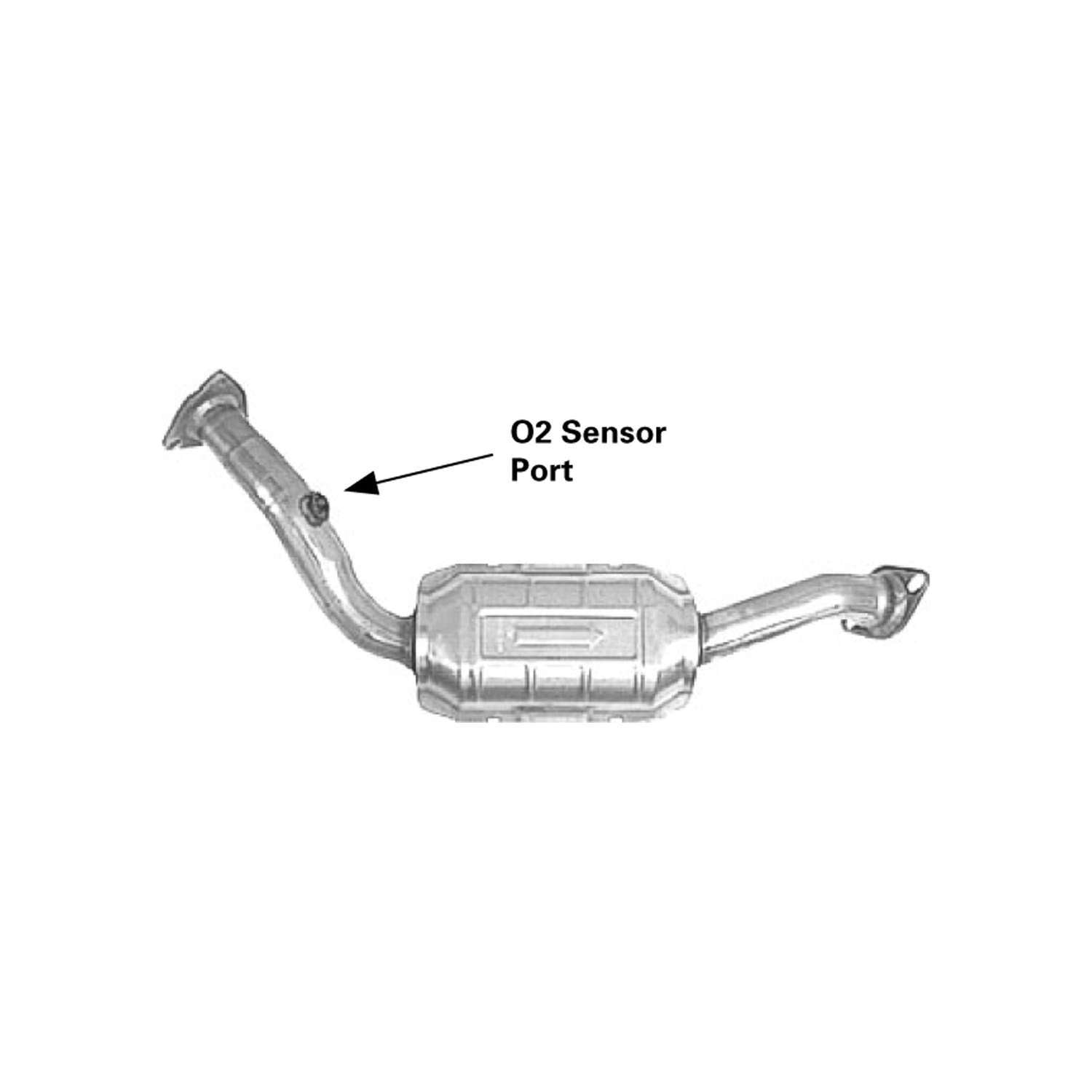
So, you're here because you're likely dealing with a catalytic converter issue on your 2000 Nissan Frontier. Don't worry, you're not alone! It's a common problem on vehicles of that age. The good news is, we can walk you through what's probably going on and what your options are.
The Case of the Failing Catalytic Converter: Why It Happens
A catalytic converter is a crucial part of your Frontier's exhaust system. Its job is to reduce harmful emissions from your engine – things like hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen oxides – into less harmful substances like carbon dioxide, water, and nitrogen. It does this through a chemical process using precious metals (platinum, palladium, and rhodium) as catalysts.
But over time, a few things can cause it to fail:
- Age and Wear: Like any other part, the catalyst materials degrade over time with heat and use.
- Contamination: This is a big one. Contamination from engine oil leaks, coolant leaks, or excessive fuel entering the exhaust system can "poison" the catalytic converter, rendering it ineffective. Even a small amount of antifreeze getting into the exhaust can ruin a catalytic converter.
- Physical Damage: Hitting a large object on the road can physically damage the converter.
- Engine Problems: Underlying engine issues like misfires or rich-running conditions can cause the converter to overheat and fail prematurely. Misfires dump unburnt fuel into the exhaust, which burns in the converter causing excessive heat.
Recognizing the Symptoms: Is it *Really* the Catalytic Converter?
Before you rush out to replace the catalytic converter, it's important to be sure that's actually the problem. Here are some common symptoms:
- Check Engine Light: This is often the first sign. The specific code you'll likely see is P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold Bank 1). Sometimes, you might see P0430 if you have two converters and the second one is the culprit. However, always get the codes read with a scan tool to confirm. A generic code reader is fine for this.
- Poor Engine Performance: You might notice a decrease in acceleration, reduced fuel economy, or a generally sluggish feeling when driving. This is because a clogged converter restricts exhaust flow, choking the engine.
- Rattling Noise: If the internal components of the converter break down, they can rattle around inside the housing. This will usually sound like loose gravel inside a metal can.
- Smell of Rotten Eggs: This distinct sulfurous odor is a sign that the catalytic converter is not properly converting hydrogen sulfide. It's not always present, but if you smell it, it's a strong indicator of a converter problem.
- Failed Emissions Test: If your Frontier fails an emissions test, the catalytic converter is a prime suspect.
Important: Just because you have a P0420 code doesn't automatically mean the catalytic converter is bad. It just means the oxygen sensors downstream of the converter are detecting that it's not working efficiently. Other issues, like exhaust leaks or faulty oxygen sensors, can also trigger this code. That's why proper diagnosis is key!
Diagnosis: Finding the Real Culprit
Here’s a breakdown of diagnostic steps you or your mechanic should take:
- Read the OBD-II Codes: Use a scan tool to confirm the P0420 (or P0430) code and check for any other related codes (e.g., misfire codes, oxygen sensor codes). Write them all down!
- Inspect for Exhaust Leaks: Carefully inspect the entire exhaust system, especially around the catalytic converter, for any signs of leaks. Even a small leak can affect the readings of the oxygen sensors and trigger the P0420 code. Look for soot deposits or listen for hissing noises.
- Check Oxygen Sensors: There are typically two oxygen sensors associated with the catalytic converter – one upstream (before) and one downstream (after). Test the performance of these sensors using a scan tool that can display live data. The upstream sensor should fluctuate rapidly, while the downstream sensor should have a more stable reading. If the downstream sensor reading mirrors the upstream sensor, it could indicate a faulty converter. You can also use a multimeter to check the sensor resistance.
- Visual Inspection of the Converter: Check the catalytic converter for any physical damage, such as dents or cracks. If possible, you can also try tapping on the converter with a rubber mallet. If you hear rattling, the internal components are likely damaged.
- Backpressure Test: A clogged catalytic converter restricts exhaust flow. A backpressure test measures the pressure in the exhaust system before the converter. Excessive backpressure indicates a blockage. This usually requires a special adapter that screws into an oxygen sensor port.
- Consider a "Catalytic Converter Cleaner": These fuel additives *sometimes* can help clean deposits from the catalyst material. However, they are often a temporary fix, and if the converter is truly damaged, they won't work. Think of it as a long shot, but if you’re on a tight budget it might be worth a try. Follow the product instructions carefully.
The Solution: Replacing the Catalytic Converter
If, after thorough diagnosis, you've determined that the catalytic converter is indeed the problem, replacement is the most likely solution. Here’s what you need to know:
Tools You'll Need:
- Socket Set and Wrenches: Metric sizes, including a deep socket for oxygen sensors.
- Penetrating Oil: Essential for loosening rusted bolts. Apply generously and let it soak for a while.
- Oxygen Sensor Socket: This specialized socket allows you to remove and install oxygen sensors without damaging them.
- Jack and Jack Stands: For safely lifting and supporting the vehicle. Safety first!
- Hammer and Chisel (Possibly): For stubborn bolts or rusted flanges.
- Gasket Scraper: To clean the mating surfaces of the exhaust flanges.
- New Gaskets and Hardware: Always replace the gaskets and hardware when replacing a catalytic converter.
- Safety Glasses and Gloves: To protect yourself from debris and hot exhaust components.
Replacement Steps (General Guide – Consult a Service Manual for Specifics):
- Disconnect the Negative Battery Cable: To prevent electrical shorts.
- Raise and Secure the Vehicle: Using a jack and jack stands. Make sure the vehicle is stable.
- Locate the Catalytic Converter: Follow the exhaust pipe from the engine to find it.
- Remove the Oxygen Sensors: Disconnect the electrical connectors and use the oxygen sensor socket to unscrew the sensors.
- Loosen the Exhaust Flange Bolts: Use penetrating oil and appropriate wrenches to loosen the bolts connecting the catalytic converter to the exhaust system. These bolts are often rusted and difficult to remove. Be patient!
- Remove the Old Catalytic Converter: Carefully remove the old converter. Be prepared for it to be heavy.
- Clean the Mating Surfaces: Use a gasket scraper to clean the exhaust flanges where the new converter will be installed.
- Install the New Catalytic Converter: Install the new gaskets and hardware. Torque the bolts to the manufacturer's specifications.
- Install the Oxygen Sensors: Reinstall the oxygen sensors. Make sure the electrical connectors are securely attached.
- Lower the Vehicle: Carefully lower the vehicle back to the ground.
- Reconnect the Negative Battery Cable:
- Clear the OBD-II Codes: Use a scan tool to clear the P0420 (or P0430) code.
- Test Drive the Vehicle: Monitor the engine performance and check for any leaks.
Important Considerations When Choosing a New Catalytic Converter:
- Direct-Fit vs. Universal: Direct-fit converters are designed specifically for your 2000 Nissan Frontier, making installation easier. Universal converters require some cutting and welding to fit. While universal converters can be cheaper, unless you're skilled at welding, a direct-fit converter is often the better choice.
- California (CARB) Compliant: If you live in California or a state that follows California emissions standards, you'll need to purchase a CARB-compliant catalytic converter. These converters are more expensive but meet the stricter emissions regulations.
- Aftermarket vs. OEM: OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) catalytic converters are typically the most expensive but are often considered the highest quality. Aftermarket converters can be a more affordable option, but quality can vary. Read reviews and choose a reputable brand.
Cost Breakdown: What to Expect
The cost of replacing a catalytic converter on your 2000 Nissan Frontier can vary depending on several factors:
- Type of Converter: Direct-fit, universal, CARB-compliant, OEM, aftermarket – all these factors influence the price.
- Labor Costs: If you're having a mechanic do the work, labor costs will add to the total. Labor rates vary by location and shop.
- Shop vs. DIY: Doing the job yourself can save you money on labor, but it requires the right tools, knowledge, and safety precautions.
Here's a rough estimate:
- Catalytic Converter (Aftermarket, Direct-Fit): $200 - $500
- Catalytic Converter (CARB Compliant): $400 - $800+
- Labor (if applicable): $100 - $300 (This can vary significantly)
- Oxygen Sensors (if needed): $50 - $150 each
- Gaskets and Hardware: $20 - $50
Total Estimated Cost (Professional Installation): $350 - $1150+ (Depending on parts and labor)
DIY Tip: If you're considering doing it yourself, watch some videos of catalytic converter replacements on similar vehicles. This will give you a better idea of what's involved.
Prevention: Keeping Your Converter Healthy
While catalytic converters eventually wear out, you can take steps to prolong their lifespan:
- Regular Engine Maintenance: Keep your engine properly tuned and address any issues promptly. This includes things like changing the oil regularly, replacing spark plugs, and fixing any leaks.
- Avoid Short Trips: Short trips don't allow the catalytic converter to reach its optimal operating temperature, which can lead to carbon buildup.
- Use Quality Fuel: Using high-quality fuel can help prevent deposits from forming in the exhaust system.
- Address Oil Leaks: Fix any oil leaks promptly. Even a small oil leak can contaminate the catalytic converter.
Replacing a catalytic converter can seem daunting, but with a proper diagnosis, the right tools, and some patience, it's a job that many DIYers can tackle. If you're not comfortable working on your exhaust system, don't hesitate to take it to a qualified mechanic. Good luck!
