2004 Nissan Maxima Cadillac Converter
If you own a 2004 Nissan Maxima, you might, at some point, encounter issues with your catalytic converter. This vital component is responsible for reducing harmful emissions from your vehicle's exhaust system. Understanding the function of a catalytic converter, common problems, and replacement options is crucial for maintaining your Maxima's performance and complying with environmental regulations. This article provides a comprehensive guide to the catalytic converter in your 2004 Nissan Maxima, including troubleshooting, replacement, and related maintenance.
Understanding the Catalytic Converter
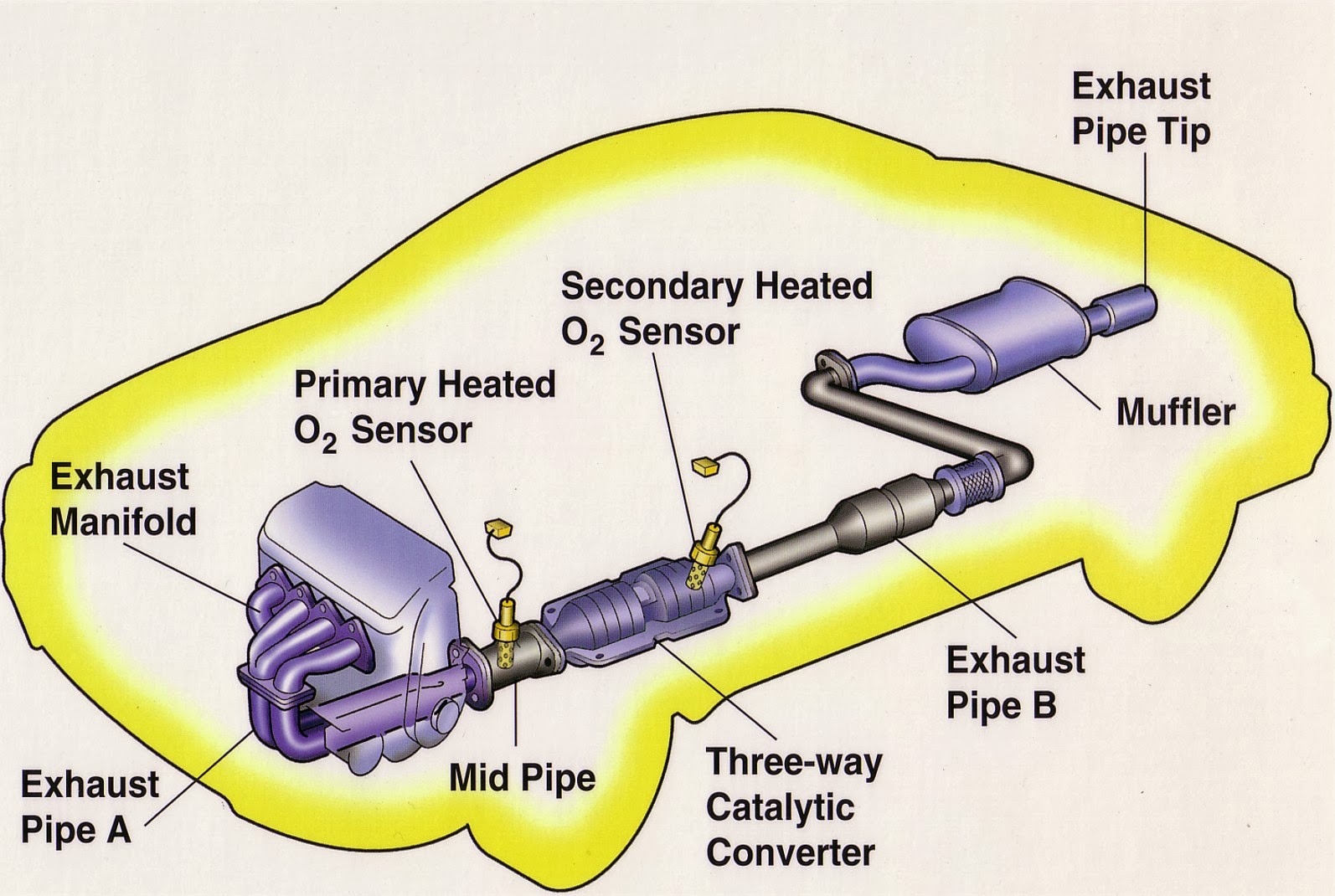
The catalytic converter is a key part of your car's emission control system. Its primary function is to convert harmful pollutants like carbon monoxide (CO), hydrocarbons (HC), and nitrogen oxides (NOx) into less harmful substances, such as carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O), and nitrogen (N2). Inside the converter, precious metals like platinum, palladium, and rhodium act as catalysts to speed up these chemical reactions.
Without a properly functioning catalytic converter, your vehicle's emissions will exceed legal limits, and you may fail emissions tests. Additionally, a failing converter can negatively impact your engine's performance and fuel efficiency.
How the Catalytic Converter Works in a 2004 Nissan Maxima
In a 2004 Nissan Maxima, the exhaust gases from the engine flow into the catalytic converter. The converter's honeycomb structure, coated with the catalyst metals, maximizes the surface area for the chemical reactions to occur. As the hot exhaust gases pass through this structure, the catalysts facilitate the conversion of harmful pollutants into less harmful substances.
The efficiency of the catalytic converter depends on several factors, including its operating temperature, the composition of the exhaust gases, and the presence of any contaminants that might poison the catalysts. Maintaining your engine properly, using the correct fuel, and addressing any underlying engine problems are essential for ensuring the longevity and effectiveness of your catalytic converter.
Common Symptoms of a Failing Catalytic Converter in a 2004 Nissan Maxima
Recognizing the symptoms of a failing catalytic converter early can save you money and prevent further damage to your vehicle. Here are some common signs to watch out for:
- Decreased Engine Performance: A clogged or damaged catalytic converter can restrict exhaust flow, leading to a noticeable reduction in engine power and acceleration. You might feel sluggishness, especially when trying to accelerate quickly.
- Poor Fuel Economy: A failing catalytic converter can disrupt the air-fuel mixture, causing the engine to consume more fuel than usual. Keep an eye on your MPG; a significant drop could indicate a problem.
- Check Engine Light: This is often the first sign of a problem. Diagnostic codes related to the catalytic converter, such as P0420 ("Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold"), are common. A mechanic can read these codes using an OBD-II scanner.
- Rattling Noise: If the internal components of the catalytic converter become damaged or broken, they can rattle around inside the converter housing, producing a distinct noise. This is usually a sign of physical damage.
- Sulfur Smell (Rotten Eggs): A failing catalytic converter can sometimes produce a sulfur-like smell, similar to rotten eggs. This is caused by the converter's inability to properly process sulfur compounds in the exhaust.
- Overheating: A plugged catalytic converter can cause excessive heat buildup in the exhaust system. This heat can damage other components and even pose a fire risk.
- Failed Emissions Test: This is a definite sign that the converter isn't functioning properly. Even if your car seems to be running fine, it may still fail the test due to excessive emissions.
Diagnosing a Catalytic Converter Issue
If you suspect that your 2004 Nissan Maxima's catalytic converter is failing, it's important to get it diagnosed properly. A qualified mechanic can perform a thorough inspection and pinpoint the exact cause of the problem. Here are some common diagnostic steps:
- OBD-II Scan: The mechanic will use an OBD-II scanner to read any diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) stored in the vehicle's computer. Common codes related to the catalytic converter include P0420, P0421, P0422, and P0430.
- Visual Inspection: The mechanic will visually inspect the catalytic converter for any signs of damage, such as dents, cracks, or rust. They'll also check the exhaust system for leaks or other issues that could affect the converter's performance.
- Exhaust Backpressure Test: This test measures the pressure in the exhaust system before the catalytic converter. High backpressure can indicate a clogged converter.
- Oxygen Sensor Testing: Oxygen sensors play a crucial role in monitoring the catalytic converter's performance. The mechanic may test the oxygen sensors to ensure they are functioning correctly and providing accurate readings.
- Temperature Readings: Using an infrared thermometer, the mechanic can compare the temperature before and after the catalytic converter. A properly functioning converter should show a significant increase in temperature after the converter.
2004 Nissan Maxima Catalytic Converter Replacement
If the diagnosis confirms that your 2004 Nissan Maxima's catalytic converter needs to be replaced, you'll have several options:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) Catalytic Converter
This is the exact same part that came with your car from the factory. OEM converters are typically the most expensive option, but they offer the best performance and longevity. They are designed to meet or exceed all emissions standards.
Pros: Guaranteed fit and performance, meets all emissions standards, typically the most durable option.
Cons: Most expensive.
Aftermarket Catalytic Converter
Aftermarket converters are manufactured by companies other than Nissan. They are generally less expensive than OEM converters, but the quality and performance can vary significantly. It's crucial to choose a reputable brand that meets EPA standards.
Pros: More affordable than OEM converters.
Cons: Quality and performance can vary, may not meet all emissions standards in some states (especially California). Careful research is crucial.
High-Flow Catalytic Converter
These converters are designed to improve exhaust flow and increase horsepower. They are often used in performance vehicles, but may not be legal for street use in all areas. Check your local emissions regulations before installing a high-flow converter. Generally, they will not meet emission standards required for a 2004 Nissan Maxima and will cause the car to fail an emissions test.
Pros: Improved exhaust flow and potentially increased horsepower.
Cons: May not be legal for street use in all areas, may not meet emissions standards, and can trigger Check Engine Light.
Installation
Catalytic converter replacement can be a relatively straightforward process, but it's often best left to a qualified mechanic. The job typically involves removing the old converter, installing the new one, and connecting the necessary sensors and exhaust pipes. Ensure that all connections are properly sealed to prevent exhaust leaks.
Important Considerations:
- California Emissions Standards: If you live in California or another state that follows California emissions standards, you'll need to ensure that the replacement catalytic converter is CARB (California Air Resources Board) compliant. CARB-compliant converters are specifically designed to meet California's strict emissions requirements.
- Warranty: Check the warranty on the replacement catalytic converter. A longer warranty can provide peace of mind and protect you against defects or premature failure.
- Professional Installation: While it's possible to replace the catalytic converter yourself, a professional mechanic can ensure that the job is done correctly and that all emissions standards are met.
Preventing Catalytic Converter Failure
While catalytic converters are designed to last for many years, several factors can contribute to their premature failure. Here are some tips to help prevent catalytic converter problems in your 2004 Nissan Maxima:
- Regular Maintenance: Follow the recommended maintenance schedule for your vehicle, including oil changes, spark plug replacements, and air filter replacements. Proper engine maintenance helps prevent excessive oil consumption and other issues that can damage the catalytic converter.
- Use Quality Fuel: Use the recommended fuel grade for your 2004 Nissan Maxima (usually regular unleaded). Avoid using fuels with high levels of lead or other contaminants, as these can poison the catalyst in the converter.
- Address Engine Problems Promptly: If you notice any engine problems, such as misfires, rough idling, or excessive oil consumption, get them fixed as soon as possible. These issues can overload the catalytic converter and lead to premature failure.
- Avoid Short Trips: Short trips don't allow the catalytic converter to reach its optimal operating temperature, which can reduce its efficiency and lifespan. Try to combine errands and take longer trips when possible.
- Don't Ignore the Check Engine Light: If the Check Engine Light comes on, don't ignore it. Have the code read and address the underlying problem as soon as possible. A seemingly minor issue could be damaging the catalytic converter.
Conclusion
A healthy catalytic converter is essential for the performance, emissions compliance, and overall longevity of your 2004 Nissan Maxima. By understanding the function of the catalytic converter, recognizing the symptoms of a failing converter, and following the preventative maintenance tips outlined in this article, you can keep your Maxima running smoothly and protect the environment.
Remember to choose a reputable brand for replacement parts and seek professional assistance if you're unsure about any aspect of the diagnosis or replacement process. Keeping your car properly maintained is key to avoiding expensive repairs down the road.
