2005 Nissan Frontier Crankshaft Position Sensor Problems
The 2005 Nissan Frontier, while generally a reliable truck, isn't immune to common automotive ailments. One persistent issue that DIY mechanics and experienced owners often encounter is related to the Crankshaft Position Sensor (CKPS). This article delves into the problems associated with the CKPS in 2005 Frontiers, providing detailed information to help you diagnose, troubleshoot, and potentially resolve these issues yourself.
What is the Crankshaft Position Sensor?
Before we dive into the problems, let's establish a clear understanding of what the CKPS does. Simply put, it's a sensor that monitors the position and rotational speed of the crankshaft. The crankshaft, the heart of your engine, converts the reciprocating motion of the pistons into rotational motion that ultimately drives the wheels. The CKPS sends this critical information to the Engine Control Module (ECM), also known as the engine computer. The ECM uses this data, along with information from other sensors like the Camshaft Position Sensor (CMP), to precisely control fuel injection timing, ignition timing, and other vital engine functions.
There are typically two types of CKPS: magnetic reluctance sensors (also known as variable reluctance sensors or VRS) and Hall-effect sensors. Magnetic reluctance sensors generate a voltage signal based on changes in the magnetic field as a toothed wheel (reluctor ring) attached to the crankshaft rotates past the sensor. Hall-effect sensors, on the other hand, use a semiconductor material that produces a voltage when exposed to a magnetic field. These sensors usually require a power supply to operate. The 2005 Frontier typically uses a magnetic reluctance sensor, but it's always best to confirm based on your specific engine and part number.
Common Symptoms of a Faulty CKPS on a 2005 Frontier
A failing or failed CKPS can manifest in a variety of ways. Recognizing these symptoms is the first step in diagnosing the problem:
- Check Engine Light (CEL) Illumination: This is often the first and most obvious sign. The ECM detects inconsistencies or a lack of signal from the CKPS and triggers the CEL. Common diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) associated with the CKPS include P0335 (Crankshaft Position Sensor "A" Circuit Malfunction), P0336 (Crankshaft Position Sensor "A" Circuit Range/Performance), P0337 (Crankshaft Position Sensor "A" Circuit Low), and P0338 (Crankshaft Position Sensor "A" Circuit High).
- Difficulty Starting or No-Start Condition: If the ECM doesn't receive a signal from the CKPS, it may not trigger the fuel injectors or ignition system, leading to a no-start condition. The engine might crank, but it won't fire up. Intermittent starting problems are also common.
- Engine Stalling: The engine may stall unexpectedly, especially at low speeds or when idling. This is because the ECM relies on the CKPS signal to maintain proper engine operation.
- Rough Idle: An erratic or unstable idle can indicate a CKPS issue. The ECM is struggling to maintain a consistent engine speed due to inaccurate crankshaft position information.
- Reduced Engine Performance: A failing CKPS can lead to a decrease in overall engine power and acceleration. The ECM may retard ignition timing to protect the engine, resulting in sluggish performance.
- Hesitation or Misfiring: The engine might hesitate during acceleration or experience misfires, where one or more cylinders fail to fire correctly. This is due to the ECM's inability to precisely control fuel and ignition timing.
- Fuel Efficiency Decrease: Inaccurate CKPS data can cause the ECM to inject too much or too little fuel, leading to poor fuel economy.
Potential Causes of CKPS Problems in the 2005 Frontier
Several factors can contribute to CKPS failure:
- Sensor Failure: The sensor itself can simply fail due to age, heat, vibration, or manufacturing defects. Internal components may break down, leading to inaccurate readings or a complete loss of signal.
- Wiring Issues: Damaged, corroded, or loose wiring connecting the CKPS to the ECM can disrupt the signal. Check the wiring harness and connectors for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Reluctor Ring Damage: The toothed wheel (reluctor ring) attached to the crankshaft can become damaged or misaligned, affecting the CKPS signal. This is less common but possible, especially if the engine has been worked on previously.
- ECM Issues: In rare cases, the ECM itself can be the source of the problem. A faulty ECM may not properly interpret the CKPS signal or may not provide the necessary power to the sensor.
- Oil Contamination: Oil leaks can contaminate the CKPS, especially if the sensor is located near the front crankshaft seal. Oil can degrade the sensor's internal components and affect its performance.
Diagnosing CKPS Problems: A Step-by-Step Approach
Diagnosing CKPS issues requires a systematic approach. Here's a step-by-step guide:
- Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve any stored DTCs. Note down all codes, as they provide valuable clues about the problem. Pay close attention to codes related to the CKPS (P0335-P0338).
- Visual Inspection: Carefully inspect the CKPS, wiring harness, and connectors for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Pay particular attention to the area where the sensor connects to the wiring harness.
- Wiring Continuity Test: Use a multimeter to test the continuity of the wiring between the CKPS and the ECM. Refer to the 2005 Frontier's wiring diagram for the correct pinout information. A break in the wiring can prevent the signal from reaching the ECM.
- Sensor Resistance Test: Use a multimeter to measure the resistance of the CKPS. Compare the reading to the manufacturer's specifications. An out-of-range reading indicates a faulty sensor. The specific resistance range will vary depending on the sensor type. Consult your vehicle's service manual.
- Signal Voltage Test (if applicable, for Hall-effect sensors): If you suspect a Hall-effect sensor, check for the presence of voltage at the sensor connector with the ignition on. Again, refer to the wiring diagram for the correct pin.
- Oscilloscope Testing (Advanced): An oscilloscope can be used to visualize the CKPS signal. This allows you to check the signal's amplitude, frequency, and waveform. A distorted or missing signal indicates a problem with the sensor or reluctor ring. This is a more advanced technique but provides the most definitive diagnosis.
Important Note: Before replacing the CKPS, it's crucial to rule out other potential causes, such as wiring problems or ECM issues. Replacing the sensor without addressing the underlying problem will not solve the issue.
Replacing the CKPS on a 2005 Frontier
If you've determined that the CKPS is faulty, replacing it is a relatively straightforward process, assuming you have some mechanical experience.
- Gather Your Tools: You'll need a socket set, wrench set, screwdrivers, a new CKPS, and potentially a new connector if the old one is damaged. A torque wrench is also recommended for tightening the sensor to the correct specification.
- Disconnect the Battery: Disconnecting the negative battery terminal is crucial for safety and to prevent electrical damage.
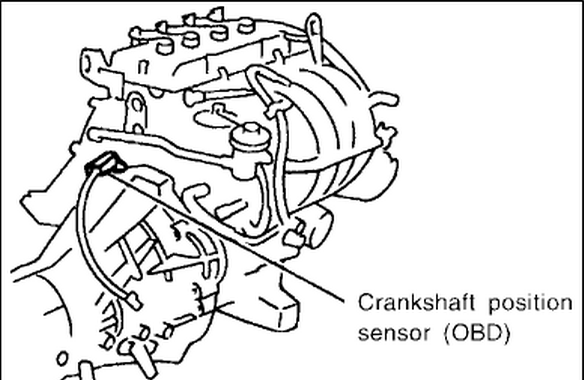
- Locate the CKPS: The location of the CKPS varies slightly depending on the engine, but it's typically located near the crankshaft pulley, usually on the engine block. Refer to a repair manual for specific instructions for your engine type.
- Disconnect the Electrical Connector: Carefully disconnect the electrical connector from the CKPS. Be gentle to avoid damaging the connector.
- Remove the Old Sensor: Use the appropriate socket or wrench to remove the bolt securing the CKPS. Carefully pull the sensor out of its mounting hole.
- Install the New Sensor: Install the new CKPS in the reverse order of removal. Make sure the sensor is properly seated and tighten the mounting bolt to the manufacturer's specified torque. Over-tightening can damage the sensor.
- Reconnect the Electrical Connector: Reconnect the electrical connector to the CKPS. Ensure it's securely attached.
- Reconnect the Battery: Reconnect the negative battery terminal.
- Clear DTCs: Use an OBD-II scanner to clear any stored DTCs.
- Start the Engine and Test: Start the engine and let it idle for a few minutes. Observe the engine's performance and check for any warning lights. Take the vehicle for a short test drive to ensure the problem has been resolved.
Preventive Measures
While you can't completely prevent CKPS failure, you can take steps to minimize the risk:
- Regular Maintenance: Follow the manufacturer's recommended maintenance schedule, including oil changes and tune-ups. Proper maintenance helps keep the engine running smoothly and reduces stress on the CKPS.
- Inspect Wiring Regularly: Periodically inspect the wiring harness and connectors for any signs of damage or corrosion. Address any issues promptly.
- Address Oil Leaks Promptly: Repair any oil leaks in the vicinity of the CKPS to prevent contamination.
- Use Quality Parts: When replacing the CKPS, use a high-quality replacement part from a reputable manufacturer. This ensures reliable performance and longevity.
Conclusion
The Crankshaft Position Sensor is a crucial component for proper engine operation. Recognizing the symptoms of a failing CKPS on your 2005 Nissan Frontier, understanding the potential causes, and following a systematic diagnostic approach can save you time and money. While replacing the sensor is often a straightforward task, remember to address any underlying issues, such as wiring problems, to prevent a recurrence. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can confidently tackle CKPS problems and keep your Frontier running smoothly.
