2005 Nissan Pathfinder 4.0 Firing Order
Alright, let's dive into the firing order for the 2005 Nissan Pathfinder with the 4.0L VQ40DE engine. Getting this right is absolutely crucial for smooth engine operation and preventing a whole host of problems. Incorrect firing order can lead to misfires, reduced power, rough idling, and even engine damage. So, pay close attention to the details. This guide assumes you have some familiarity with automotive terms and basic mechanical skills.
Understanding Firing Order
First things first, what exactly is firing order? Simply put, it's the sequence in which the engine's cylinders fire, or in other words, the order in which the spark plugs ignite the air-fuel mixture. In a multi-cylinder engine like the VQ40DE, this sequence is carefully designed to ensure balanced engine operation. This is why it is important to know the firing order.
The firing order is not arbitrary. It's determined by the crankshaft design, camshaft profile, and the overall engine architecture. The goal is to minimize vibration and distribute the power pulses evenly. Deviating from the correct firing order throws this balance off, leading to the issues mentioned earlier.
2005 Nissan Pathfinder 4.0L Firing Order: The Specifics
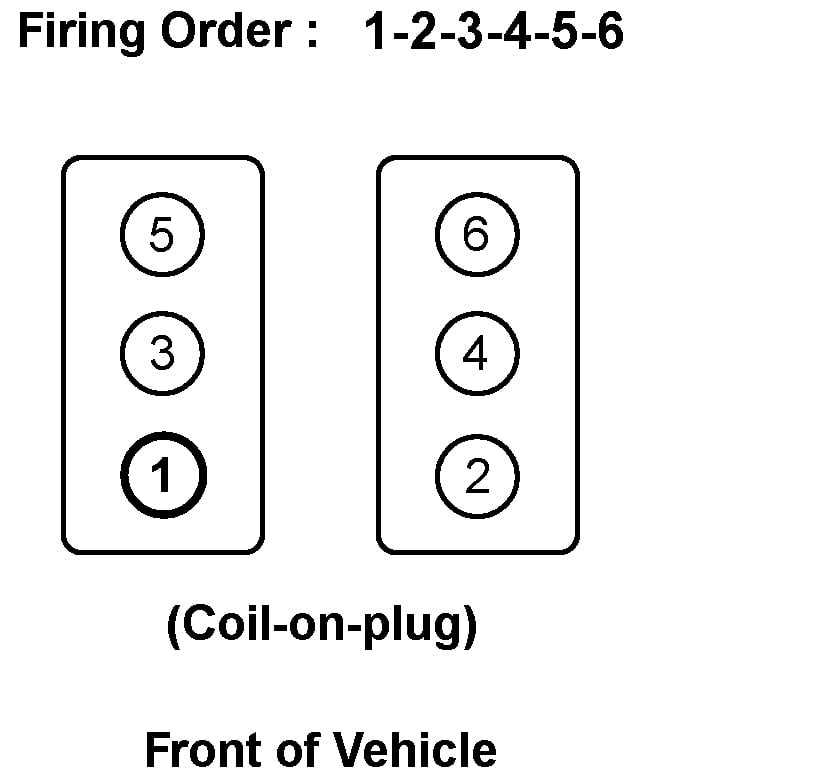
For the 2005 Nissan Pathfinder equipped with the 4.0L VQ40DE V6 engine, the firing order is:
1-2-3-4-5-6
That's right, it's a straightforward numerical sequence. But before you go plugging wires in haphazardly, you need to know which cylinder is which.
Cylinder Numbering and Layout
This is where things get a little more involved. The VQ40DE is a V6 engine, meaning it has two banks of three cylinders each. Understanding the cylinder numbering convention is essential for proper spark plug wire installation (or coil pack identification, depending on your setup). We will assume that your Nissan Pathfinder has the coil-on-plug ignition system as this was more common than distributor ignition, so we are addressing coil pack identification.
Imagine you're standing in front of the engine bay, facing the engine. This is the orientation we'll use for describing cylinder locations.
- Bank 1: This is typically the bank on the *right* side of the engine (from your perspective, looking at the engine), closest to the firewall. Cylinders in this bank are numbered 1, 3, and 5, starting from the front of the engine. So, cylinder 1 is the front-most cylinder on the right bank, cylinder 3 is the middle one, and cylinder 5 is the one closest to the firewall.
- Bank 2: This is the bank on the *left* side of the engine (again, from your perspective). Cylinders in this bank are numbered 2, 4, and 6, also starting from the front of the engine. Cylinder 2 is the front-most on the left bank, cylinder 4 is the middle, and cylinder 6 is near the firewall.
To reiterate, the cylinder locations are:
(Front of Engine)
Bank 2: 2 - 4 - 6
Bank 1: 1 - 3 - 5
(Firewall)
It's absolutely critical to get this numbering right. Double-check it, print out a diagram, do whatever it takes to make sure you're clear on which cylinder is which. Trust me, a small mistake here can cause big problems.
Coil Pack Identification
Since the 2005 Pathfinder uses a coil-on-plug (COP) system, each cylinder has its own dedicated ignition coil. This eliminates the need for a distributor and spark plug wires. However, you still need to ensure that each coil is connected to the correct cylinder.
The engine control unit (ECU) sends signals to each coil to fire the spark plug at the precise moment dictated by the firing order. The ECU knows where each cylinder is in its combustion cycle thanks to the crankshaft position sensor (CKP) and the camshaft position sensor (CMP). These sensors provide the ECU with vital information about engine speed and the position of the pistons and valves.
To ensure the coils are correctly identified, you can use a multimeter to test for continuity between the coil connector and the corresponding ECU pin. The wiring diagram for the 2005 Pathfinder will provide the pinout information. This method is more technical and requires some electrical knowledge.
Another approach is to visually inspect the wiring harness. The coil connectors are usually labelled (though sometimes the labels are faded or missing). You can also trace the wires back to the ECU connector and identify the corresponding pins based on the wiring diagram.
A Helpful Tip: Before disconnecting any coil connectors, label them clearly. Use masking tape and a permanent marker to identify each coil with its corresponding cylinder number. This will save you a lot of headaches during reassembly.
Troubleshooting Firing Order Issues
So, what happens if you suspect a firing order problem? Here are some common symptoms and diagnostic steps:
- Misfires: This is the most common symptom. The engine will run rough, especially at idle. The check engine light will likely illuminate, and you may get diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to misfires (e.g., P0300, P0301, P0302, etc.).
- Reduced Power: If a cylinder isn't firing correctly, the engine won't produce as much power. You may notice a lack of acceleration or difficulty climbing hills.
- Rough Idling: An incorrect firing order can cause the engine to shake and vibrate excessively at idle.
- Poor Fuel Economy: Misfires can lead to incomplete combustion, resulting in wasted fuel and reduced fuel efficiency.
- Engine Knocking or Pinging: In severe cases, an incorrect firing order can cause abnormal combustion that leads to engine knocking or pinging.
If you experience any of these symptoms, start by verifying the firing order and checking that the coils are connected to the correct cylinders. Here are some additional troubleshooting steps:
- Scan for Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve any DTCs stored in the ECU. Misfire codes can help you pinpoint the specific cylinder that's causing the problem.
- Inspect the Coils: Check the coils for any signs of damage, such as cracks, burns, or corrosion. Use a multimeter to test the coil resistance and ensure it's within the manufacturer's specifications.
- Check the Spark Plugs: Inspect the spark plugs for wear, damage, or fouling. Replace any plugs that are in poor condition. Ensure that the spark plug gap is correct.
- Check the Fuel Injectors: A faulty fuel injector can also cause misfires. Use a stethoscope to listen to the injectors and ensure they're clicking properly. You can also perform a fuel injector balance test to check the fuel delivery of each injector.
- Perform a Compression Test: A compression test can help you identify any cylinders with low compression, which could be caused by worn piston rings, leaky valves, or a blown head gasket.
Important Considerations
- Torque Specifications: When reinstalling the coils, be sure to tighten the mounting bolts to the correct torque specification. Overtightening can damage the coils or the cylinder head.
- Cleanliness: Keep everything clean during the process. Dirt and debris can contaminate the ignition system and cause problems.
- Safety First: Disconnect the negative battery cable before working on the ignition system to prevent electrical shocks.
- Reference Materials: Always consult the factory service manual for your 2005 Nissan Pathfinder for specific instructions and torque specifications. The manual will have diagrams and information specific to your vehicle.
Working on your car's ignition system can be intimidating, but with a little knowledge and attention to detail, you can successfully diagnose and repair firing order issues. Remember to double-check your work, and don't hesitate to seek help from a qualified mechanic if you're unsure about anything.
