2012 Nissan Juke Battery
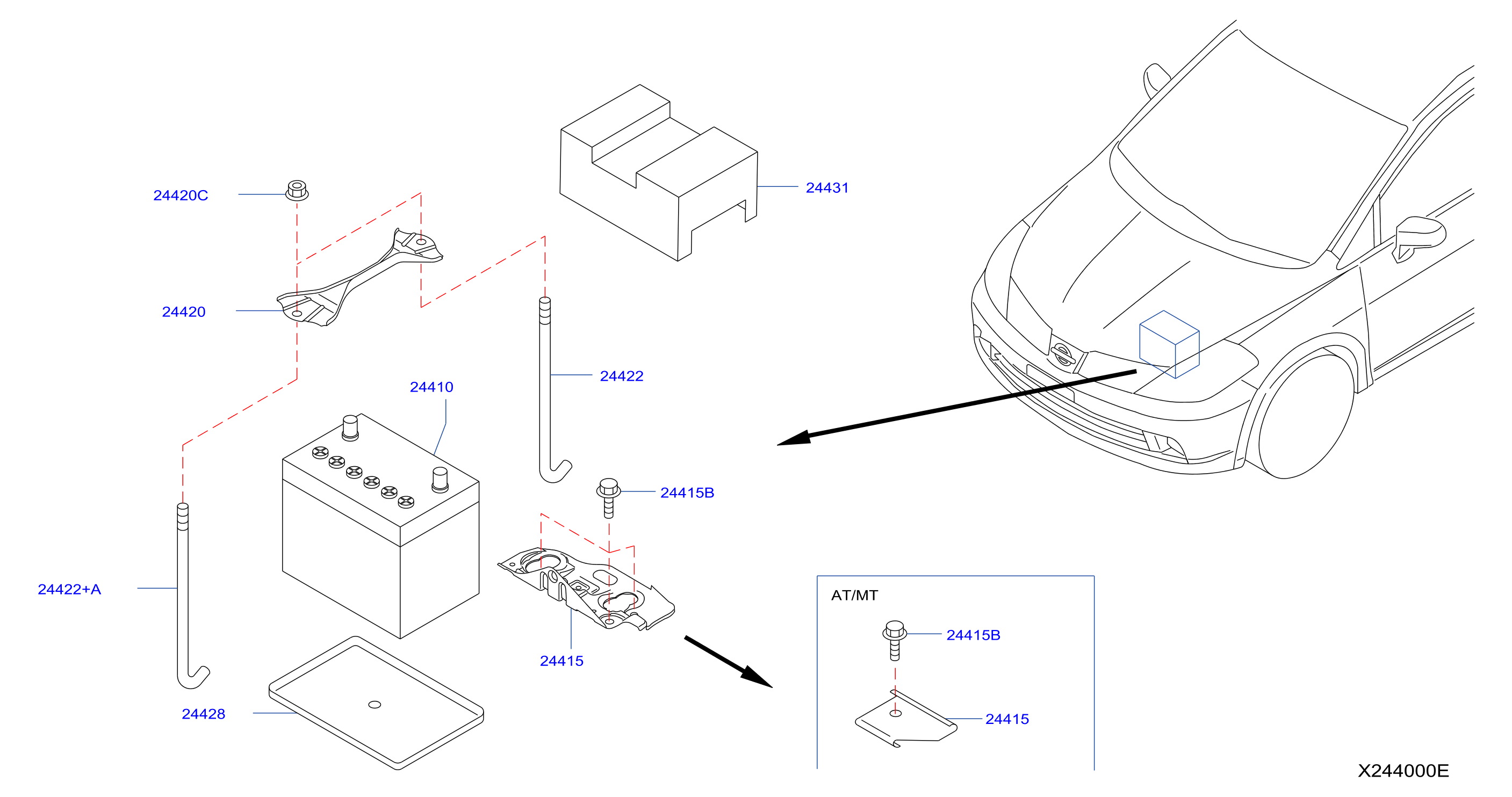
The 2012 Nissan Juke, while a distinctive and fun-to-drive crossover, relies on a dependable starting, lighting, and ignition (SLI) battery like any other vehicle. Understanding the specifics of the Juke's battery – its type, requirements, troubleshooting common issues, and proper maintenance – can empower you to keep your Juke running smoothly and avoid unexpected breakdowns. This article will delve into these aspects, providing the technical information you need while remaining accessible and practical.
Battery Specifications and Requirements
The 2012 Nissan Juke typically utilizes a Group Size 35 battery. This designation refers to a standardized Battery Council International (BCI) specification. The BCI assigns group sizes based on the battery's physical dimensions (length, width, and height) as well as terminal placement. Using the correct group size is crucial for a proper fit within the Juke's battery tray and secure terminal connections.
Beyond the group size, key electrical characteristics determine a battery's suitability. These include:
- Cold Cranking Amps (CCA): This rating indicates the battery's ability to deliver a large amount of current for a short period at 0°F (-18°C). This is critical for starting the engine in cold weather. A higher CCA rating is generally desirable, particularly in colder climates. The minimum CCA for the 2012 Juke's battery is usually around 550 CCA, but check your owner's manual or a reputable battery fitment guide for the exact specification.
- Ampere-Hour (Ah) Capacity: The Ah rating represents the amount of current a battery can deliver over a specific period. For example, a 50 Ah battery can theoretically deliver 5 amps for 10 hours. A higher Ah rating translates to a greater reserve capacity, allowing the battery to power accessories for longer periods when the engine is off.
- Voltage: Automotive batteries are nominally 12-volt systems. Deviations from this voltage can indicate problems.
The 2012 Juke usually ships with a lead-acid battery. Within lead-acid technology, there are two primary types:
- Flooded Lead-Acid (FLA): These are the traditional type, containing liquid electrolyte that requires periodic topping off with distilled water. While less expensive, they are prone to spilling and self-discharge faster than AGM batteries.
- Absorbent Glass Mat (AGM): AGM batteries are a type of sealed lead-acid battery where the electrolyte is absorbed into a fiberglass mat. They are more resistant to vibration, have a longer lifespan, and can handle deeper discharges compared to flooded batteries. While more expensive, they are often considered a worthwhile upgrade due to their performance and longevity. The Internal Resistance is typically lower in an AGM, meaning it can deliver higher currents easier.
When replacing your Juke's battery, consider the climate you live in and your driving habits. If you frequently drive short distances or use a lot of accessories while the engine is off, an AGM battery with a higher CCA and Ah rating might be a better choice.
Common Battery Problems and Troubleshooting
Batteries don't last forever. Several factors can contribute to battery failure, including:
- Age: Over time, the internal components of a battery degrade, reducing its capacity and performance. Most automotive batteries have a lifespan of 3-5 years.
- Extreme Temperatures: Both high and low temperatures can negatively impact battery performance and lifespan. Heat accelerates corrosion and electrolyte evaporation, while cold temperatures reduce the battery's ability to deliver current.
- Corrosion: Corrosion on the battery terminals can impede the flow of electricity, leading to starting problems.
- Parasitic Draw: Even when the engine is off, certain components in the vehicle (e.g., security systems, clocks, computers) continue to draw a small amount of current. Excessive parasitic draw can drain the battery over time.
- Overcharging: A faulty charging system can overcharge the battery, leading to damage and reduced lifespan.
- Deep Discharge: Repeatedly discharging the battery to very low levels can also shorten its lifespan.
Here are some common symptoms of a failing battery:
- Slow Engine Cranking: The engine takes longer than usual to start.
- Dim Headlights: Headlights appear dim, especially when the engine is idling.
- Electrical Issues: Intermittent problems with other electrical components, such as the radio or power windows.
- Warning Lights: The battery warning light or check engine light may illuminate on the dashboard.
- Battery Swelling or Leaking: Physical signs of damage to the battery casing.
Troubleshooting a battery issue involves a few key steps:
- Visual Inspection: Check the battery terminals for corrosion. Clean them with a wire brush and baking soda solution if necessary. Inspect the battery case for any signs of damage. Make sure the battery is securely mounted and that the terminals are properly connected.
- Voltage Test: Use a multimeter to measure the battery's voltage. A fully charged battery should read around 12.6 volts. A reading below 12.4 volts indicates a partially discharged battery, and a reading below 12.0 volts indicates a significantly discharged battery. Important: let the car sit for at least 30 minutes before taking a voltage reading, to ensure an accurate surface charge reading.
- Load Test: A load test simulates the electrical load of starting the engine and measures the battery's ability to maintain voltage under load. This requires a specialized load tester, which can be purchased or borrowed from an auto parts store.
- Charging System Test: If the battery voltage is low, test the charging system (alternator) to ensure it is properly charging the battery. This can also be done with a multimeter. With the engine running, the voltage at the battery terminals should be between 13.5 and 14.5 volts.
- Parasitic Draw Test: To check for excessive parasitic draw, disconnect the negative battery cable and connect an ammeter (multimeter set to measure amps) between the cable and the negative battery terminal. The current draw should be less than 50 milliamps (0.05 amps). A higher reading indicates a parasitic draw that needs to be investigated. This often involves systematically pulling fuses to isolate the circuit causing the draw. Be careful not to trigger airbags or other sensitive systems when pulling fuses.
Warning: When working with car batteries, always wear eye protection and gloves. Batteries contain corrosive acid that can cause burns. Ensure adequate ventilation when charging a battery, as it can release explosive hydrogen gas.
Battery Replacement Procedure
Replacing the battery on a 2012 Nissan Juke is a relatively straightforward process, but it's important to follow the proper steps to avoid damaging the vehicle or injuring yourself.
- Gather your tools: You'll need a wrench (typically 10mm or 13mm) to loosen the battery terminals and hold-down clamp, a battery terminal cleaner, a wire brush, and optionally, a memory saver.
- Disconnect the old battery: Always disconnect the negative (-) terminal first, followed by the positive (+) terminal. This prevents accidental short circuits. Use the wrench to loosen the terminal clamps and carefully remove them from the battery posts.
- Remove the battery hold-down: The battery is typically secured by a clamp or strap. Remove the hold-down to free the battery.
- Lift out the old battery: Carefully lift the old battery out of the tray. Be mindful of its weight and avoid tilting it excessively, as it may contain acid.
- Clean the battery tray and terminals: Clean the battery tray with a wire brush to remove any dirt or corrosion. Clean the battery terminals and cable clamps with a battery terminal cleaner and wire brush.
- Install the new battery: Place the new battery into the tray, ensuring it is properly aligned. Secure it with the hold-down clamp.
- Connect the new battery: Connect the positive (+) terminal first, followed by the negative (-) terminal. Make sure the terminal clamps are securely tightened.
- Memory Saver: Use a memory saver to prevent the loss of radio presets, seat settings, and other electronic configurations. Connect the memory saver to the cigarette lighter socket *before* disconnecting the original battery. This provides a temporary power source to maintain the vehicle's settings. If you don't use a memory saver, you may need to re-enter these settings after replacing the battery.
After replacing the battery, start the engine and verify that the charging system is working properly. Check the voltage at the battery terminals with the engine running. It should be between 13.5 and 14.5 volts.
Battery Maintenance Tips
Proper maintenance can extend the life of your Juke's battery and prevent unexpected problems.
- Keep the terminals clean: Regularly inspect the battery terminals for corrosion and clean them as needed.
- Avoid deep discharges: Minimize the use of accessories when the engine is off to avoid draining the battery.
- Check the charging system: Periodically check the charging system voltage to ensure it is working properly.
- Park in the shade: When possible, park your Juke in the shade to protect the battery from extreme heat.
- Use a battery maintainer: If you frequently drive short distances or store your Juke for extended periods, consider using a battery maintainer to keep the battery fully charged. These devices provide a slow, controlled charge that helps prevent sulfation, a buildup of lead sulfate crystals on the battery plates that reduces its capacity.
By understanding the specifics of your 2012 Nissan Juke's battery and following these maintenance tips, you can ensure its longevity and reliability, keeping your Juke on the road for years to come.
