2012 Nissan Rogue Speed Sensor Location
Alright, let's talk about the speed sensors on your 2012 Nissan Rogue. Specifically, where they are located. Knowing this is crucial if you're experiencing issues like erratic speedometer readings, trouble with your ABS or traction control systems, or even difficulty with shifting if you have an automatic transmission. We'll cover the locations of both the input and output speed sensors, along with some tips for identification and troubleshooting.
Understanding Speed Sensors: Input and Output
Before we dive into the specific locations, let's briefly define what these sensors do and why they are important. A vehicle speed sensor (VSS) is essentially a transducer that converts rotational speed (of a wheel or transmission component) into an electrical signal that the vehicle's computer (the Engine Control Unit, or ECU) can understand. This signal is used for various functions, including:
Speedometer/Odometer: The most obvious use – displaying your current speed and tracking mileage.
ABS (Anti-lock Braking System): The ABS relies on wheel speed data to detect when a wheel is locking up during braking. This allows it to modulate brake pressure and prevent skidding.
Traction Control System (TCS): Similar to ABS, TCS uses wheel speed data to detect wheel slip during acceleration. It can then reduce engine power or apply brakes to regain traction.
Automatic Transmission Control: Automatic transmissions use speed sensor data to determine when to shift gears. Incorrect sensor data can lead to harsh shifting, delayed shifting, or even prevent the transmission from shifting at all.
Cruise Control: The cruise control system needs accurate speed data to maintain a set speed.
In the context of the 2012 Rogue's Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT), you'll typically find two key speed sensors: the input speed sensor and the output speed sensor. While some vehicles have wheel speed sensors that contribute to overall vehicle speed calculations, we'll focus on the sensors integral to the CVT's operation.
Input Speed Sensor
The input speed sensor, sometimes referred to as the primary speed sensor, monitors the rotational speed of the transmission's input shaft. This shaft is directly connected to the engine, so the sensor essentially tracks the engine's speed as it enters the transmission. The input speed sensor is crucial for the ECU to understand how fast the engine is turning *before* the CVT modifies the ratio. This information is fundamental for proper CVT operation, shift scheduling (even though it's a CVT, it still simulates shifts for driver feel), and overall engine management.
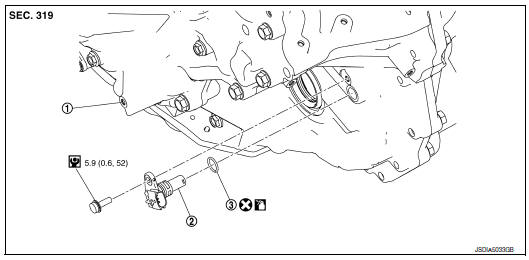
Location: On the 2012 Nissan Rogue, the input speed sensor is typically located on the driver's side of the CVT, towards the front of the vehicle. It's usually mounted on the transmission case itself. It will appear as a small sensor held in place by a bolt or two, with a wire harness connector attached to it.
Finding it: Here's a breakdown of how to locate it:
Safety First: Always disconnect the negative battery terminal before working on any electrical components.
Access: You'll likely need to jack up the front of the vehicle and secure it with jack stands for safe access. Refer to your owner's manual for proper jacking points.
Visual Inspection: Crawl underneath the vehicle and locate the CVT. Look on the driver's side, towards the front. You're looking for a sensor that's typically black or gray plastic, cylindrical in shape, with a wire harness plugged into it. It will be bolted directly to the transmission case.
Follow the Wires: If you're having trouble spotting it visually, try tracing the wiring harness from the transmission control module (TCM) to the sensor. This can help you pinpoint its location.
Output Speed Sensor
The output speed sensor, also called the secondary speed sensor, monitors the rotational speed of the transmission's output shaft. This shaft is connected to the driveshaft that ultimately turns the wheels. Therefore, the output speed sensor provides the ECU with information about the actual speed at which the wheels are rotating after the CVT has adjusted the gear ratio. This information is essential for accurate speedometer readings, ABS/TCS operation, and overall vehicle stability control.
Location: On the 2012 Nissan Rogue, the output speed sensor is usually found on the passenger side of the CVT, towards the rear of the vehicle. Like the input speed sensor, it's mounted directly on the transmission case and secured with bolts. It will also have a wire harness connector attached.
Finding it: Here's how to find it:
Safety First: Ensure the negative battery terminal is disconnected.
Access: Raise and secure the front of the vehicle with jack stands.
Visual Inspection: Crawl under the vehicle and locate the CVT again. This time, focus on the passenger side, towards the rear. Look for the same type of sensor as the input speed sensor: a small, typically black or gray, cylindrical sensor bolted to the transmission case with a wire harness plugged into it.
Tracing Wires: If needed, trace the wiring harness from the TCM to the sensor to help locate it precisely.
Sensor Identification and Replacement
Both the input and output speed sensors will look very similar. The easiest way to differentiate them, apart from their location, is often by their part number. If you are replacing one or both sensors, always verify that you are using the correct part number for the specific sensor you are replacing.
Replacement Considerations:
OEM vs. Aftermarket: While aftermarket sensors are available, using an Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) sensor is generally recommended. OEM sensors are designed to meet the exact specifications of your vehicle, ensuring optimal performance and reliability. Aftermarket sensors can sometimes have compatibility issues or shorter lifespans.
Sensor Condition: Before replacing a sensor, inspect the wiring harness and connector for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Sometimes, a simple wiring issue can mimic a faulty sensor. Also, check for any debris or contamination on the sensor itself.
Proper Installation: When installing a new sensor, make sure the mounting surface on the transmission case is clean. Torque the retaining bolts to the manufacturer's specified torque value to avoid damage.
Troubleshooting Speed Sensor Issues
Several symptoms can indicate a problem with a speed sensor:
Erratic Speedometer Readings: The speedometer needle may jump around erratically or display incorrect speed.
ABS/TCS Light Illumination: The ABS or TCS warning lights may illuminate on the dashboard.
Transmission Problems: Automatic transmission may shift erratically, delay shifting, or refuse to shift at all.
Cruise Control Malfunction: Cruise control may not engage or may disengage unexpectedly.
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): The ECU will likely store DTCs related to the speed sensors. Common codes include P0500 (Vehicle Speed Sensor Malfunction), P0720 (Output Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction), and P0725 (Engine Speed Input Circuit Malfunction). A scan tool can be used to retrieve these codes.
Diagnostic Steps:
Scan for DTCs: Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve any stored DTCs.
Inspect Wiring and Connectors: Visually inspect the wiring harness and connectors for any signs of damage or corrosion. Clean the connectors with electrical contact cleaner.
Test Sensor Resistance: Use a multimeter to measure the resistance of the sensor. Compare the resistance value to the manufacturer's specifications. An incorrect resistance value can indicate a faulty sensor.
Check Sensor Output: With the wheel spinning (safely!), use a multimeter to check the sensor's voltage output. The voltage should fluctuate as the wheel rotates. A lack of voltage or an inconsistent voltage reading can indicate a faulty sensor.
Important Note: Testing speed sensor output often requires specialized equipment and knowledge. If you are not comfortable performing these tests, it's best to consult a qualified mechanic.
By understanding the location and function of the input and output speed sensors on your 2012 Nissan Rogue, you'll be better equipped to diagnose and repair any related issues. Remember to always prioritize safety and consult your vehicle's repair manual for specific instructions and torque specifications.
