2016 Nissan Rogue Intake Manifold Runner Control Valve Location
The 2016 Nissan Rogue, like many modern vehicles, utilizes sophisticated engine management systems to optimize performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions. A critical component within this system is the Intake Manifold Runner Control (IMRC) system. This guide will provide a detailed examination of the IMRC system on the 2016 Rogue, focusing specifically on the location and function of the Intake Manifold Runner Control Valve (IMRC valve).
Understanding the Intake Manifold Runner Control System
Before pinpointing the IMRC valve's location, it's essential to grasp the underlying principles of the IMRC system. The core idea revolves around manipulating the length of the intake runners within the intake manifold. These runners are pathways that guide air into the engine's cylinders. Varying their length, typically through the use of electronically controlled valves, allows the engine to optimize airflow for different operating conditions.
At low engine speeds (e.g., idling or cruising), the IMRC system closes the valves, effectively lengthening the intake runners. This longer path promotes increased air velocity. The higher velocity air enters the cylinder, creating more swirl and tumble within the combustion chamber. This improved air-fuel mixing leads to more complete combustion, boosting low-end torque and improving fuel economy. The swirl and tumble is induced by the longer runners due to higher friction, giving air more velocity and direction.
Conversely, at high engine speeds (e.g., during acceleration or when demanding more power), the IMRC system opens the valves, shortening the intake runners. This shorter path reduces intake restriction and allows for a higher volume of air to enter the engine more quickly. This increased airflow is vital for achieving maximum power output at higher RPMs. The shorter runners do not generate as much swirl or tumble, but there is higher volume of air. The valve position is controlled by the engine computer.
Essentially, the IMRC system acts as a variable intake geometry system, adapting to the engine's needs in real-time to provide the best possible balance of torque, power, and fuel efficiency. The operation of the system is governed by the engine control unit (ECU), which receives inputs from various sensors such as the engine speed (RPM), throttle position, and mass airflow (MAF) sensor to determine the optimal runner length.
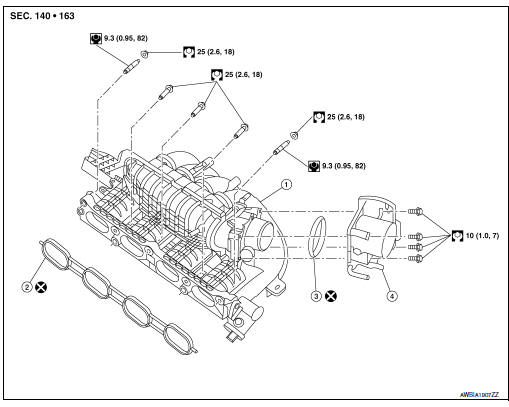
Identifying the Intake Manifold Runner Control Valve
The IMRC valve (sometimes referred to as a swirl control valve) is the actuator responsible for opening and closing the intake runners within the intake manifold. In the 2016 Nissan Rogue, equipped with the 2.5L QR25DE engine, the IMRC valve is typically located on the intake manifold itself. The exact placement can vary slightly depending on the specific model year and engine configuration, but it’s generally accessible.
Location Description: The IMRC valve is usually found mounted on the side or rear of the intake manifold. It is often situated close to the throttle body. Look for a small, electrically operated actuator with a linkage or rod that connects to the intake manifold runners. The valve itself is usually black plastic or metal. There is no specific side. It all depends on the space and engine design.
Visual Clues:
- Check for a vacuum line running to a diaphragm actuator (older systems). The 2016 Rogue uses a electronic actuator, however, older systems used vacuum actuation.
- Locate an electrical connector leading to a solenoid or small electric motor. This is the electrical connector that sends signal to the IMRC valve.
- Trace the linkage or rod connected to the valve to see how it interacts with the intake manifold runners.
- Visually trace the intake manifold runners. The valve should be close to the point where the runners diverge.
Safety Precautions: Before attempting to locate or inspect the IMRC valve, ensure that the engine is cool and the ignition is turned off. Disconnecting the negative battery terminal is also recommended as a safety precaution to prevent accidental electrical shock or damage to the vehicle's electrical system. Take great caution if the engine is hot. The engine can stay hot for a while, so it is recommended to let it cool. Wear proper gloves to protect your hands from hot surfaces and sharp objects.
Detailed Inspection and Testing
Once you've located the IMRC valve, a thorough inspection can help determine its condition. The following steps outline a basic inspection and testing procedure:
Visual Inspection:
Begin by visually inspecting the IMRC valve, looking for any signs of damage, such as cracks, leaks, or corrosion. Examine the electrical connector for loose or damaged wiring. Also, inspect the vacuum lines (if applicable) for cracks, leaks, or disconnections. The vacuum lines can dry-rot over time.
Manual Operation (Engine Off):
With the engine off, try to manually move the IMRC valve's linkage or rod. It should move freely without binding or excessive resistance. Any stiffness or binding could indicate a problem with the valve or the intake manifold runners. Do not use excessive force, as you might damage the linkage.
Electrical Connector Test:
Use a multimeter to check for voltage at the electrical connector when the engine is running. Consult the vehicle's service manual for the correct voltage specifications. A lack of voltage could indicate a problem with the wiring harness, the ECU, or the IMRC valve itself. Make sure that you use the correct wiring diagram.
OBD-II Code Scan:
Connect an OBD-II scanner to the vehicle's diagnostic port and check for any IMRC-related trouble codes. Common codes include P2004 (Intake Manifold Runner Control Stuck Open Bank 1), P2005 (Intake Manifold Runner Control Stuck Open Bank 2), P2006 (Intake Manifold Runner Control Stuck Closed Bank 1), P2007 (Intake Manifold Runner Control Stuck Closed Bank 2), and P2015 (Intake Manifold Runner Position Sensor/Switch Circuit Range/Performance). These codes can provide valuable clues about the nature of the problem. It is important to troubleshoot the problem. Just replacing the parts alone will not fix the error code. You need to find the root cause of the error.
Potential Problems and Solutions
Several issues can arise with the IMRC system, leading to reduced engine performance, poor fuel economy, and diagnostic trouble codes. Here are some common problems and potential solutions:
- Stuck or Binding Valve: Carbon buildup or debris can cause the IMRC valve to stick in either the open or closed position. This can be addressed by cleaning the valve and the surrounding area with a suitable carburetor or throttle body cleaner. If the valve is severely damaged or corroded, replacement may be necessary.
- Vacuum Leaks (Older Systems): Leaks in the vacuum lines can prevent the IMRC valve from operating correctly. Inspect all vacuum lines for cracks or leaks and replace them as needed.
- Faulty Electrical Connector or Wiring: Damaged or corroded electrical connectors or wiring can disrupt the signal to the IMRC valve. Clean the connectors with electrical contact cleaner and repair any damaged wiring. If the connector is severely damaged, it may need to be replaced.
- Defective IMRC Valve Actuator: The solenoid or electric motor that controls the IMRC valve can fail. Use a multimeter to test the actuator's resistance. If the resistance is outside of the specified range, the actuator should be replaced.
- ECU Malfunction: In rare cases, a malfunctioning ECU can cause problems with the IMRC system. However, this is usually only considered after all other possible causes have been ruled out.
Importance of Proper Function
The IMRC system is an integral part of the 2016 Nissan Rogue's engine management system. Its proper function is critical for maintaining optimal engine performance, fuel economy, and emissions control. A malfunctioning IMRC system can lead to a variety of problems, including reduced power, poor fuel economy, rough idling, and diagnostic trouble codes. It is important to address any IMRC-related issues promptly to prevent further damage and ensure the vehicle is running efficiently. Remember to consult the factory service manual for all the necessary torque specifications.
By understanding the IMRC system and its components, specifically the IMRC valve, you can effectively diagnose and address potential problems, ensuring your 2016 Nissan Rogue continues to perform at its best. Regular maintenance and prompt attention to any symptoms of IMRC system malfunction are essential for preserving the vehicle's longevity and reliability.
