2017 Nissan Titan Starter Replacement
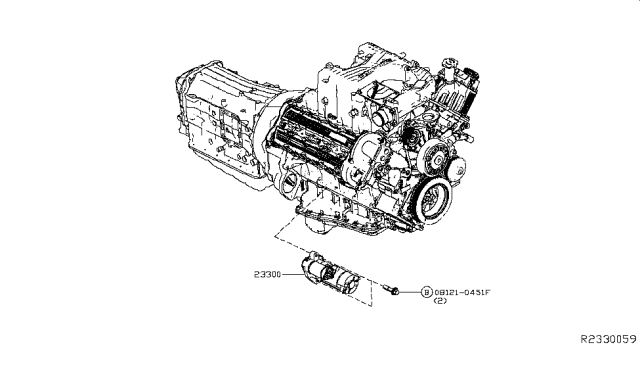
The 2017 Nissan Titan, a robust and capable pickup truck, relies on a healthy starter motor to crank its engine to life. A failing starter can manifest in several ways – a slow, labored cranking sound, a clicking noise with no engine rotation, or even complete silence when you turn the key. While a professional mechanic can certainly handle a starter replacement, understanding the process and undertaking it yourself is a rewarding experience, blending practical automotive repair with a deeper appreciation for how the vehicle’s electrical and mechanical systems interact. This guide will walk you through the process of replacing the starter on a 2017 Nissan Titan, focusing on the technical aspects and rationale behind each step.
Understanding the Starter System
Before diving into the replacement procedure, it's crucial to understand the function of the starter. The starter motor is essentially a high-torque electric motor designed to spin the engine's crankshaft, initiating the combustion cycle. When you turn the ignition key, the following sequence occurs:
- The ignition switch sends a low-current signal to the starter relay (often located in the engine bay's fuse box).
- The starter relay, a magnetically operated switch, closes, allowing high-current power from the battery to flow to the starter solenoid.
- The starter solenoid, mounted directly on the starter motor, serves two primary functions:
- It acts as a high-current relay, handling the substantial electrical load required by the starter motor.
- It mechanically engages the starter's pinion gear with the engine's flywheel (or flexplate in automatic transmissions).
- As the solenoid engages the pinion gear, it simultaneously closes heavy-duty electrical contacts within the solenoid, sending current to the starter motor itself.
- The starter motor spins, turning the engine over until it reaches a self-sustaining speed. Once the engine is running, the ignition switch is released, the solenoid disengages, and the starter motor stops.
Failure in any of these components – the ignition switch, relay, solenoid, or motor – can lead to starting problems. However, the starter motor itself is a common culprit due to the high stresses it endures.
Tools and Materials Required
Having the right tools is paramount for a successful and safe repair. Here’s a comprehensive list:
- Socket set: Metric sockets are essential. You'll likely need 10mm, 12mm, 13mm, and 14mm sockets, both standard and deep well.
- Wrench set: Matching the socket sizes mentioned above. Combination wrenches are ideal.
- Torque wrench: Absolutely crucial for tightening bolts to the manufacturer's specified torque, preventing over-tightening and potential damage.
- Screwdrivers: Both flathead and Phillips head.
- Pliers: Needle-nose and standard pliers for disconnecting wiring connectors and manipulating components.
- Jack and jack stands: Raising the vehicle safely is essential for accessing the starter motor. Never work under a vehicle supported only by a jack.
- Wheel chocks: For added safety, especially when working on an incline.
- Gloves: To protect your hands from dirt, grease, and sharp edges.
- Safety glasses: To protect your eyes from debris.
- Penetrating oil: To loosen stubborn bolts and connections.
- Wire brush: For cleaning battery terminals and connections.
- Multimeter: Useful for diagnosing electrical issues, although not strictly necessary for a straight starter replacement.
- New starter motor: Ensure it's the correct part number for your 2017 Nissan Titan and engine configuration.
- Battery terminal cleaner: For cleaning battery posts and cable ends.
- Rags or shop towels: For wiping up spills and cleaning parts.
- Zip ties: For securing wiring harnesses after the replacement.
Step-by-Step Starter Replacement Procedure
Safety First! Before commencing any work, disconnect the negative battery cable. This prevents accidental short circuits and potential electrical shock. Secure the cable away from the battery terminal.
Step 1: Accessing the Starter Motor
The location of the starter motor can vary slightly depending on the engine type and drivetrain (2WD or 4WD). Typically, it's mounted on the engine block near the transmission bellhousing. You'll likely need to raise the vehicle to gain adequate access. Here's the procedure:
- Loosen the lug nuts on the front wheel (or both front wheels, depending on the location of the starter) on the side where the starter is located.
- Position the jack under the designated jacking point on the frame. Consult your owner's manual for the correct jacking points.
- Raise the vehicle until the tire is off the ground.
- Carefully place jack stands under the frame rails near the jacking point. Ensure they are securely positioned and rated for the vehicle's weight.
- Slowly lower the vehicle onto the jack stands. Double-check that the vehicle is stable before proceeding.
- Remove the wheel(s) for improved access.
Step 2: Disconnecting Electrical Connections
Before removing the starter motor, disconnect the electrical connections. There are typically two wires connected to the starter solenoid:
- A large-gauge wire from the battery, providing the main power to the starter motor. This is often secured with a nut.
- A smaller-gauge wire from the ignition switch, providing the signal to activate the solenoid. This may be connected with a nut or a push-on connector.
Important: Before disconnecting any wires, carefully note their original positions and wire routing. Taking pictures can be extremely helpful for reassembly. Use penetrating oil to loosen any corroded nuts or connections. Use the appropriate size wrench to avoid rounding off the nuts. Disconnect the wires one at a time and immediately label them with masking tape and a marker to avoid confusion later. Be gentle when disconnecting the wires to avoid damaging the terminals.
Step 3: Removing the Starter Motor
The starter motor is typically held in place by two or three bolts. These bolts are usually fairly long and may be difficult to access. Here's the process:
- Use the appropriate size socket and wrench to loosen the starter mounting bolts. Penetrating oil can be helpful if the bolts are seized.
- Once the bolts are loosened, carefully remove them completely. Support the starter motor with your hand as you remove the last bolt to prevent it from dropping.
- Gently maneuver the starter motor out of its mounting location. You may need to rotate or angle it to clear any obstructions.
Step 4: Installing the New Starter Motor
Installation is essentially the reverse of removal. However, pay close attention to these details:
- Compare the new starter motor to the old one to ensure they are identical in size and configuration. Verify that the pinion gear has the same number of teeth and that the mounting holes align correctly.
- Clean the mounting surfaces on the engine block with a wire brush to ensure good contact.
- Carefully position the new starter motor into its mounting location. Ensure it aligns properly with the mounting holes.
- Install the mounting bolts and tighten them by hand initially.
- Use a torque wrench to tighten the mounting bolts to the manufacturer's specified torque. This is a critical step. Consult your vehicle's repair manual or a reliable online resource for the correct torque specifications. Overtightening can damage the engine block or starter housing, while undertightening can lead to loose bolts and starter failure.
Step 5: Reconnecting Electrical Connections
Reconnect the electrical wires to the starter solenoid, ensuring they are connected to the correct terminals. Refer to your notes or pictures taken during disassembly.
- Clean the terminals with a wire brush before connecting the wires.
- Secure the wires with the nuts, tightening them to the appropriate torque. Avoid overtightening, which can damage the terminals.
- Ensure the wires are routed correctly and secured with zip ties to prevent them from rubbing against other components.
Step 6: Final Steps and Testing
- Reinstall the wheel(s) and tighten the lug nuts by hand.
- Raise the vehicle slightly to remove the jack stands.
- Lower the vehicle to the ground.
- Torque the lug nuts to the manufacturer's specified torque.
- Reconnect the negative battery cable.
- Start the engine to test the new starter motor. It should crank the engine smoothly and quickly.
- Listen for any unusual noises. If you hear clicking or grinding, recheck the wiring connections and starter mounting bolts.
- Check the vehicle for any warning lights.
Troubleshooting
If the engine still doesn't start after replacing the starter, consider these troubleshooting steps:
- Check the battery voltage: A weak battery can prevent the starter from engaging properly.
- Check the starter relay: A faulty starter relay can prevent power from reaching the starter solenoid.
- Check the ignition switch: A faulty ignition switch may not send the signal to activate the starter relay.
- Check the wiring connections: Loose or corroded wiring connections can impede the flow of electricity.
- Check the engine's grounding: A poor engine ground can prevent the starter from functioning correctly.
Conclusion
Replacing the starter motor on a 2017 Nissan Titan is a straightforward process that can save you money and provide a valuable learning experience. By understanding the function of the starter system, following the steps outlined in this guide, and paying attention to detail, you can successfully complete this repair and keep your Titan running reliably. Remember to always prioritize safety and consult a professional mechanic if you are unsure about any aspect of the repair. Good luck!
