2jz-gte Swap Wiring Harness And Ecu Configuration Guide
So, you've taken the plunge and are embarking on the legendary 2JZ-GTE swap! Congratulations, you're about to unleash some serious power. But let's be honest, the wiring harness and ECU configuration can be the trickiest part of this project. It's where dreams can turn into frustrating nightmares if you're not prepared. This guide aims to demystify the process, troubleshoot common issues, and get you closer to that sweet sound of a boosted inline-six.
Understanding the Beast: 2JZ-GTE Wiring Harness and ECU Basics
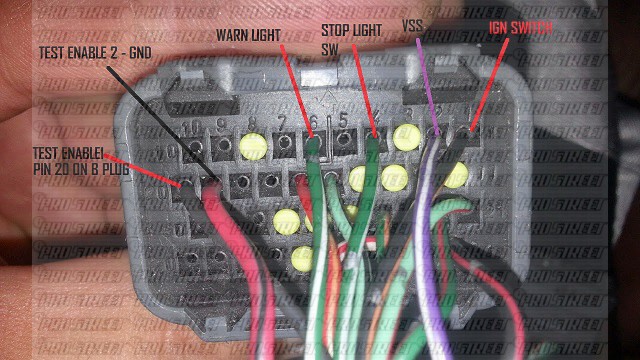
Before diving into the nitty-gritty, let's lay some groundwork. The 2JZ-GTE harness is a complex web of wires responsible for connecting the engine's various sensors, actuators, and components to the ECU (Engine Control Unit). The ECU, in turn, acts as the brain, interpreting sensor data and controlling engine parameters like fuel injection, ignition timing, and boost. Different generations of 2JZ-GTEs, sourced from different vehicles like the Toyota Supra MKIV or Aristo, have slightly different wiring schematics. Knowing the exact origin of your engine and harness is crucial.
Common ECUs encountered are the stock Toyota ECUs, aftermarket standalone ECUs (like Haltech, AEM, Link ECU), and piggyback systems. Stock ECUs are generally reliable but require specific tuning and can be limiting for heavily modified engines. Standalone ECUs offer maximum flexibility and control but require extensive knowledge and tuning experience. Piggyback systems modify the signals to the stock ECU, a compromise offering simpler installation but less precise control.
Essential Tools and Materials
Before you start, gather the right tools. Having the right equipment can save you hours of frustration and prevent damage to your harness or ECU. Here’s a list of essentials:
- Multimeter: For testing continuity, voltage, and resistance. A must-have for troubleshooting.
- Wiring diagrams: Absolutely essential for identifying wires and their functions. Get the correct diagram for your specific engine and ECU.
- Wire strippers and crimpers: For clean and secure connections.
- Soldering iron and solder: For permanent and reliable wire connections. Heat shrink tubing for insulation.
- Terminal removal tools: For safely removing pins from connectors without damage.
- Label maker: Label everything as you go. It will save you headaches later.
- Zip ties and wire loom: For organizing and protecting your wiring harness.
- Diagnostic scan tool: For reading and clearing diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Laptop with ECU tuning software: If you're using a standalone ECU or need to tune the stock ECU.
- Patience: This is not a quick job. Take your time and double-check your work.
Common 2JZ-GTE Wiring Issues and Solutions
Here are some of the most common wiring challenges you'll likely encounter during a 2JZ-GTE swap, along with troubleshooting tips and solutions:
1. Incorrect Wiring Connections
Problem: This is the most frequent issue. Wires are connected to the wrong pins on the ECU or other components, leading to various symptoms, from a no-start condition to erratic engine behavior.
Solution:
Verify, verify, verify! Use your wiring diagrams to meticulously check every connection. Color-coding can be inconsistent, so rely on pin numbers and wire functions. Cross-reference your wiring with reputable online resources and forums. Use your multimeter to test continuity between the sensor and the ECU pin. If using an aftermarket harness, double-check the manufacturer's documentation.
Pro Tip: Focus on one system at a time (e.g., fuel injection, ignition) to simplify the process. Isolate the issue before moving on.
2. Grounding Issues
Problem: Insufficient or improper grounding can cause a multitude of problems, including poor sensor readings, misfires, and ECU malfunction. The 2JZ-GTE requires multiple reliable ground points.
Solution:
Ensure that all ground wires are securely connected to the chassis. Clean the grounding points to bare metal for optimal contact. Add additional ground straps from the engine block to the chassis and from the ECU to the chassis. Check the resistance of your ground circuits with a multimeter. Ideally, you want less than 0.5 ohms resistance.
Pro Tip: Dedicated grounding kits are available that offer a convenient way to ensure proper grounding.
3. Sensor Malfunctions
Problem: Faulty sensors can provide inaccurate data to the ECU, leading to poor engine performance or a no-start condition. Common culprits include the crank position sensor (CPS), cam position sensor (CAS), mass airflow sensor (MAF), and oxygen sensors.
Solution:
Use a diagnostic scan tool to check for DTCs related to specific sensors. Test the sensors using a multimeter according to the manufacturer's specifications. Replace faulty sensors with new or known good units. Inspect the wiring and connectors leading to the sensors for damage or corrosion.
Pro Tip: Before replacing a sensor, check its wiring and connections. A loose or corroded connector can often mimic a faulty sensor.
4. Injector Wiring Problems
Problem: Issues with injector wiring can lead to fuel delivery problems, causing misfires, poor idle, or a no-start condition. This can be due to damaged wires, faulty connectors, or incorrect wiring.
Solution:
Check the injector wiring harness for any signs of damage, such as frayed wires or cracked insulation. Test the continuity of the injector wiring using a multimeter. Ensure that the injectors are properly connected to the harness and that the connectors are clean and secure. Verify that the injectors are receiving the correct voltage. If using aftermarket injectors, ensure they are correctly sized and compatible with your ECU.
Pro Tip: Use a noid light to test if the injectors are receiving a pulse signal from the ECU.
5. ECU Pinout Errors and Damage
Problem: Incorrectly identified ECU pins or damage to the ECU itself can cause serious problems, ranging from minor malfunctions to complete ECU failure.
Solution:
Double-check the ECU pinout against your wiring diagrams. Be absolutely certain you are connecting the correct wires to the correct pins. Inspect the ECU for any signs of physical damage, such as burned components or damaged connectors. If you suspect ECU damage, have it tested by a qualified technician. If you're using a used ECU, ensure it is from a compatible vehicle and that it hasn't been previously damaged.
Pro Tip: Always disconnect the battery before working on the ECU wiring. Static electricity can damage sensitive electronic components.
ECU Configuration and Tuning Considerations
Once the wiring is sorted, the ECU needs to be properly configured and tuned to optimize engine performance. This is where things get more complex, especially if you're using a standalone ECU.
Stock ECU Tuning: Stock ECUs can be tuned using various software packages. This is a good option if you're not making significant modifications to the engine. However, stock ECUs have limitations in terms of boost control and fuel management.
Standalone ECU Tuning: Standalone ECUs offer unparalleled flexibility but require extensive tuning knowledge. You'll need to configure parameters like fuel maps, ignition timing, boost control, and sensor calibrations. This is best left to experienced tuners.
Key Tuning Considerations:
- Injector sizing: Ensure that your injectors are properly sized for your engine's horsepower goals.
- Fuel pressure: Maintain proper fuel pressure to ensure consistent fuel delivery.
- Boost control: Set up boost control parameters carefully to avoid overboost conditions.
- Air/Fuel Ratio (AFR): Monitor AFRs during tuning to ensure the engine is running safely and efficiently.
- Knock control: Implement a robust knock control strategy to protect the engine from detonation.
Pro Tip: Start with a base map provided by the ECU manufacturer or a reputable tuner. Gradually refine the tune based on data logs and dyno testing.
Cost Estimates
The cost of wiring harness repair and ECU configuration can vary significantly depending on the complexity of the issue and the type of ECU used. Here's a rough estimate:
- Basic wiring repair: $100 - $500 (depending on the extent of the damage)
- ECU troubleshooting and diagnosis: $100 - $300
- Stock ECU tuning: $500 - $1000
- Standalone ECU tuning: $1000 - $3000 (including dyno time)
- New wiring harness: $500 - $1500 (depending on the manufacturer and complexity)
Important Note: These are just estimates. Prices can vary depending on your location and the specific shop you choose.
Seeking Professional Help
If you're feeling overwhelmed or uncertain about any aspect of the wiring harness or ECU configuration, don't hesitate to seek professional help. A qualified mechanic or tuner with experience in 2JZ-GTE swaps can save you time, money, and potential engine damage.
Remember, a well-wired and properly tuned 2JZ-GTE is a powerful and reliable engine. Take your time, be meticulous, and don't be afraid to ask for help when needed. Good luck, and enjoy the ride!
