Caja De Fusibles Nissan Pathfinder 1997
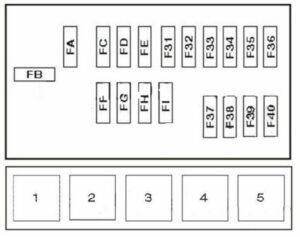
The 1997 Nissan Pathfinder, a rugged and reliable SUV of its era, relies on a well-designed electrical system to power its various functions. At the heart of this system lies the fuse box, or as it's known in Spanish, the Caja de Fusibles. This article delves into the intricacies of the 1997 Pathfinder's fuse box, exploring its location, function, fuse types, and providing a basic understanding of circuit protection.
Location and Layout
The 1997 Pathfinder boasts two primary fuse box locations, a common design in vehicles to distribute electrical load and minimize wiring complexity:
Interior Fuse Box
The main fuse box resides inside the vehicle's cabin, usually located on the driver's side. Specifically, it's commonly found beneath the dashboard, to the left of the steering column. Accessing this fuse box usually involves removing a small access panel, either by unscrewing it or using a trim tool to carefully pop it off. The exact method can be found in your vehicle's owner's manual. It's crucial to consult the manual, as forcing the panel open could damage the retaining clips.
Engine Compartment Fuse Box
A secondary fuse box is situated within the engine compartment. Its precise location typically varies, but it's usually near the battery or along one of the fender wells. This fuse box typically houses fuses and relays that control high-current components, such as the headlights, cooling fan, and starter motor. This location is chosen to minimize the length of high-current wiring runs, reducing voltage drop and improving efficiency. Finding this box involves locating a black plastic container with a lid marked with fuse symbols.
Inside each fuse box, you'll find an array of fuses of varying amperage ratings, each clearly labeled (though the labels can fade or become damaged over time). A fuse puller, often attached to the inside of the fuse box lid, is a handy tool for removing and replacing fuses without damaging them. Using pliers is strongly discouraged, as they can easily crush the fuse or damage the surrounding terminals.
Fuse Types and Ratings
The 1997 Pathfinder primarily utilizes blade-type fuses, also known as spade fuses. These fuses are characterized by their flat, blade-like terminals that plug into the fuse box. Blade fuses are color-coded according to their amperage rating, making identification easier. Common amperage ratings found in the Pathfinder include 5A, 7.5A, 10A, 15A, 20A, 25A, and 30A.
Understanding the amperage rating of a fuse is critical. The amperage rating indicates the maximum amount of electrical current that the fuse can safely handle before it blows, interrupting the circuit and preventing damage. Using a fuse with a higher amperage rating than specified is extremely dangerous, as it could allow excessive current to flow through the circuit, potentially causing a fire. Conversely, using a fuse with a lower amperage rating will cause the fuse to blow prematurely, interrupting the circuit unnecessarily.
Here's a general breakdown of common fuse colors and their corresponding amperage ratings (always verify with your vehicle's specific fuse diagram):
- Orange: 5A
- Brown: 7.5A
- Red: 10A
- Blue: 15A
- Yellow: 20A
- Clear: 25A
- Green: 30A
In addition to blade fuses, the 1997 Pathfinder may also use relays. Relays are electromechanical switches that allow a low-current circuit to control a high-current circuit. They're typically used to control components like headlights, fuel pumps, and starter motors. Relays are not fuses, but they are often located in the fuse box and play an essential role in the electrical system.
Function of the Fuse Box
The primary function of the fuse box is to protect the vehicle's electrical circuits from overcurrent conditions. Overcurrent can occur due to a short circuit (where a wire accidentally touches ground) or an overload (where a circuit is drawing more current than it's designed to handle). When an overcurrent condition occurs, the fuse blows, interrupting the circuit and preventing damage to the wiring, components, and potentially the vehicle itself.
Each fuse in the fuse box protects a specific circuit or group of circuits. The fuse box diagram, typically located on the inside of the fuse box lid or in the owner's manual, identifies which fuse protects which circuit. This diagram is essential for troubleshooting electrical problems, as it allows you to quickly identify the fuse that's responsible for the malfunctioning component.
For example, if your headlights aren't working, you would consult the fuse box diagram to locate the fuse that protects the headlight circuit. If the fuse is blown, replacing it with a new fuse of the correct amperage rating should restore the headlights. If the fuse blows again immediately, it indicates a more serious problem in the headlight circuit, such as a short circuit. In this case, further diagnosis is required to identify and repair the underlying issue.
Troubleshooting and Replacement
Diagnosing and replacing blown fuses is a relatively straightforward process, but it's important to follow a few basic steps to ensure safety and prevent further damage:
- Identify the problem: Determine which electrical component is not working.
- Locate the fuse box diagram: Consult the diagram to identify the fuse that protects the malfunctioning component.
- Inspect the fuse: Visually inspect the fuse to see if the filament is broken or the fuse is otherwise damaged. A blown fuse will typically have a visible break in the filament.
- Test the fuse (optional): Use a multimeter to test the fuse for continuity. A good fuse will have continuity (zero resistance), while a blown fuse will have no continuity (infinite resistance).
- Replace the fuse: If the fuse is blown, replace it with a new fuse of the same amperage rating.
- Test the circuit: After replacing the fuse, test the circuit to see if the component is now working.
- If the fuse blows again: If the fuse blows again immediately, it indicates a more serious problem in the circuit, such as a short circuit or an overload. Further diagnosis is required to identify and repair the underlying issue. Consult a qualified mechanic if you are not comfortable performing electrical troubleshooting.
Important Safety Precautions:
- Always turn off the ignition and remove the key before working on the fuse box.
- Never replace a fuse with a fuse of a higher amperage rating.
- If a fuse blows repeatedly, do not continue replacing it without diagnosing the underlying problem.
- If you are not comfortable working with electrical systems, consult a qualified mechanic.
Common Issues and Solutions
Several common issues can arise with the fuse box in a 1997 Nissan Pathfinder:
- Corrosion: Moisture and humidity can corrode the fuse box terminals, causing poor connections and electrical problems. Clean the terminals with a wire brush and electrical contact cleaner.
- Loose connections: Vibrations and wear and tear can loosen the fuse box terminals, causing intermittent electrical problems. Inspect the terminals and tighten them as needed.
- Damaged fuse box: Physical damage to the fuse box can cause short circuits and other electrical problems. Replace the fuse box if it is severely damaged.
- Incorrect fuse installation: Installing the wrong type or rating of fuse can lead to component malfunction or even electrical fires. Always ensure the fuse matches the specified rating on the diagram.
Conclusion
The fuse box is a critical component of the 1997 Nissan Pathfinder's electrical system. Understanding its location, function, and fuse types is essential for maintaining the vehicle's electrical health and troubleshooting electrical problems. By following the guidelines outlined in this article, you can effectively diagnose and repair common fuse box issues and keep your Pathfinder running smoothly for years to come. Remember to always prioritize safety and consult a qualified mechanic if you are not comfortable performing electrical troubleshooting.
