Differential Gear Ratio Selection And Performance Impact
Understanding the differential gear ratio is crucial for optimizing your vehicle's performance, fuel efficiency, and towing capabilities. Often overlooked, the gear ratio within your differential plays a significant role in how power is delivered to your wheels. This article will explain differential gear ratios, their impact on performance, and how to choose the right one for your needs.
What is a Differential Gear Ratio?
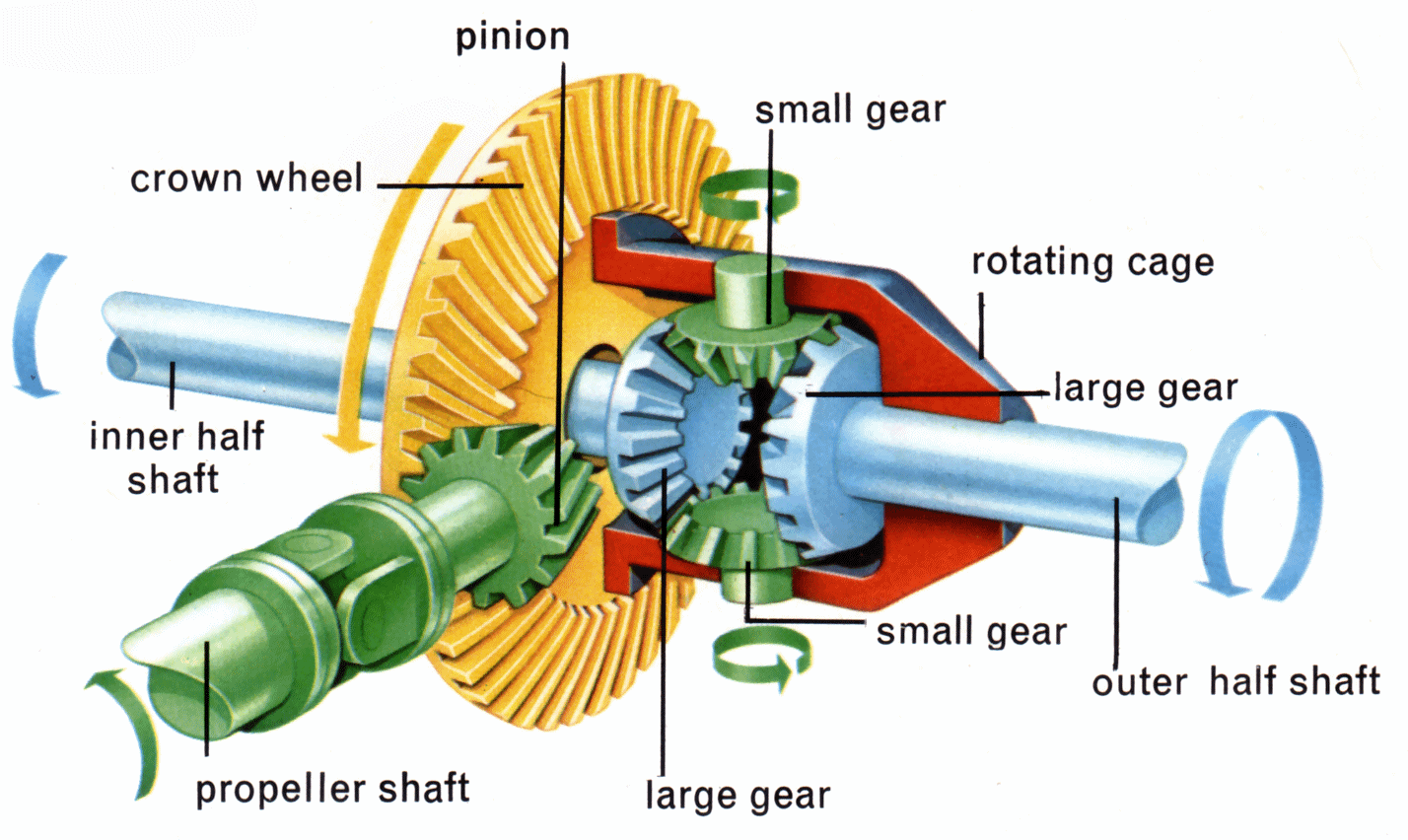
The differential gear ratio is the ratio between the number of teeth on the ring gear and the pinion gear within your differential. Essentially, it represents how many times the pinion gear needs to rotate for the ring gear to complete one full revolution. This rotation ultimately determines how many times your wheels turn for each revolution of the engine.
The gear ratio is typically expressed as a number like 3.73:1 or 4.10:1. In the example of 3.73:1, the pinion gear needs to rotate 3.73 times to turn the ring gear once. A higher number (like 4.10) signifies a numerically higher gear ratio, while a lower number (like 3.08) represents a numerically lower gear ratio.
Understanding the numerical relationship is key: a higher gear ratio means more engine revolutions per wheel revolution, and vice versa.
Impact on Performance: Acceleration, Top Speed, and Fuel Economy
The differential gear ratio significantly affects several aspects of your vehicle's performance:
Acceleration
A higher (numerically) gear ratio (e.g., 4.10:1 or 4.56:1) provides better acceleration. This is because the engine reaches its peak torque and horsepower range faster, allowing for quicker launches and improved responsiveness. Think of it like a bicycle: using a smaller gear on the front makes it easier to pedal up a hill, but you won't cover as much distance with each pedal stroke. Similarly, a higher gear ratio provides more torque to the wheels for faster acceleration.
However, there's a trade-off. With a higher gear ratio, the engine will be running at a higher RPM at any given speed, which can negatively impact fuel economy and potentially reduce top speed.
Top Speed
A lower (numerically) gear ratio (e.g., 3.08:1 or 3.55:1) generally results in a higher top speed. With a lower gear ratio, the engine spins fewer times for each wheel revolution, allowing the vehicle to reach a higher speed before hitting the engine's RPM limit. Again, consider the bicycle analogy: using a larger gear on the front allows you to cover more distance with each pedal stroke, but it takes more effort to get going.
The downside is that acceleration suffers. The engine takes longer to reach its peak power band, resulting in slower off-the-line performance.
Fuel Economy
Fuel economy is intricately linked to the gear ratio. Generally, a lower (numerically) gear ratio tends to offer better fuel economy, especially on the highway. This is because the engine operates at lower RPMs at cruising speeds, reducing fuel consumption. However, if the engine is constantly struggling to maintain speed due to the lower gear ratio (e.g., when towing or driving uphill), fuel economy can actually worsen.
A higher (numerically) gear ratio can decrease fuel economy, particularly at higher speeds. The engine spins at a higher RPM, consuming more fuel. However, in stop-and-go traffic or when towing, the improved acceleration can sometimes offset the higher RPM, resulting in comparable or even slightly better fuel economy.
The ideal gear ratio for fuel economy depends heavily on driving conditions and vehicle usage.
Towing Considerations
When it comes to towing, the differential gear ratio becomes even more critical. A higher (numerically) gear ratio is generally preferred for towing heavy loads. The increased torque multiplication helps the vehicle pull the load more easily and prevents excessive strain on the engine and transmission.
Using a lower gear ratio for towing can lead to several problems, including:
- Overheating of the engine and transmission
- Reduced braking performance
- Increased wear and tear on drivetrain components
- Difficulty maintaining speed on inclines
If you frequently tow heavy loads, upgrading to a higher gear ratio can significantly improve your vehicle's towing performance and extend the lifespan of its components.
Choosing the Right Differential Gear Ratio
Selecting the correct differential gear ratio is a balancing act. You need to consider your primary driving needs and the characteristics of your vehicle. Here's a breakdown to help you make the right choice:
- Daily Driver: If you primarily use your vehicle for daily commuting and highway driving, a lower (numerically) gear ratio (e.g., 3.08:1 to 3.55:1) is often the best choice. It will provide a good balance of fuel economy and reasonable acceleration.
- Performance Enthusiast: If you prioritize acceleration and performance, a higher (numerically) gear ratio (e.g., 3.73:1 to 4.10:1 or even higher) is recommended. Be prepared to sacrifice some fuel economy for the added performance.
- Towing and Off-Roading: If you frequently tow heavy loads or engage in off-road driving, a higher (numerically) gear ratio (e.g., 4.10:1 to 4.56:1 or even higher) is essential. The increased torque multiplication will make towing easier and improve off-road traction.
- Larger Tires: Installing larger tires effectively changes your overall gear ratio. Larger tires require more torque to turn, so if you've upgraded to larger tires, you may need to re-gear to a higher (numerically) gear ratio to restore performance.
Consulting with a professional mechanic or drivetrain specialist is highly recommended. They can assess your specific needs and recommend the optimal gear ratio for your vehicle and driving style.
How to Find Your Current Gear Ratio
There are several ways to determine your vehicle's current differential gear ratio:
- Check the Vehicle's Service Manual: The service manual often lists the gear ratio for your specific vehicle model and trim level.
- Look for a Tag on the Differential Housing: Some vehicles have a metal tag attached to the differential housing that indicates the gear ratio.
- Count the Teeth: You can manually count the teeth on the ring gear and pinion gear and divide the ring gear teeth by the pinion gear teeth. This is the most accurate method but requires disassembling the differential.
- Online VIN Decoder: Many online VIN decoders can provide information about your vehicle's specifications, including the differential gear ratio.
Re-Gearing: What to Expect
Changing your differential gear ratio (re-gearing) is a significant modification that requires specialized knowledge and tools. It's crucial to have the work done by a qualified mechanic. The process involves replacing the ring and pinion gears within the differential.
Here are some factors to consider before re-gearing:
- Cost: Re-gearing can be relatively expensive, as it involves labor and the cost of new gears.
- Downtime: Your vehicle will be out of commission while the work is being performed.
- Professional Installation: Improper installation can lead to premature wear, noise, and even differential failure.
- Matching Front and Rear: If you have a four-wheel-drive vehicle, it's essential to re-gear both the front and rear differentials to the same ratio to prevent damage to the transfer case.
Despite the potential costs and complexities, re-gearing can be a worthwhile investment if it aligns with your driving needs and significantly improves your vehicle's performance.
Conclusion
The differential gear ratio is a critical component that profoundly impacts your vehicle's performance, fuel economy, and towing capabilities. By understanding how different gear ratios affect these aspects, you can make informed decisions about optimizing your vehicle for your specific needs. Whether you're looking for better acceleration, improved fuel economy, or enhanced towing performance, selecting the right differential gear ratio is a key step towards achieving your goals.
