Extended Wheel Stud Installation And Torque Specifications
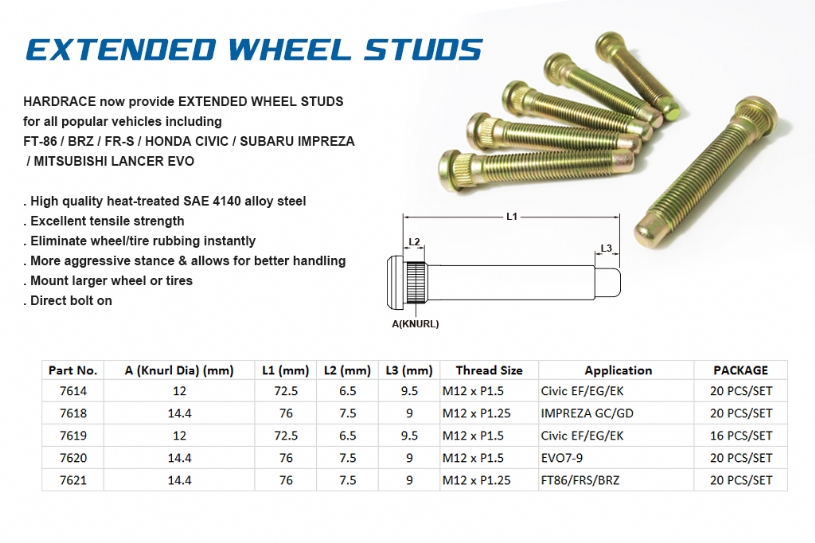
Are you experiencing difficulty installing wheels on your vehicle, especially after upgrading to aftermarket wheels or using wheel spacers? You might be facing an issue with your wheel studs. Factory wheel studs are often too short to safely accommodate these changes. Fortunately, installing extended wheel studs is a common and effective solution. This article will guide you through the process, explain the importance of proper torque specifications, and provide some helpful tips to ensure a safe and reliable installation.
The Problem: Insufficient Wheel Stud Length
The core problem stems from insufficient thread engagement between the lug nuts and the wheel studs. When you add thicker wheels, wheel spacers, or aftermarket wheels with a different offset, the factory studs may not protrude far enough to allow for proper and safe tightening. This leads to several potential issues:
- Reduced Clamping Force: Not enough thread engagement means the lug nuts won't be able to apply sufficient clamping force to hold the wheel securely against the hub.
- Stud Fatigue and Failure: The limited engagement puts undue stress on the exposed threads, leading to premature fatigue and potentially catastrophic stud failure, especially under heavy braking or cornering.
- Damaged Threads: Forcing lug nuts onto short studs can damage both the stud and the lug nut threads, making it even harder to achieve proper torque in the future.
- Vibration and Wheel Loosening: Insufficient clamping force can cause the wheel to vibrate and eventually loosen, which is a serious safety hazard.
Ignoring this issue is extremely dangerous and can lead to wheel separation while driving. This can result in a loss of control and a serious accident. Don't compromise safety; address the issue properly.
The Solution: Installing Extended Wheel Studs
The solution is straightforward: replace your factory wheel studs with longer, extended studs. These longer studs provide the necessary thread engagement for safe and reliable wheel mounting. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
1. Preparation: Gather Your Tools and Materials
Before you begin, make sure you have all the necessary tools and materials. This will save you time and frustration.
- New Extended Wheel Studs: Purchase studs that are the correct thread size and pitch for your vehicle. Measure your existing studs to determine the necessary length increase. It’s generally recommended to have at least the diameter of the stud exposed after installing the lug nut.
- Lug Nut Torque Wrench: A calibrated torque wrench is essential for achieving the correct clamping force. Don’t rely on guesswork!
- Impact Wrench (Optional): An impact wrench can speed up the removal and installation of components, but be cautious and use it only for loosening and initial tightening. Always finish with a torque wrench.
- Socket Set: You’ll need sockets to remove the wheel, brake caliper, and potentially the hub assembly.
- Hammer and Punch: To remove the old studs. Use a brass punch to avoid damaging the hub.
- Wheel Bearing Grease or Anti-Seize Compound: To lubricate the new studs and prevent corrosion.
- Brake Cleaner: To clean the hub surface before installing the new studs.
- Safety Glasses and Gloves: Protect yourself!
- Jack and Jack Stands: Never work under a vehicle supported only by a jack.
2. Removal of Old Wheel Studs
This is often the most challenging part of the process. Here's how to do it:
- Loosen the Lug Nuts: Before lifting the vehicle, loosen the lug nuts on the wheel you're working on.
- Lift the Vehicle and Secure it with Jack Stands: Raise the vehicle and securely support it with jack stands. Never work under a vehicle supported only by a jack.
- Remove the Wheel: Take the wheel off completely.
- Remove the Brake Caliper (If Necessary): In some cases, the brake caliper and rotor need to be removed to access the wheel studs. If so, carefully remove the caliper, being mindful of the brake lines. Support the caliper so it's not hanging by the brake line. Remove the rotor.
- Remove the Hub (If Necessary): Depending on your vehicle's design, you might need to remove the entire hub assembly to access the wheel studs. This usually involves disconnecting the ABS sensor and any other attached components. Consult your vehicle's repair manual for specific instructions.
- Remove the Old Studs: Place a punch against the back of the stud and use a hammer to drive the stud out of the hub. Be careful not to damage the hub. A hydraulic press can be used if studs are particularly stubborn.
3. Installation of New Extended Wheel Studs
With the old studs removed, you can now install the new extended studs.
- Clean the Hub: Thoroughly clean the hub surface where the new studs will sit. Use brake cleaner to remove any dirt, rust, or debris.
- Lubricate the New Studs: Apply a small amount of wheel bearing grease or anti-seize compound to the splines of the new studs. This will make installation easier and prevent corrosion.
- Install the New Studs: There are two common methods for installing the studs:
- Using a Lug Nut and Washer: Place the new stud into the hub. Put a thick, hardened washer over the stud and thread a lug nut onto it backwards (flat side against the washer). Tighten the lug nut to draw the stud into the hub. Important: Ensure the stud is fully seated against the hub flange. You’ll feel it bottom out. Be careful not to overtighten and strip the threads.
- Using a Hydraulic Press: If you have access to a hydraulic press, you can use it to press the studs into the hub. This is often the easiest and most reliable method.
- Reinstall the Hub (If Removed): If you removed the hub assembly, carefully reinstall it, following the reverse of the removal procedure. Ensure all components are properly connected and torqued to the manufacturer's specifications.
- Reinstall the Brake Caliper (If Removed): Reinstall the brake caliper and rotor, making sure everything is properly aligned and torqued.
4. Torque Specifications: The Key to Safety
This is the most crucial step! Proper torque is absolutely essential for ensuring the safety and reliability of your wheels.
- Consult Your Vehicle's Repair Manual: The correct torque specification for your lug nuts is typically found in your vehicle's repair manual or on a sticker inside the driver's side door jamb. Do not guess!
- Use a Calibrated Torque Wrench: Use a calibrated torque wrench to tighten the lug nuts to the specified torque. Ensure the wrench is set to the correct units (foot-pounds or Newton-meters).
- Tighten in a Star Pattern: Tighten the lug nuts in a star pattern (opposite nuts) to ensure even clamping force across the wheel.
- Re-torque After Driving: After driving approximately 50-100 miles, re-torque the lug nuts. This is a critical step, as the studs and wheels can settle, and the lug nuts may loosen slightly.
Ignoring proper torque specifications is a major safety risk. Overtightening can damage the studs and wheels, while undertightening can lead to wheel loosening and potential separation.
Example Torque Specifications (Illustrative Only - Always Check Your Vehicle's Specifications):
Example 1: 2015 Honda Civic: 80 ft-lbs
Example 2: 2018 Ford F-150: 150 ft-lbs
5. Final Checks and Considerations
Before you hit the road, perform these final checks:
- Wheel Clearance: Verify that the wheels have adequate clearance from the brake calipers, suspension components, and fender liners.
- Lug Nut Engagement: Double-check that the lug nuts have sufficient thread engagement on the new studs. As a general rule, the lug nut should engage at least the diameter of the stud.
- Brake System Function: If you removed the brake calipers, ensure that the brake system is functioning properly before driving. Pump the brake pedal several times to restore brake pressure.
Estimated Costs and Time
The cost of installing extended wheel studs can vary depending on several factors, including the type of vehicle, the cost of the studs, and whether you choose to do it yourself or have a professional mechanic perform the work.
- Parts (Extended Wheel Studs): $50 - $200 (depending on quality and quantity)
- Labor (Professional Installation): $100 - $400 (depending on the shop rate and complexity)
The time required for installation can also vary. If you're experienced and have all the necessary tools, you might be able to complete the job in a few hours. However, if you're unfamiliar with the process, it's best to allow yourself plenty of time or consider hiring a professional.
When to Seek Professional Help
If you're not comfortable working on your vehicle's brakes or suspension, or if you encounter any difficulties during the installation process, it's best to seek professional help. A qualified mechanic will have the experience, tools, and knowledge to ensure that the job is done safely and correctly. You should especially consider professional help if:
- You are unfamiliar with brake system components.
- You lack the necessary tools.
- You are unsure about the proper torque specifications.
- You encounter difficulties removing the old studs or installing the new ones.
Conclusion
Installing extended wheel studs is a relatively straightforward process that can significantly improve the safety and performance of your vehicle, especially if you've upgraded your wheels or are using wheel spacers. By following these guidelines and paying close attention to proper torque specifications, you can ensure a safe and reliable installation. Remember, safety is paramount, so don't hesitate to seek professional help if you're unsure about any aspect of the process. With the right tools and knowledge, you can enjoy the benefits of extended wheel studs with confidence.
