Fiberglass Door Construction And Safety Considerations
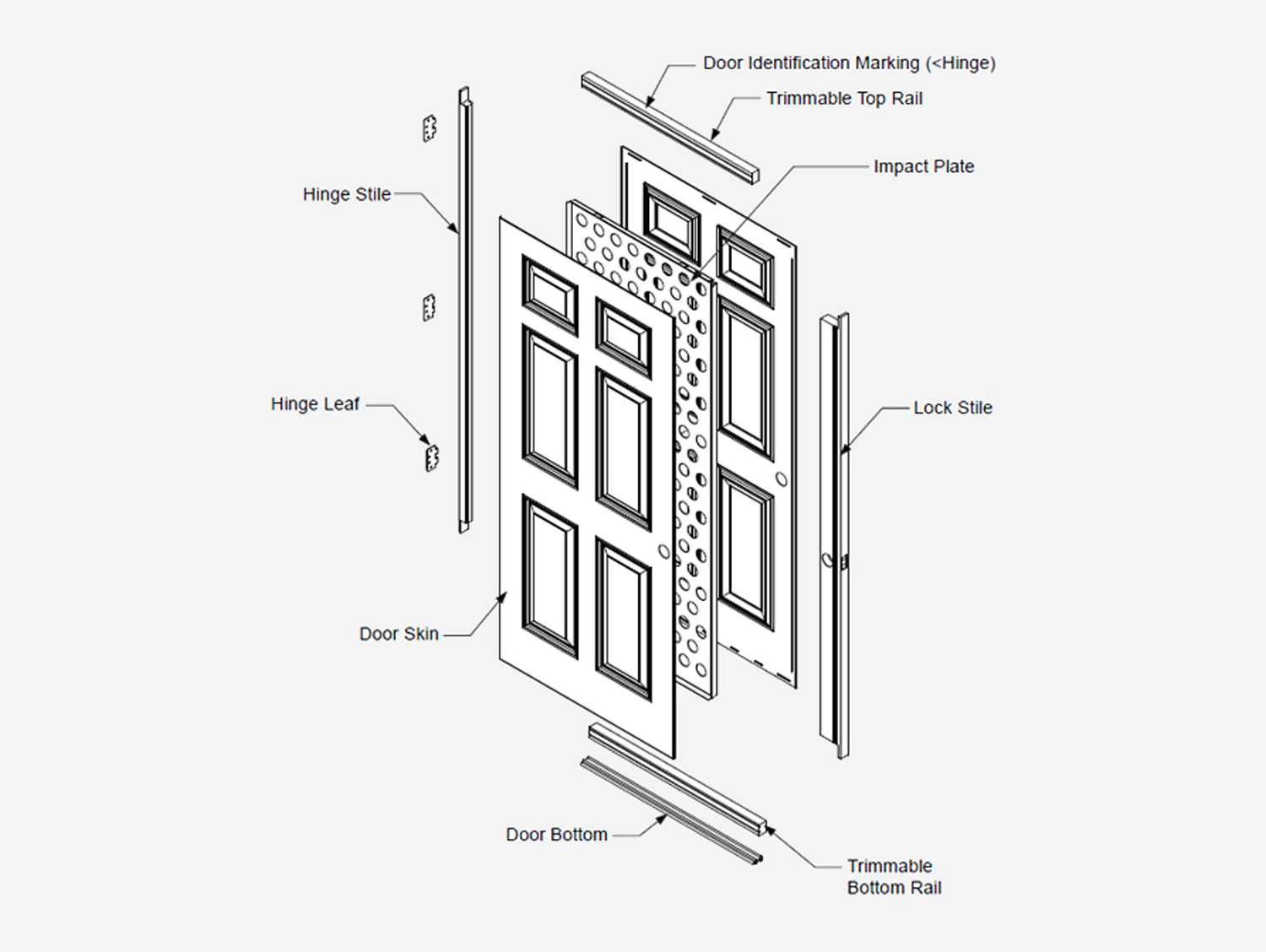
Fiberglass doors have surged in popularity, offering a compelling blend of durability, energy efficiency, and aesthetic versatility. Unlike their wooden or steel counterparts, fiberglass doors resist warping, rotting, and denting, making them a long-lasting and low-maintenance choice. But what exactly goes into constructing these resilient barriers? Let's delve into the intricate engineering and safety considerations that define a high-quality fiberglass door.
Core Composition: The Foundation of Strength
At the heart of a fiberglass door lies its core, which provides structural integrity and insulation. The most common core material is polyurethane foam, chosen for its excellent thermal resistance. This foam is injected into the door cavity, expanding to fill the space and bonding to the fiberglass skins. The density of the polyurethane foam directly impacts the door's insulation value (R-value) and its resistance to impact damage. Higher density foams offer superior insulation and impact resistance, but also increase the door's weight and cost.
An alternative core material, though less prevalent, is polystyrene foam. Polystyrene offers a more economical option but generally provides lower insulation values compared to polyurethane. Its susceptibility to moisture absorption can also be a concern in humid environments.
Regardless of the core material, uniform density and complete filling of the cavity are crucial for preventing weak spots and ensuring consistent performance across the entire door surface. Manufacturers employ sophisticated injection techniques and quality control measures to achieve this uniformity.
Fiberglass Skins: The Weatherproof Armor
The outer surfaces of a fiberglass door are constructed from composite skins made of glass fibers embedded in a resin matrix. These skins provide the door's defining characteristics: weather resistance, impact resistance, and the ability to mimic the appearance of wood. Several factors influence the quality and performance of the fiberglass skins:
Fiberglass Type and Orientation
The type of glass fibers used and their orientation within the resin matrix significantly affect the door's strength and stiffness. Chopped strand mat (CSM) is a common type, consisting of randomly oriented short fibers. While cost-effective, CSM offers lower strength compared to continuous strand fibers, which are aligned in specific directions. By strategically orienting the fibers along the door's length and width, manufacturers can optimize its resistance to bending and twisting.
Resin System
The resin system that binds the glass fibers together plays a crucial role in the door's durability and resistance to environmental degradation. Polyester resins are a common choice, offering a good balance of cost and performance. However, for enhanced weather resistance and longevity, some manufacturers opt for more advanced resins such as vinyl ester or epoxy. These resins provide superior resistance to UV radiation, moisture absorption, and chemical attack.
Surface Texture and Finish
Fiberglass doors can be manufactured with a variety of surface textures, ranging from smooth to embossed wood grain patterns. The texture is typically applied during the molding process, creating a permanent and realistic wood-like appearance. A high-quality gel coat finish is then applied to protect the fiberglass skin from UV damage and provide a smooth, paintable surface. The gel coat also contributes to the door's overall aesthetic appeal, allowing for a wide range of color options and finishes.
Edge Reinforcement: Preventing Weak Points
The edges of a fiberglass door are particularly vulnerable to damage, especially in high-traffic areas. To reinforce these critical areas, manufacturers typically incorporate edge rails made of wood, composite materials, or even fiberglass. These edge rails provide additional support and prevent the fiberglass skins from delaminating or cracking under stress. In some designs, the edge rails are chemically bonded to the core material, creating a monolithic structure that further enhances the door's strength and durability. These are important considerations when thinking about security.
Lock and Hinge Block: The Foundation of Security
The lock and hinge block, strategically located within the door, provide a secure mounting point for the door's hardware. These blocks are typically made of solid wood or composite materials, and are carefully sized and positioned to ensure proper alignment and functionality. The strength and integrity of the lock block are paramount for security, as it must withstand repeated stress from locking and unlocking the door. Manufacturers often reinforce the lock block with metal plates or screws to further enhance its resistance to forced entry.
Glazing Options: Illuminating and Securing Entryways
Fiberglass doors are often equipped with glass panels, allowing natural light to enter the home. These glass panels are typically made of tempered glass or laminated glass, both of which offer enhanced safety compared to standard annealed glass. Tempered glass shatters into small, relatively harmless pieces when broken, reducing the risk of serious injury. Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded together with an interlayer of polyvinyl butyral (PVB), which holds the glass fragments in place if broken, preventing them from scattering. For added security, some fiberglass doors feature impact-resistant glass, designed to withstand extreme force and prevent forced entry. Decorative glass options, such as stained glass or etched glass, can also be incorporated into fiberglass doors to enhance their aesthetic appeal.
Safety Considerations: Protecting Homeowners and the Environment
The design and construction of fiberglass doors must adhere to stringent safety standards to protect homeowners and the environment. Several key safety considerations include:
Fire Resistance
Fiberglass doors are typically designed to meet specific fire resistance ratings, which indicate the amount of time the door can withstand exposure to flames and high temperatures before failing. These ratings are crucial for slowing the spread of fire and providing occupants with valuable time to escape. Manufacturers often incorporate fire-resistant materials, such as mineral wool insulation, into the door's core to enhance its fire resistance.
Impact Resistance
Fiberglass doors must be able to withstand impact from wind-borne debris and other objects to protect occupants from injury and prevent damage to the home. The impact resistance of a fiberglass door is determined by its core composition, fiberglass skin thickness, and edge reinforcement. Doors designed for hurricane-prone areas often feature reinforced construction and impact-resistant glass.
Security
As mentioned earlier, the lock block's integrity is a key factor in overall door security. Beyond that, strong hinges and a robust frame-to-door connection all contribute to preventing forced entry.
Consider a multi-point locking system for enhanced security, engaging multiple latches along the door's frame.
Environmental Impact
The manufacturing process for fiberglass doors can have a significant environmental impact, particularly due to the use of energy-intensive processes and potentially hazardous materials. However, many manufacturers are taking steps to reduce their environmental footprint by using recycled materials, implementing energy-efficient manufacturing practices, and developing more sustainable resin systems. Furthermore, the long lifespan and energy efficiency of fiberglass doors can contribute to reducing overall energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions over the product's life cycle.
In conclusion, the construction of a fiberglass door involves a complex interplay of materials, engineering principles, and manufacturing processes. By understanding these elements, homeowners and amateur engineers can appreciate the inherent value and durability of these increasingly popular entryways. Furthermore, by prioritizing safety considerations such as fire resistance, impact resistance, and security, we can ensure that fiberglass doors provide not only beauty and efficiency but also peace of mind.
