Fuel Pump Wiring Circuit Protection And Relay Setup
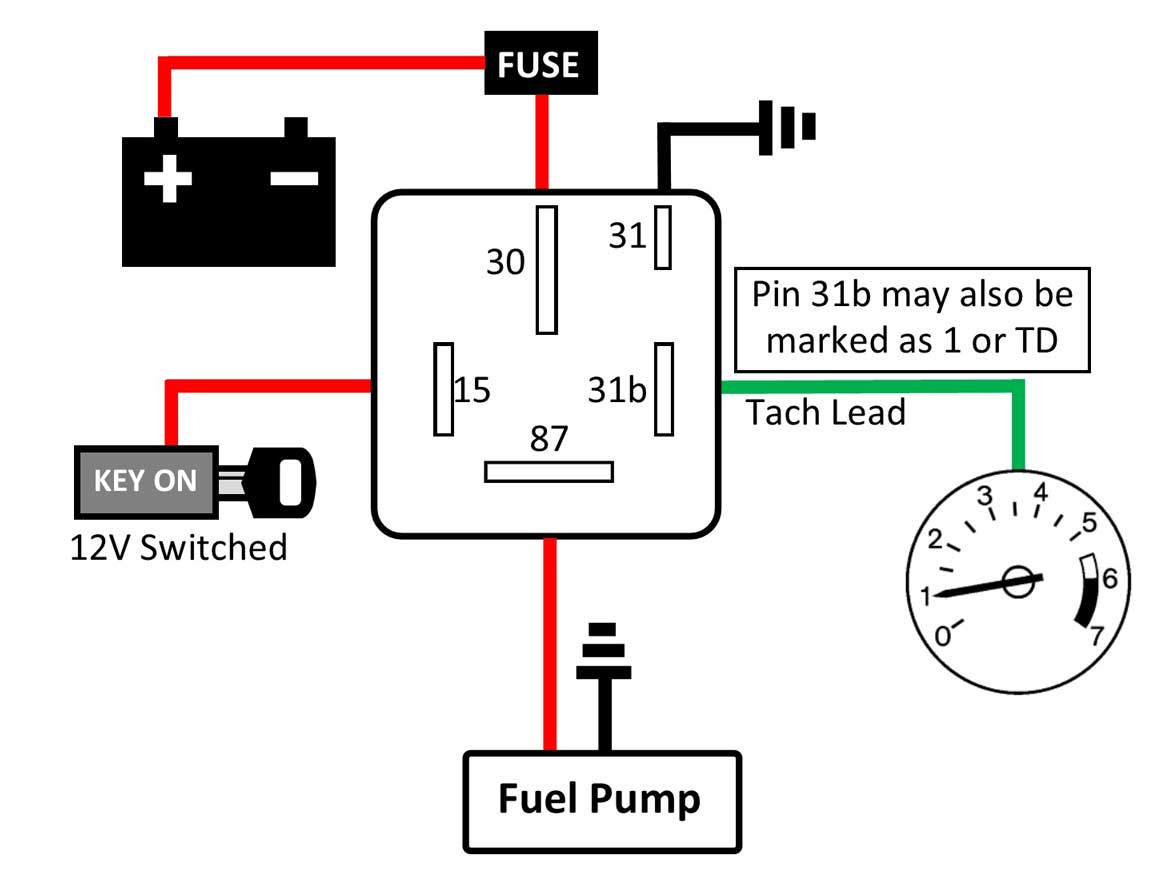
Hey folks, let's talk about something that can leave you stranded and scratching your head: fuel pump wiring, circuit protection, and relay setups. A healthy fuel system is the lifeblood of your engine, and a properly functioning fuel pump is crucial. But what happens when things go wrong? Often, the problem isn't the pump itself, but rather the wiring, fuse, or relay that controls it. This article will walk you through common issues, troubleshooting steps, and solutions to keep your fuel flowing smoothly.
Common Fuel Pump Circuit Problems
Before we dive into fixes, let's identify the usual suspects:
- Blown Fuse: This is the simplest and most common issue. A short circuit or an overloaded pump can cause the fuse to blow.
- Faulty Relay: The fuel pump relay acts like a switch, allowing power to reach the pump. Relays can fail internally, preventing the pump from receiving power.
- Wiring Issues: Corrosion, frayed wires, or loose connections can interrupt the electrical circuit, starving the pump of voltage. This is especially common in older vehicles.
- Grounding Problems: A poor ground connection can also impede current flow, causing the pump to malfunction or not work at all.
- Inertia Switch (Fuel Cut-off Switch): Some vehicles have an inertia switch that cuts power to the fuel pump in the event of an accident. This switch can sometimes be tripped accidentally.
Troubleshooting Your Fuel Pump Circuit
Okay, your car won't start or is experiencing fuel starvation issues. Let's get to work. Here's a systematic approach to troubleshooting:
1. Check the Fuse
This is always the first step. Locate the fuel pump fuse in your fuse box (consult your owner's manual for its location). Remove the fuse and inspect it. If the filament is broken, the fuse is blown. Replace it with a fuse of the exact same amperage. Don't just slap in a higher amperage fuse – that could cause a fire! If the new fuse blows immediately, you have a short circuit that needs to be investigated further.
Tools Needed: Fuse puller (usually located in the fuse box), spare fuses of the correct amperage.
Approximate Cost: A few dollars for a pack of fuses.
2. Test the Fuel Pump Relay
The fuel pump relay is another common point of failure. Here's how to test it:
- Locate the Relay: Again, consult your owner's manual for the fuel pump relay's location. It's typically in the fuse box under the hood or dash.
- Swap with a Known Good Relay: If possible, swap the fuel pump relay with a relay of the same type from another non-essential circuit (like the horn or rear window defogger). If the fuel pump now works, the original relay is faulty.
- Test with a Multimeter: You can also test the relay with a multimeter. You'll need to identify the relay's terminals (usually a diagram is printed on the relay itself). Check for continuity between the coil terminals and test if the relay clicks when voltage is applied to the coil terminals. If you're not comfortable with this, seek professional help.
Tools Needed: Multimeter (optional), small screwdriver or pry tool to remove the relay.
Approximate Cost: $10-$30 for a new fuel pump relay.
3. Check the Inertia Switch (If Equipped)
If your vehicle has an inertia switch, try resetting it. The location of the switch varies, but it's often in the trunk, under the dashboard, or in the passenger footwell. There will be a button or switch to reset it. Press it firmly.
Tools Needed: None (usually).
Approximate Cost: Free!
4. Inspect the Wiring
This is where things can get a bit more involved. You'll need to trace the wiring from the fuel pump relay to the fuel pump itself. Look for:
- Corrosion: Check for green or white corrosion on the wires and connectors. Clean any corrosion with a wire brush or electrical contact cleaner.
- Frayed or Damaged Wires: Look for any signs of damage to the insulation. Repair any damaged wires with electrical tape or heat shrink tubing. Properly repairing the wire is crucial, as exposed wires can cause short circuits.
- Loose Connections: Ensure all connectors are securely attached. You might need to clean and tighten the connectors for a good contact.
- Voltage Drop Testing: This is an advanced technique that uses a multimeter to measure the voltage drop along the wiring circuit. Excessive voltage drop indicates a high resistance connection, which can starve the fuel pump.
Tools Needed: Multimeter, wire brush, electrical contact cleaner, electrical tape, heat shrink tubing, wire stripper/crimper.
Approximate Cost: $10-$50 depending on the repair materials needed. Voltage drop testing might require professional assistance.
5. Check the Ground Connection
The fuel pump needs a good ground connection to function properly. Locate the ground wire for the fuel pump (usually attached to the chassis near the fuel tank). Ensure the connection is clean and tight. Clean any corrosion and tighten the bolt.
Tools Needed: Wrench or socket, wire brush.
Approximate Cost: Free (cleaning supplies may cost a few dollars).
DIY vs. Professional Repair
Troubleshooting and repairing fuel pump wiring can range from simple tasks like replacing a fuse to more complex tasks like tracing wiring and performing voltage drop tests. If you're comfortable working with electrical systems and have some basic tools, you can tackle some of these repairs yourself. However, if you're not confident or if you encounter a complex issue like a short circuit or damaged wiring harness, it's best to seek professional help. A qualified mechanic has the expertise and equipment to diagnose and repair these problems safely and effectively.
Potential Costs for Professional Repair: Depending on the issue, expect to pay anywhere from $100-$500 or more for professional fuel pump wiring repair. This includes diagnostic time, labor, and parts.
Preventative Measures
Here are a few tips to help prevent fuel pump wiring problems:
- Regular Inspections: Periodically inspect your fuel system for any signs of corrosion, damage, or leaks.
- Proper Fuel: Use the correct octane fuel recommended for your vehicle.
- Avoid Running on Empty: Running your fuel tank consistently low can cause the fuel pump to overheat and fail prematurely.
- Consider a Fuel Pump Relay Upgrade: For older vehicles or those with known fuel pump relay issues, consider upgrading to a heavy-duty relay. This can provide more reliable power to the fuel pump and prevent relay failure.
- Proper Wiring Practices: If you are doing any work on your fuel system wiring, use proper wiring techniques, including soldering connections and using heat shrink tubing for insulation.
By following these troubleshooting steps and preventative measures, you can keep your fuel pump wiring in good condition and avoid the dreaded feeling of being stranded on the side of the road. Remember, safety first! If you're unsure about any aspect of fuel pump wiring repair, consult a qualified mechanic.
